![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What meninges cover the spinal cord? |
All three: dura mater, arachnoid, pia |
|
|
What fills the epidural spaces in the spinal cord? |
fat, blood vessels, and connective tissue |
|
|
Where is the spinal cord positioned? |
forament magnus to L1 L2 |
|
|
The end of the spinal cord is called what? |
conus medullaris |
|
|
What is the cauda equina? |
The complex that includes the filum terminale and the long ventral and dorsal roots that extend caudal to the conus medullaris. Looks like a horse's tail |
|
|
Where does the cauda equina exit? |
Sacral foramina |
|
|
What is the filum terminale? |
Ligament that tethers conus medullaris to the sacral vertebrae via the coccygeal ligament and prevents superior movement. |
|
|
What is the conus medullaris? |
Where the spinal cord tapers to a conical tip at or inferior to the level of the first lumbar vertebra. |
|
|
Spinal cord carries ____ impulses up towards brain and ________ impulses down from the brain. |
sensory, motor |
|
|
What are the five steps of the reflex arc? |
1. Arrival of stimulus and activation of a receptor 2. Activation of a sensory neuron 3. Information processing in CNS 4. Activation of a motor neuron 5. Response by effector |
|
|
Where is gray matter found in the spinal cord? |
Central |
|
|
What does gray matter in spinal cord contain? |
Mostly cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons |
|
|
What is the central canal surrounded by? |
Gray commissure |
|
|
What is found in the central canal? |
CSF |
|
|
What is the gray commissure? |
It is a neuron crossover site |
|
|
What are the three arrangements in the gray matter of spinal cord? |
Posterior (dorsal) horns Anterior horn lateral horn |
|
|
Dorsal root is afferent/efferent |
afferent |
|
|
Ventral root is afferent/efferent |
efferent |
|
|
The posterior (dorsal) horn contains _______ __________ fibers and interneurons |
somatic sensory |
|
|
Anterior (ventral) horn has __________ ____________ cell bodies |
somatic motor |
|
|
Lateral horn has _________ ___________ and ___________ _____________ neurons |
visceral sensory, visceral motor |
|
|
The white matter of spinal cord is situated where? |
Peripheral |
|
|
What is the white matter of spinal cord made of? |
Myelinated and unmyelinated axon |
|
|
How is the white matter of spinal cord arranged? |
Lateral column, anterior column, posterior column |
|
|
Each of the columns of the white matter in spinal cord contains |
tracts |
|
|
What are tracts? |
Axons that share structural or functional similarities. |
|
|
How many directions can tracts travel in? |
3 directions |
|
|
Spinal nerves are in ___ pairs |
31 |
|
|
Spinal nerves carry ____ and ____ neurons |
sensory, motor |
|
|
The spinal nerves are formed through fusion of ___ and ____ ____. |
ventral, dorsal roots |
|
|
Where do the spinal nerves innervate? |
Muscle, skin, and glands of neck and body |
|
|
Spinal nerves branch off of ___ ___. |
spinal cord |
|
|
Spinal nerves split to form ___ ___ and ___ ___ |
dorsal ramus, ventral ramus |
|
|
Dorsal ramus innervates ___ |
back, T1-L2 only |
|
|
Ventral ramus innervates ___ |
sides and front and all plexuses |
|
|
What are the four plexuses? |
1. Cervical 2. Brachial 3. Lumbal 4. Sacral |
|
|
Lumbar plexus leads ____ |
anterior |
|
|
Sacral plexus leads ___ |
posterior |
|
|
What are dermatomes? |
The area of the body that is monitored by a specific sensory nerve. Map of somatic sensory innervation. |
|
|
What are autonomic ganglia? |
Interconnects sympathetic neurons branching from T1-L2 and contains axons and cell bodies of sympathetic fibers |
|
|
What chemical messenger is used in somatic (voluntary) motor division? |
Acetylcholine |
|
|
What chemical messenger is used in visceral (involuntary autonomic) motor division? |
1st neuron- acetylcholine 2nd neuron- acetylcholine/n-epi |
|
|
The sympathetic nervous system has ___ pre-ganglionic neuron and ___ post-ganglionic neurons. |
short, long |
|
|
The parasympathetic nervous system has a ___ pre-ganglionic neuron and a ___ post-ganglionic neuron |
long, short |
|
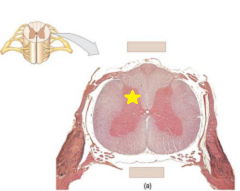
|
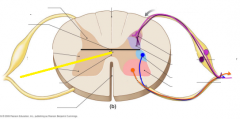
Posterior horn |
|
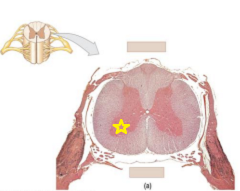
|
Anterior horn |
|
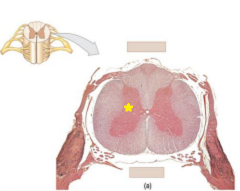
|
Lateral horn |
|

