![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Species Diversity:
|
1) Species diversity is the number of different species and the abundance of each species within a community.
2) The the species diversity of plants and trees in an area is directly linked to the species diversity of insects, animals and birds, due to habitat and food source variety. 3) Diversity can be measured to help monitor ecosystems and identify areas where it has been dramatically reduced. |
|
|
Index of Diversity:
|
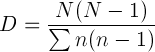
1) The simplest way to measure diversity it to count the number of different species, but this doesn't take into account the population size of each species.
2) The index of diversity is calculated using an equation that takes different population sizes into account. 3) The higher the number, the more diverse the area is. |
|
|
Impact of Deforestation:
|
1) Deforestation directly reduces the number of trees and sometimes the number of different tree species.
2) Deforestation also destroys habitats, so some species could lose their shelter and food source, which could result in death or migration, further reducing species diversity. 3) The migration of organisms into increasingly smaller areas of remaining forest may temporarily increase species diversity in those areas. |
|
|
Impacts of Agriculture:
|
1) Woodland clearance - increases area of farmland, reducing species diversity.
2) Hedgerow removal - increases area of farmland, reducing species diversity. 3) Monoculture - only one type of plant is grown, reducing species diversity. 4) Pesticides - kill organisms that feed on crops, reducing species diversity. 5) Herbicides - kills unwanted plants, reducing species diversity. |
|
|
Benefits of Deforestation:
|
1) Wood and land for homes to build.
2) Local areas become more developed by attracting businesses. |
|
|
Risks of Deforestation:
|
1) Diversity is reduced - species may become extinct.
2) Less carbon dioxide is stored because there are fewer plants and trees, contributing to climate change 3) Many medicines come from organisms found in rain forests - possible future discoveries are lost. 4) Natural beauty is lost. |
|
|
Benefits of Agriculture:
|
1) More food can be produced.
2) Food is cheaper to produce, so food prices are lower. 3) Local areas become more developed by attracting businesses. |
|
|
Risks of Agriculture:
|
1) Diversity is reduced - because of monoculture, woodland and hedgerow clearance, herbicide and pesticide use.
2) Natural beauty is lost. |

