![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Structural Functionism -deviance serves a purpose. Deviance is a failure of social functions to work together properly. *jobs w/o a living wage will encourage theft. |
● affirms our norms ● clarify moral good/bad boundaries ● brings people together *MADD ● creates social change *break an unjust law, Rosa Parks |
|
|
Strain Theory - deviance depends on the strain between your cultural goals and the means of achieving those goals. You can accept or reject the goal and the means. |
● Total acceptance - conformity ● Innovation -still trying to get the goals, but using original strategies “thinking outside the box” ● Ritualism -wants the job, but not in it for the money. *teacher, social worker ● Retreatism -dropped out of society *street people by choice ● Rebellion -drop out, but they reject all and create a different society. Counter-culturalists *Amish, Hippie |
|
|
Symbolic Interactionist |
small group dynamics, how people are influenced in a small group. With deviance, how people learn to be criminals and how labels influence. |
|
|
Hirschi’s Control Theory |
whether or not you are deviant depends on if you anticipate the consequences of your actions. |
|
|
4 Social Controls that influence your level of anticipation: |
1. Attachment -those with strong social attachments (connections to community) tend toward high conformity. 2. Committment -if you are committed to achieving goals in society, you are more likely to conform. *Don’t want to hurt my futurechances. 3. Involvement -people engaging in non-deviant/legitimate activities are more likely to conform. 4. Belief - people who believe in conventional morality and respect the laws and authority, are more likely to conform. |
|
|
Conflict Theory |
maintain power and privilege of a few over the many. Criminals are victims of a conflict structure. Social inequality and privilege status gives people a greater chance of getting out of punishment. |
|
|
Four primary reasons for incarcerating criminals |
1. Incapacitation-remove person from doing furtherharm. 2. Deterrence -being punished deters from repeating and serves as a deterrent for others seeing the punishment. *Actually gives them status and more skills 3. Rehabilitation -take out of environment and with proper care and treatment we can reform them. *Depends on if they choose to reform 4. Retribution - revenge, punish for what they have done wrong. *Continues after they have done their time. |
|
|
Four principles of social stratification |
1. trait of society and not a reflection of individual differences *rich people get better test scores because they have access to more resources and support 2. persists across generations *poor stay poor, rich stay rich 3. universal,but variable; happens everywhere, but varies as to how much *US has biggest wage gap, Western nations have small gap. 4. belief system justifies the inequality *blame the individual, they deserve what they get |
|
|
Systems of stratification |
1. Caste system = Birth. Social stratification or hierarchy based on birth. Born there and stay there. CLOSED system. Determines who you marry and the kind of work you are eligible for. 2. Class system= Birth + Achievement. Can move up or down. OPEN system. Chances are low, but you have the ability/possibility. *Industrialized nations, like U.S. 3. Merit Class = Achievement. Does not exist in real life. Exists in our minds. This is our belief of how things are. |
|
|
3 sociological theories of social stratification/class |
1. Structural Functionism -we have hierarchy because it plays a vital role in the operation of society. ● rank in terms of importance *skill, education, training, responsibility ● give more reward to jobs at the top ● career ladder ● promotes productivity and hard work 2. Social Conflict Theory - argues that social stratification benefits some, while hurting others *more have’s than have not’s 3. Symbolic Interactionist -focus on how interactions help to display class status or reinforce boundaries between class. *leave your class, hard to fit in when you come back ● display - the way you act, objects you buy, food |
|
|
Types of social mobility -can be up and down, but since we are on an OPEN system, we tend to think just up. *all three types can happen at once! |
1. Structural (social mobility) - a shift in social position among a large number of population, typically due to some change within society *stock market crash led to great depression 2. Intragenerational(social mobility) - change inposition over one’s lifetime 3. Intergenerational (social mobility) - change in social position of children in relation to their parents. Comparing two generations. |
|
|
Film: People Like Us |
● WASP lessons - silver spoon people - have to be born into it,can’t learn it. ● Bourgeois Blues - black people becoming middle class and never really fitting in with blacks or whites - going against their racial roots. ● Tammy’s Story - lives in a trailer home, 4 kids, walks 10 miles toschool. Grew up poor, now she is poor. Son sees himself in a class above. |
|
|
Merton’s typology for Prejudice + Discrimination |
● Not prejudice - “liberal” ● Prejudiced non-discriminators - “timid bigot” - has belief without acting on it -- fears consequences ● Prejudiced discriminators - has the belief of inequality and acts on it - “all weather bigot” ● Non-prejudiced discriminators - “fair weather liberal” - institutionalized discriminator - they don’t believe one group is superior or inferior, but they will succumb and go along with peer pressure. |
|
|
Film: Blue Eyed |
● Purpose: to give blue-eyed white folks a chance to experience what it’s like to be a minority. ● Message minorities get in this society is to assimilate = to act white. ● Real life experiences that mimic this - kids in school (man’s story of his son), any form of discrimination/segregation |
|
|
Minority status/Majority and minority patterns of interaction |
1. Pluralism -state where people of all different races and ethnicity are distinct, but have social parody or equal access to resources/equality. Pluralistic society recognizes differences,but doesn’t treat people different. *U.S. laws are equalistic 2. Assimilation - process where minorities gradually adopt patterns ofthe dominant culture *melting pot - learn english 3. Segregation - physical or social separation of categories of people. Can be voluntary or involuntary. Even if people are mixed,you can feel it socially. *Amish, black vs. white 4. Genocide -systematically killing one category of people by another. Most motivated by race/ethnicity. *Holocaust |
|
|
Anne Fausto Sterling’s 3 examples that challenge ideas about sex and gender |
1. Transgender- believes they are born in the body of the wrong sex 2. Berdache - “2spirit” - “multiple genders” -embodies masculine and feminine 3. Intersexual- person born as a combination of make and female biology. More than 5% of population. |
|
|
Social Stratification & Gender |
gender stratification - a hierarchy where men have greater access to resources than women. a. Labor work force - women in 1900s were 20%, now 60%. Men 75%. b. Occupational sex segregation c. Wage Gap d. Gender socialization - socialize women toward certain characteristics to perform better at those particular jobs e. Discrimination- glass elevator vs. glass ceiling f. Stalled Revolution - 1) in the home with unequal sharing of duties and 2)by employers not offering paid ways to balance work and family |
|
|
Institutions & gender inequality: Gender inequalities in health and health care, families, education, and economy |
● Nurses;Elementary school teachers; Librarians; Social workers ● Men’s tokenism is experienced as a positive - “glass elevator” ● Women in men’s fields have to work doubly as hard to prove themselves “glass ceiling” ● Men earn more money than women in every occupation, even female dominated jobs ● There are stereotypes about characteristics of men & women than may or may not be accurate |
|
|
Seven rape myths |
1. Victim was asking for it 2. Victims “cry” Rape - she made it up - 2% are false, like all crimes 3. Says “no” when she means “yes” - playing hard to get 4. Victim should have prevented the rape - victim blaming 5. Most rapes are committed by strangers - 85% are known to victim 6. Those who commit rape are mentally ill 7. Rape does not cause harm - some signs aren’t visible;STD; pregnancy; PTSD |
|
|
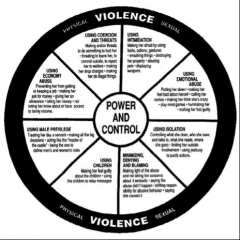
Power and Control Wheel |
|

