![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is hCG human chorionic gonadotropin?
|
Hormone secreted by placenta-peaks at 8 wks.--pregnancy test.
|
|
|
2 urine tests, that are used to detect pregnancy:
|
Modified enzyme immunoassay and, slide test-agglutination inhibition test.
|
|
|
Other abnormal conditions that can be detected by hCG positive reaction?
|
Ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole of the uterus, and choriocarcinoma (cancer of the lung, stomach, pacreas, colon, or breast.
|
|
|
3 quality control precautions?
|
1.Kits must be stored and used at manufacturer's directed temperature.
2. reagents must not be used after expiration date. 3. Manufacturer's instructions must be followed precisely for particular test used. |
|
|
What result does one get by the slide test based on inhibition of agglutination (clumping) of hCG-coated latex beads mixed with hCG antiserum (antibody) against hCG) if it indicates are negative?
|
Negative agglutination is positive pregnancy.
|
|
|
EIA-enzyme immunoassay is?
|
Another, but, complex procedure than agglutination
|
|
|
What is the name of the infection of lymphocytes by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)?
|
Mono or infectious mononucleosis (IM)-transmission by saliva.
|
|
|
Symptoms of Mono or infectious mononucleosis (IM)?
|
Found in children and young adults. Incubation 4-50 days; 7-14 days are average.fever, swollen glands lasting 3-5 days. Over 7-20 days-patient may develop headache; malaise; chest pain; a cough; tonsillitis; rash; soft, swollen lymph nodes; and a swollen spleen.
|
|
|
Treatment for Mono or infectious mononucleosis (IM)?
|
REST!
|
|
|
Diagnosis of Mono (IM)?
|
Blood test, serologic test and patient's symptoms.
|
|
|
IM tests are CLIA waived, what does that mean?
|
MA's in POL's are able to use approved kits for IM .
|
|
|
What is Prothrombin Time/ProTime/INR?
|
International normalized ratio = test of blood clotting ability.
|
|
|
What is a desired INR?
|
a desired INR is 2.0-3.0.
|
|
|
What is blood typing based on?
|
It is based on presence or absence of certain antigens on the surface of RBC's.
|
|
|
What are immunoglobulins - Ig?
|
Antibodies in protein molecules that are found in serum.
|
|
|
What are the 2 major blood typing catagories?
|
ABO blood group and Rh factor.
|
|
|
ABO blood groups are?
|
Types A, B, AB, and O.
|
|
|
RH factors?
|
Rh factor positive and Rh factor negative (no factor.)
|
|
|
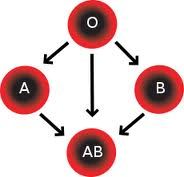
What are the reactions to different blood types?
|
O blood has no reaction to either anti-A or anti-B.
AB blood would have a reaction to both |
|
|
Pigmented bilirubin is?
|
Yellowing or jaundice of newborn's skin and tissues.
|
|
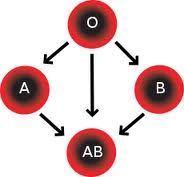
What blood group(s) are compatible?
|
|
|
|
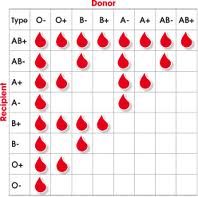
Compatible blood types & Rh factors
|
|
|
|
What is Phenylketonuria (PKU)
|
It is a rare condition in which a baby is born without the ability to properly break down an amino acid called phenylalanine.
|
|
|
What does a semen analysis determine?
|
1. A semen analysis to determine fertility should be performed on a minimum of two samples at least seven days apart over a period of two to three months because the sperm count and semen consistency will vary from day to day and some conditions can temporarily affect sperm levels.
2. evaluation for vasectomy 3. determine paternity 4. substantiate rape cases |
|
|
Tuberculosis (TB) cause?
|
Mycobacterium turberculosis, rod-shaped bacterium.
|
|
|
4 factors determined as part of fertility workup of semen analysis?
|
1. sperm count
2. percentage of motility 3. presence of aggultination 4. percentage of normally formed sperm cells |
|
|
Diagnosis of TB?
|
PPD-purified protein derivative is used in Mantoux test 0.1 mL of 5 TU (toxin unit), using 1 mL TB syringe #26 or 27 gauge needle and form a wheal.
|
|
|
Hypoglycemia
|
Low blood glucose level
|
|
|
Hyperglycemia
|
High blood glucose level--this occurs in diabetes mellitus and liver dysfunction.
|
|
|
Where is insulin come from?
|
Pancreas
|
|
|
FBG
|
fasting blood glucose.
|
|
|
Another condition caused by Hyperglycemia?
|
Cushing's syndrome and acute stress response
|
|
|
What is the glycosylated hemoglobin test, or Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) used for?
|
It is a test used to give you and your doctor the most accurate picture of your overall diabetes control.
|
|
|
What is cholesterol?
|
Cholesterol is a white, waxy, fatlike substance that occurs in the tissues of all vertebrates, and is found, in association with other sterols, throughout the animal kingdom; it seldom occurs in significant amounts in higher plants.
