![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
7 Nations of South Asia are?
|
India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Maldives
|
|
|
Important mountain systems?
|
Himalayas - highest mountain chain on Earth
Karakoran (Pakistan, India, China) Hindu Kush (West of Karakoram) Ghats (East west coast of S India) Deccan Plateau (South India) |
|
|
Monsoon climate
- What is a monsoon climate? - Other name? - Where is it dominant? - Summer + winter? |
- Monsoon climate is a reversal of seasonal wind and precipitation patterns
- Dominant over central and Eastern portion - Also known as "Tropical wet climate" - Summer: Moisture laden, onshore SW winds, heavy precipitation - Winter: Dry, offshore wind flow - almost no precipitation |
|
|
Where are the deserts and semi-deserts found?
|
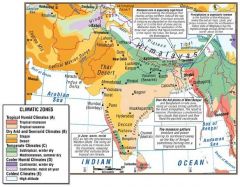
Pakistan and India
|
|
|
Where are the major population concentrations? Rural or urbanised?
|
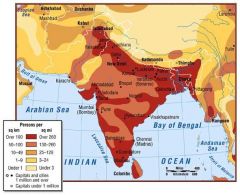
In major river plains (Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra) and coastal lowlands. Heavy rural population densities. Low urbanisation (India 25%, others less)
|
|
|
Dominant agriculture society type?
|

Primitive, low yield inefficient agricultural practices
|
|
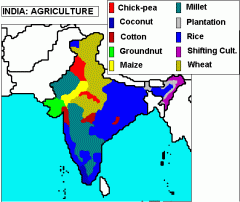
India's agriculture - NW, N, NE, Centre, SW, S, SE?
|
NW: Groundnut, Millet, Corn, Chickpea (GMCC)
N: Wheat, rice, chickpea (WRC) NE: Plantation, rice, shifting cultivation (PRS) C: Cotton, Millet, Rice, Wheat (CMRW) SW: Rice, millet, cotton (RMC) S: Coconut, millet, rice (CMR) SE: Rice, millet (RM) |
|
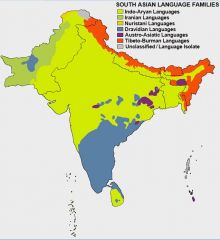
Language families of India
- Indo-European? - Dravidian? - Sino - Tibetan? - Autro-Asiatic? - Adamanese? |
Indo-Euro--> NW, N, Central, E, NE
Dravidian--> S, Centre, Tamil Sino-Tibetan--> N, NE Austro-Asiatic--> NE Adamanese--> Adaman Islands |
|
|
Population in India?
|
1 billion/1.5% increase
|
|
|
Population of Pakistan?
|
170 million/2.5% increase
|
|
|
Population of Bangladesh?
|
150 million/2% increase
|
|
|
Where are most population concentrations?
|
Along river plains (Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra)
|
|
|
What type of societies exist?
|
Largely peasant, subsistence agriculture societies (primitive, low-yield, inefficient agriculture)
|
|
|
Where is Hinduism dominant & where is it a minority?
|
Dominant in India and Nepal
Minority in Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka |
|
|
Where is Islam dominant and a minority?
|
Dominant in Pakistan, Bangladesh (Both sides of India)
Minority in India (yet its the 3rd largest Muslim country) |
|
|
Where is Buddhism dominant & where is it a minority? Where did it originate?
|
Dominant in Sri Lanka, Bhutan
Minority in Nepal, India Origins: Buddha in 6th century in NE asia, it is the state religion of ancient religion |
|
|
Where did the invasion of Islam take place? What was the name of the Empire?
|
West and North West, "Mogul Empire"
|
|
|
Who held a commercial outpost on the west coast of India until 1960?
|
The Portuguese and the French
|
|
|
What colony held commercial influence in SE spices?
|
The Dutch
|
|
|
What colony was the last to arrive?
|
The British in 1600
|
|
|
What was the British India company?
|
Colonial administration and exploration
|
|
|
What happened during the 1857 rebellion in India?
|
It was crushed by the British, and they established direct control under British government
|
|
|
When were the years of the British raj?
What was established? |
1857-1947
Establishment of "colonial economic pattern" |
|
|
Why was India hard to administer? What was the solution?
|
Hard to administer due to cultural & political complexity, densely populated.
Solution was rule by proxy, considerable degree of local autonomy granted. |
|
|
What are some economic benefits of the British colonial rule?
|
Transportation infrastructure (best railroad network)
Seaports Manufacturing industries Trains bring mining's to seaports |
|
|
What major city seaports where established?
|
- Mumbai (Bombay) = largest city, economic capital
- Kolkata (Calcutta) = Was once a capital, climate too bad - Chennai - Karachis = largest city in Pakistan |
|
|
When was India's partition & independence?
|
1947
|
|
|
What was the problem in India's independence? What was the solution?
|
Problem: Religious regionalism
Solution: Partition (India/Pakistan) - religions found in wrong countries |
|
|
Who are the 3 strong native leaders that emerged during the time of Independence?
|
Ghandi: leader of India nationalism in British-rule
Nehru: First prime minister in India Jinnah: First governor general in Pakistan |
|
|
What volatile region couldn't divide between religions?
|
Jammu & Kashmir
|
|
|
What happened in 1971 with Pakistan/Bangladesh
|
Islamic republic
|
|
|
What is the name for India's "Silicon Valley" and where is it found?
|
Bangalore, in south India
|
|
|
What country was formerly known as East Pakistan until 1971 and is deficient in energy & other natural resources? What is its capital?
|
Bangladesh
Capital = Dhaka |
|
|
What is Bangladesh prone to, due to its flat topography?
|
Natural disasters (Ie: Cyclones, floods)
|
|
|
What country has a legacy of ethnic tensions & insurgency? How is their population split (religiously)? And what is their economy?
|
Sri Lanka (capital=Colombo)
Pop = 20 million. 70% Buddhism, 15% Hindu, 15% other. Economy = tropical produce (tea, wheat, coconut, rubber, rice) |
|
|
What countries are Himilayan states?
|
Nepal & Bhutan
|
|
|
What country is an absolute monarchy? What is its state religion? Whats its population like?
|
Bhutan (capital=Thimphu)
It is remote and underdeveloped Very traditional, throwback to the middle ages State religion = Buddhism |
|
|
Former name of Sri Lanka?
|
Ceylon, until 1972
|
|
|
Where is the Indus, Brahmaputra and Ganges rivers?
|
Indus: Pakistan, India
Brahmaputra: Bhutan Ganges: India |

