![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the layers of olfactory organs |
Olfactory epithelium and lamina propria |
|
|
Give the olfactory pathway |
Sensory neurons➡olfactory epithelium in cribriform plate➡olfactory bulb➡olfactory tract➡olfactory cortex➡hypothalamus (limbic system) |
|
|
Name the different taste receptors |
Vallate papillae Fungiform papillae Filliform papillae |
|
|
Which if the three taste receptors on the tongue has no taste buds? What us it's purpose? |
Filliform papillae It provides friction |
|
|
List the order from the anterior to posterior to of where taste sensations are recognised on the tongue |
Sweet salty bitter sour |
|
|
How many days do gustatory cells survive? |
10 days |
|
|
List the cranial nerves involved in taste |
Facial, glassopharyngeal, and vagus |
|
|
Nane the three regions of the ear |
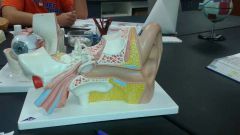
Outer, middle and inner |
|
|
Give the function of the outer ear |
Directs sound waves towards the middle ear |
|
|
Name the parts if th outer ear |
Auricle (elastic cartilage) External acoustic meatus (has ceruminous glands which produces cerumen that keeps foreign objects from getting deeper Tympanic membrane lies at the end of external acoustic meatus and separates outer ear from middle ear |
|
|
Describe the middle ear |
Air full tube connected to the pharynx by the auditory tube |
|
|
What is the function of the auditory tube |
Connects middle ear to pharynx Equalizes the pressure on either side of the Tympanic membrane |
|
|
Name the three auditory ossicles |
Malleus, incus, stapes |
|
|
The inner ear s divided into: |
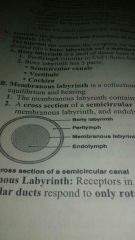
The bony and membranous labyrinth |
|
|
Give the function ion if and parts of the bony labyrinth |
Protects the membranous labyrinth Semicircular canals Vestibule Cochlea |
|
|
Membranous labyrinth |
Fluid filled tubes and chambers that house receptors for hearing and equilibrium |
|
|
Crista |
Area of the ampulla that has receptors. Each crista is bound to a cupula |
|
|
Sound pathway |
Sound waves➡external acoustic meatus➡Tympanic membrane➡auditory ossicles➡oval window➡pressure waves in perilymph➡distortion if hair cells in tectorial membrane➡cochlear nerves |
|
|
Palprebral fissure |
Gap separating j the free margin of the eyelid |
|
|
Tarsal gland |
Secretes fluid that prevents eyelids form sticking to each other |
|
|
Conjunctiva |
Thin mucous membrane that lines the inner eyelids and us reflected on the anterior surface of the sclera. |
|
|
Purpose of tears |
Provide nutrients and oxygen to corneal cells Lubricate the eyes Antimicrobial lysozymes |
|
|
Layers if the eye |
Fibrous Vascular Inner |
|
|
Fibrous layer of eye |
Outer coat of the eyeball Sclera white of the eye Cornea |
|
|
Conjunctivitis (pink eye) |
Results from damage to, and irritation if the conjunctival surface |
|
|
Choroid |
Part of vascular layer of eye Absorbs light so that it isn't reflected inside the eye |
|
|
Iris |
In vascular layer of eye Changes the shape of the pupil |
|
|
Visual pathway |
Photo receptors in retina(rods and cones➡bipolar cells➡ganglion cells➡optic nerve |
|
|
Accommodation |
Changing of the shape of the lens in eye to keep focal distance constant |
|
|
Near point of vision |
Minimum distance from the eye that an object can be clearly seen |
|
|
Optic disc |
Where the optic nerve leaves the eye |
|
|
Transduction |
Absorption of light by visual pigments in rods and cones which is then converted into graded potential |
|
|
Visual pathway |
Photo receptors➡bipolar neurons➡ganglion neuron➡optic nerve➡optic chiasm➡optic tract➡thalamus➡occipital lobe |
|
|
Depth perception |
Interpretation of 3 - dimensional relationships of objects in view |
|
|
Emmetropia |
Normal vision:when cilia muscle is relaxed in the normal eye the lens is flattened. Distance images are always focused on the retina surface |
|
|
Myopia(nearsightedness) |
Eyeball is too long. Can't focus on distant objects, corrected by concave lens |
|
|
Hyperopia (farsightedness) |
Corrected by convex lens eyeball too short or lens too flat |
|
|
Vertigo |
Illusion of movement. Caused by conditions, that alter the function of th inner ear receptor complex |
|
|
Blepharitis |
Inflammation of the eyelid |
|
|
Glaucoma |
Abnormally high intra ocular pressure from build up of aqueous humor, which destroys neurons of the retina. Second most common cause of blindness especially in the elderly |
|
|
Meniere's syndrome |
Too much endolymph, may cause deafness and loss of equilibrium |
|
|
Visual acuity |
Refers to the Sharpness or clarity of vision Tested using Snelling chart. |
|
|
Astigmatism |
Eye disorder where the lens or cornea are abnormally shaped resulting in out-of-focus vision |