|
|
|
Function of cholesterol?
|
Cholesterol is an important component for the manufacture of bile acids, steroid hormones, and vitamin D.
|
|
|
2 kinds of Lipoproteins?
|
HDL-high density lipoprotein (helpful) and LDL-low density lipprotein (lousy)--they are transported o liver and excreted in form of bile.
|
|
|
Triglycerides?
|
They are ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.[1] There are many triglycerides, depending on the oil source, some are highly unsaturated, some less so.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of vegetable oil (typically more unsaturated) and animal fats (typically more saturated).[2] In humans, triglycerides are a mechanism for storing unused calories, and their high concentrations in blood correlates with the consumption of starchy and fatty foods. |
|
|
Bood urea nitrogen test (BUN)
|
BUN tests measure concentration of urea in blood.
|
|
|
Calcium test?
|
A blood calcium test is ordered to screen for, diagnose, and monitor a range of conditions relating to the bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth. Blood calcium levels do not directly tell how much calcium is in the bones, but rather, how much calcium is circulating in the blood.
|
|
|
Chloride test?
|
Blood chloride testing is often ordered, along with other electrolytes, as part of a regular physical to screen for a variety of conditions. These tests may also be ordered to help diagnose the cause of signs and symptoms such as prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, and respiratory distress.
|
|
|
Carbon Dioxide-CO2 test?
|
CO2 test is the laboratory test to measures the amount of carbon dioxide in the liquid part of your blood, called the serum.
|
|
|
Creatinine test?
|
The creatinine blood test is used along with a BUN (blood urea nitrogen) test to assess kidney function. Both are frequently ordered as part of a basic or comprehensive metabolic panel (BMP or CMP), groups of tests that are performed to evaluate the function of the body’s major organs. BMP or CMP tests are used to screen healthy people during routine physical exams and to help evaluate acutely or chronically ill patients in the emergency room and/or hospital. If the creatinine and BUN tests are found to be abnormal or if you have an underlying disease, such as diabetes, that is known to affect the kidneys, then these two tests may be used to monitor the progress of kidney dysfunction and the effectiveness of treatment. Blood creatinine and BUN tests may also be ordered to evaluate kidney function prior to some procedures, such as a CT (computed tomography) scan, that may require the use of drugs that can damage the kidneys.
|
|
|
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)?
|
The LDH test is generally used to screen for tissue damage. This damage may be acute (as in the case of a traumatic injury) or chronic (due to a long-term condition such as liver disease or certain types of anemia). It also may be used to monitor progressive conditions, such as muscular dystrophy and HIV. Normal level: 105-133 International Units/L
|
|
|
Phosphorus (Phosphate) test?
|
Phosphorus tests are most often ordered along with other tests, such as those for calcium, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and/or vitamin D, to help diagnose and/or monitor treatment of various conditions that cause calcium and phosphorus imbalances.
While phosphorus tests are most commonly performed on blood samples, phosphorus is sometimes measured in urine samples to monitor elimination by the kidneys. Normal level: 2.4-4.1 mg/dL |
|
|
Potassium (K) test?
|
Potassium testing is frequently ordered, along with other electrolytes, as part of a routine physical. It is used to detect concentrations that are too high (hyperkalemia) or too low (hypokalemia). The most common cause of hyperkalemia is kidney disease, but many drugs can decrease potassium excretion from the body and result in this condition. Hypokalemia can occur if someone has diarrhea and vomiting or if is sweating excessively. Potassium can be lost through the kidneys in urine; in rare cases, potassium may be low because someone is not getting enough in their diet. Normal level: 3.7-5.2 mEq/L
|
|
|
Sodium blood test?
|
Blood sodium testing is used to detect abnormal concentrations of sodium, termed hyponatremia (low sodium) and hypernatremia (high sodium). A doctor may order this test, along with other electrolytes, to identify an electrolyte imbalance. It may be ordered to determine if a disease or condition involving the brain, lungs, liver, heart, kidney, thyroid, or adrenal glands is causing or being exacerbated by a sodium deficiency or excess. In patients with a known electrolyte imbalance, a blood sodium test may be ordered at regular intervals to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. It may also be ordered to monitor patients taking medications that can affect sodium levels, such as diuretics. Normal level: 135-145 mEq/L
|
|
|
Total protein blood test?
|
Total protein measurements can reflect nutritional status and may be used to screen for and help diagnose kidney disease, liver disease, and many other conditions. Sometimes conditions are first detected with routine testing before symptoms have begun to appear. If total protein is abnormal, further tests must be performed to identify which specific protein is abnormally low or high so that a specific diagnosis can be made. normal level 6.0-8.3 mg/dL
|
|
|
Uric Acid blood test?
|
The uric acid blood test is used to detect high levels of this compound in the blood in order to help diagnose gout. The test is also used to monitor uric acid levels in people undergoing chemotherapy or radiation treatment. Rapid cell turnover from such treatment can result in an increase in uric acid.
The uric acid urine test is used to help diagnose the cause of recurrent kidney stones and to monitor people with gout for stone formation. Normal level: 3.0-7.0 mg/dL |