|
Lateral column |
|
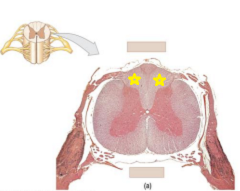
|
Posterior column |
|

|
Lateral column |
|
|
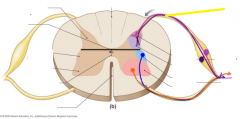
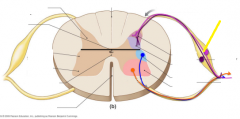
Dorsal root |
|
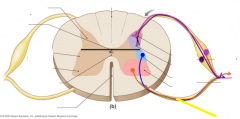
|
Ventral root |
|
|
Dorsal root ganglion |
|
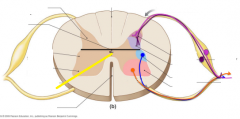
|
Gray commissure |
|
|
Central canal |
|
|
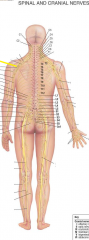
Cervical plexus is made of what nerves? |
C1-C4 and some fibers from C5 |
|
|
What are some major nerves the cervical plexus produce? |
Hypoglossal nerve, accessory nerve Lesser occipital nerve Supraclavicular nerves phrenic nerve |
|
|
Brachial plexus forms from what nerves? |
C5-T1 |
|
|
Brachial plexus forms what major nerves? |
Dorsal scapular nerve, suprascapular nerve, lateral and medial pectoral nerve, axillary nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, thoracic nerve, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve, median nerve, ulnar nerve, radial nerve |
|
|
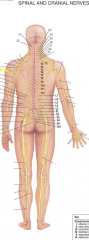
Lumbar plexus is formed from what nerves? |
T12-L4 |
|
|
What major nerves does the lumbar plexus form? |
Illiohypogastric, ilioinguinal nerve, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, genitofemoral nerve and femoral nerve |
|
|
From what nerves do the sacral plexus come from? |
L4-S4 |
|
|
What major nerves does the sacral plexus form? |
Gluteal, sciatic, posterior femoral, cutaenous nerve, pudendal, tibial and fibular nerve |
|
|
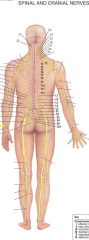
Musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
axillary nerve |
|
|
Median nerve |
|
|
radial nerve |
|
|
ulnar nerve |
|
|
femoral nerve |
|
|
sciatic nerve |
|

|
common fibular nerve |
|
|
tibial nerve |
|
|
Where is a lumbar puncture done?
|
Between L3 and L4 or L4 and L5 (right below tip of the spinal cord)
|
|
|
What sample is taken from a lumbar puncture and from what exact space?
|
CSF taken from the subarachnoid space (goes through the dura mater)
|
|
|
What is an epidural?
|
Catheter is inserted into epidural space and left in place with continuous analgesic (does NOT go through the dura mater)
|
|
|
What are the ligaments on the spinal cord that anchors cord laterally?
|
Denticulate ligament
|
|
|
The denticultate ligament is composed of ____ and attaches to the ___
|
pia mater, arachnoid
|
|
|
How long is the spinal cord?
|
About 18 inches
|
|
|
What are some responses of the parasympathetic division?
|
Pupils constrict, increase salivation, decrease heart rate, and increase digestion
|
|
|
What are some of the responses by the body by the sympathetic divisions?
|
Pupils dilate, decrease salivation, increase heart rate, decrease digestion
|

