![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Morphology |
Form, structure, and organization of a soil (color, texture, structure, aggregates) |
|
|
Genesis |
Factors and processes leading to soil formation |
|
|
Classification |
Categorization of soils into groups by physical, mineralogical, and chemical properties |
|
|
Pedon |
Smallest 3d unit that contains all the properties of a studied soil |
|
|
Solum |
Horizons that have undergone the same soil forming conditions (A, E, and B horizons) |
|
|
5 Soil forming factors |
Cl - Climate
O - Organisms R - Relief P - Parent material T - Time |
|
|
4 Soil forming processes |
Additions
Losses Transformations Translocations |
|
|
Horizon differentiation |
Horizons are determined by color, texture, structure, accumulations, pH, roots |
|
|
Textural Triangle |
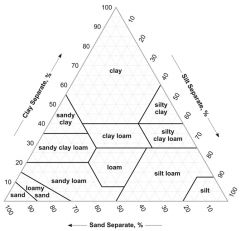
|
|
|
Texture in mm (Clay - vc sand) |
Clay - less than 0.002 Silt - 0.002 to 0.05 Vf Sand - 0.05 to 0.10 F Sand - 0.10 to 0.25 M Sand - 0.25 to 0.50 C Sand - 0.50 to 1.0 Vc Sand - 1.0 to 2.0 |
|
|
Concepts of Soil Genesis |
Processes have been consistent over time Many processes act in unison Five factors (Clorpt) drive the processes Present soils may reflect past processes Soils in a location may change over time Soil time is shorter than geologic time Complexity in genesis is more common Soils are clay factories Genesis is useful Knowledge of genesis is essential |
|
|
Organic vs Mineral
|
Less than 18% C for 60% clay Sliding scale Less than 12% C for no clay |
|
|
Gelic Cryic Frigid Mesic Thermi Hyperthermi Iso |
Less than 0 C, no swing 0 - 8 C, no swing 0 - 8 C 8 - 15 15 - 22 C 22+ C No 6 C swing between seasons |
|
|
Aquic Aridic Udic Ustic Xeric |
Saturated Moist less than 90 consecutive days Dry less than 90 days Dry/moist 90/180 days Dry/moist 45/45 consecutive days |
|
|
Parent Material types |
Siliceous crystalline rocks
Sediments and sedimentary rocks Glacial deposits Volcanic ash |
|
|
Catena |
Toposequence based on drainage |
|
|
Oxidation Reduction Oxidation - Reduction Hydration Hydrolysis Solution Chelation |
Loss of electrons
Gain of electrons Fluctuation Sorption of h2o Attack of silicate by hydrogen ion Dissolving of carbonates or salts Formation of ring bond to metal ion |
|
|
Order Suborder Great group Subgroup Family Series |
Alfisol Xeralf Durixeralf Abruptic Durixeralf Fine mixed active thermic Abruptic Durixeralf Redding |
|
|
Smectite Kaolinite Vermiculite Halloysite |
2:1 high CEC shrink swell 1:1 low CEC 2:1 high CEC Volcanic |

