![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are three things that need to be listed on each axis of a graph?
|
1. range of variable
2. units of measurement 3. name of variable |
|
|
What variable goes on the X axis? 2 terms
|
manipulated variable
independent variable |
|
|
What variable goes on the Y axis? 2 terms
|
responding variable
dependent variable |
|
|
Give 2 liquids with high viscosity.
|
syrup and honey
|
|
|
Give 2 liquids with low viscosity.
|
water and milk
|
|
|
Describe the motion and arrangements of particles in a solid.
|
tightly packed so that they can only vibrate
|
|
|
Describe the motion and arrangements of the particles in a liquid.
|
a little less tightly packed than a solid so they can flow freely
|
|
|
Describe the motion and arrangement of particles in a gas.
|
very spread out so they can move in all directions
|
|
|
Define Boyle's Law.
|
at constant temperature
If pressure increases, the volume decreases If pressure decreases, the volume increases |
|
|
Define Charles's Law.
|
at constant pressure
If temperature increases, the volume increases. If temperature decreases, the volume decreases. |
|
|
Give examples of Charles's Law.
|
1. A ball inflated inside and then taken outdoors on a winter day shrinks slightly.
2. A slightly underinflated rubber life raft left in bright sunlight swells up 3. The plunger on a turkey syringe thermometer pops out when the turkey is done (The volume of air trapped under the plunger increases when the temperature inside the turkey climbs). |
|
|
Give examples of Boyle's Law.
|
1. The bubbles exhaled by a scuba diver grow as the approach the surface of the ocean. (The pressure exerted by the weight of the water decreases with depth, so the volume of the bubbles increases as they rise.)
2. Deep sea fish die when brought to the surface. (The pressure decreases as the fish are brought to the surface, so the volume of gases in their bodies increases, and pops bladders, cells, and membranes). 3. Pushing in the plunger of a plugged-up syringe decreases the volume of air trapped under the plunger. |
|
|
Explain what happens to a full balloon in a hot car. Include thermal energy and particle motion.
|
As the thermal energy increases, the particles move more. The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules inside would increase, creating more frequent and forceful collisions with the inside walls of the balloon. The balloon would look very puffy and full, and because Mylar balloons are not stretchy and elastic, the balloon might even burst.
|
|
|
Explain what happens as a wet towel dries on a clothesline. Describe the thermal energy and particle motion.
|
The water in the towel evaporates from the surface of the towel because energy from the sun is transferred to the water in the towel giving them enough energy to increase their motion and vaporize.
|
|
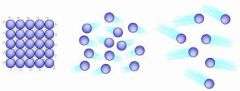
Which state of matter is which?
|
solid - liquid - gas
|
|
|
What is the difference between an amorphous and a crystalline solid?
|
amorphous - without a definite crystalline shape or geometric pattern
crystalline - having a repeating geometric pattern and a definite shape |
|
|
Give 2 amorphous solids.
|
plastic
wax butter glass |
|
|
Give 2 crystalline solid.
|
salt
sugar |
|
|
What is sublimation? What happens to the thermal energy and the motion of the particles?
|
when a material goes from a solid directly to a gas
Thermal energy increases, and particle motion increases. |
|
|
What is freezing? What happens to the thermal energy and the motion of the particles?
|
when a material goes from a liquid to a solid
Thermal energy decreases, and particle motion decreases. |
|
|
What is melting? What happens to the thermal energy and the motion of the particles?
|
when a material goes from a solid to a liquid
Thermal energy increases, and particle motion increases. |
|
|
What is condensation? What happens to the thermal energy and the motion of the particles?
|
when a material goes from a gas to a liquid
Thermal energy increases, and particle motion increases. |
|
|
What is vaporization? What happens to the thermal energy and the motion of the particles?
|
when a material goes from a liquid to a gas
The thermal energy increases, and the particle motion increases. |
|
|
solid to a liquid
|
melting
|
|
|
liquid to a solid
|
freezing
|
|
|
solid directly to a gas
|
sublimation
|
|
|
liquid to a gas
|
vaporization
|
|
|
gas to a liquid
|
condensation
|
|
|
What is the formula to calculate pressure?
|
pressure = force/area
|
|
|
Define pressure.
|
the force exerted on a surface divided by the total area
|
|
|
Explain how condensation forms on the outside of a cup of cold lemonade on a hot day. Remember to describe thermal energy and particle motion.
|
Condensation causes the vapor in the nearby air around the glass to condense to form very tiny droplets of water on the outside of the glass.
|
|
|
When you open a solid air freshener, the solid slowly loses mass and volume. How does this happen? Describe thermal energy and particle motion.
|
Through sublimation, the particles in the air freshener gain thermal energy and escape to the air where they can move more freely in all directions.
|
|
|
How is the thermal energy of a substance related to its physical state?
|
Kinetic theory says that the particles in matter are in constant motion. Increasing thermal energy increases the movement of the particles, and the material goes from a solid to a liquid to a gas . Ice melts to water with increased heat. The water vaporized to gas as the thermal energy is increased again.
|
|
|
How does heating a gas in a rigid container change its pressure. Explain.
|
The increased thermal energy makes the particles move more and faster. They hit the inside of the container more frequently creating more pressure.
|
|
|
definite shape and volume
|
solid
|
|
|
definite volume but no definite shape
|
liquid
|
|
|
no definite shape or volume
|
gas
|
|
|
Which state of matter can be compressed?
|
gas
|
|
|
What are the two types of vaporization, and how are they different?
|
1. evaporation - from the surface of the liquid
2. boiling - from within the liquid |

