![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the functions of spinal nerves?
|
• Pathway for sensory and motor impulses
• Responsible for reflexes |
|
|
Where would you find: cell bodies of somatic motor neurons?
|
Anterior horn of spinal cord
|
|
|
Where would you find: cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons?
|
Anterior horn of spinal cord
|
|
|
Where would you find: terminal axons of sensory neurons and cell bodies of interneurons?
|
Posterior horn of spinal cord
|
|
|
Where would you find: unmyelinated axons that communicate between the left and right spinal cord?
|
Gray commissure
|
|
|
Draw a cross section of the spinal cord. Label the following: grey and white matter, anterior and posterior roots, dorsal root ganglia, sensory and motor neurons (cells bodies and axons).
|
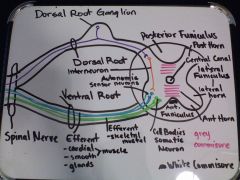
|
|
|
Define a reflex and reflex arc.
|
• Reflexes are rapid, automatic involuntary reactions of muscle or glands to a stimulus
• Reflex arc is the neural “wiring” of a single reflex. It always begins at a receptor in the PNS, communicates with the CNS, and ends at a peripheral effector, such as a muscle or gland cell. |
|
|
Is a reflex arc monosynaptic or polysynaptic?
|
Monosynaptic
|
|
|
Be able to define and apply the terms: monosynaptic,
|
sensory axon synapse directly on the motor neurons, whose axons project to the effector: no interneurons are involves= quick respond. E.i. knee
|
|
|
Be able to define and apply the terms: polysynaptic,
|
are more complex neural pathways that exhibit a number of synapses involving interneurons within the reflex arc: more components=slower respond time. E.i. foot is in pain, other muscles active to “catch you”
|
|
|
Be able to define and apply the terms: ipsilateral,
|
when both the receptor and effector organs of the reflex are on the same side of the spinal cord. E.i. when your left arm muscle pulls out your left had from the fire
|
|
|
Be able to define and apply the terms: contralateral,
|
when the sensory impulses from a receptor organ cross over through the spinal cord to activate effector organs in the opposite limb. E.i. step on a tact with left foot. You jump and right leg catches you.
|
|
|
Be able to define and apply the terms: Ascending and descending.
|
In the direction of the spinal cords “highway”
|
|
|
Are somatosensory pathways ascending or descending?
|
Ascending
|
|
|
Are somatosensory pathways ascending or descending?:
Do their pathways decussate? |
Yes
|
|
|
Where do motor pathways originate?
|
Cerebral cortex and brainstem
|
|
|
From the spinal cord to the muscle: How many neurons make up a somatic motor pathway?
|
2
|
|
|
Where do descending motor pathways most commonly decussate?
|
Pyramids in the medulla oblongata
|
|
|
Compare and contrast the autonomic and somatic nervous system.
|
Autonomic Nervous System actives the involuntary actions
Somatic Nervous System actives voluntary actions |
|
|
Draw the (general) 2 neuron chain of the ANS and label the pre- and postganglionic cells and axons, spinal cord, autonomic ganglion, preganglion neuron is mylenated, the noy postganlion neuron and an effector organ.
|
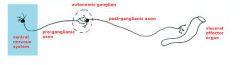
|
|
|
What are the functions of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions of the ANS?
|
Sympathetic – flight or fight
Parasympathetic – rest or digest |
|
|
From which region of the spinal cord, approximately, does each originate?
|
Sympathetic - T1 to L2
Parasympatheric - brainstem and sacrum 2 to sacrum 4 |
|
|
What are the anatomic differences between the organization of parasympathetic and sympathetic neurons?
|
The preganglionic axon of the sympathetic neuron is short but branched, the postganglionic axon is long so the autonomic ganglion is farther to the effector.
The preganglionic axon in the parasympathetic neuron is longer but not branched, the postganglionic axon is shorter so the autonomic ganglion is closer to the effectro. |
|
|
What is the significance of the paravertebral ganglia?
|
House sympathetic ganglionic neuron cell bodies
|
|
|
How do they contribute to convergence and divergence?
|
–each postganglionic cell may receive synapses from multiple preganglionic cells: neuronal convergence
– each preganglionic fiber branches and synapses with multiple postganglionic fibers: neuronal divergence |

