![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
154 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do you define close relationships and intimacy?
|
-shared knowledge, extensive and personal--have joy and happiness with them
-feeling of caring and affection -interdependent: need and influence each other -lives overlap, have a mutual existence -trust: expectations of others good intentions--this can vary over obstacles--may be strengthened or weakened -relationship is indefinite: commitment |
|
|
What is the best predictor of overall life satisfaction? according to a 1971 survey
|
-marriage and family life
-interconnectedness helps improve life satisfaction -single consistent predictor of well being in 42 countries studied was the quality of close relationships -the better the relationship, the higher the well being -the happiest people (top 10%) the one thing they all had in common was -good relationships (romantic and other) -necessary, but not sufficient conditions for happiness -some in good relationships but not happy |
|
|
What is the connection between relationship and stress?
|
study that asked what is the last "bad" thing that happened to you?
-some said interpersonal conflicts and problems -death of significant others -economic/legal/work problems -health problems (self or others) -sometimes relationships can cause stress |
|
|
What is the study of close relationship and mortality? what is the connection?
|
-there was a epidemiological study
-assessed their social integration (marriage, contact with friends/family, group affiliations ex: church) -followed up 9 years later -age-adjusted relative risk ratio: women: 2.3 men: 2.8 -those less social 2.3-2.8 died before 9 year follow-up -found that time with marriage and family and friends more important than having a church membership |
|
|
What was the study of baboons and sociality?
|
-followed 108 baboons for 16 years
measures of sociality: -if there were adults within 5 meters -if they were grooming one another -if they were being groomed -calculated infant survival: -the more social, the more infants survived -if fought over resources then not as good for infant and not as well protected -assistance from ohter group members help infants and males protect them |
|
|
What was the study about relationship, health and the common cold?
|
measured their sociability 2-4 weeks before study, number of people and time socially interacting
-exposed to virus, quarantined days 1-5 symptoms Objective: mucus weight -self-report of symptoms: runny nose sore throat the lower the sociability the higher chance that they got a cold high sociability the less severe the cold was |
|
|
What is this need to belong?
|
-human beings have a fundamental need to form and maintain a minimum quantity of lasting, positive and significant interpersonal relationships
|
|
|
Why is there a fundamental need to belong?
|
-produces strong effects under all but the most adverse conditions?
-have emotional consequences? -direct cognitive processing..the way we think about the world around us -lead to ill effects if not met? -exist universally? among all people -short comings in physical/mental health and risk of mortality |
|
|
How does evolution influence our socialization?
|
-natural selection for adaptive mechanisms
--can protect kin/group offspring -larger union will survive over time -Men and women faced different reproductive challenges -parental investment-male less investment -paternity uncertainty-female more certain, know if it's their child |
|
|
What are the gender differences in distress over external involvement?
|
83% of women would be distressed with emotional involvement
60% of men would be distressed with physical involvement men don't know for sure if it's their kids, investing in kids that not sure if its theirs women don't want the men to support other women |
|
|
What is the marriage norm now compared to before?
|
people are marrying when they are older
-the poorer the country, the younger people are marrying |
|
|
Are women and different really that different?
|
nope, they are more alike on variables than different
|
|
|
What are the Personality differences in men and women?
|
in the OCEAN big five test
-agreeableness-more social support, gives assistance when you need it -Neuroticism- decrease in relationship satisfaction in men and women if they are high in neuroticism |
|
|
How does self esteem affect relationship satisfaction?
|
the more self esteem they have the higher the relationship satisfaction
but... is it higher relationship satisfaction that creates higher self esteem or higher self esteem that creates higher relationship satisfaction? |
|
|
How does relationship history affect current relationships?
|
if prior relationship had problems, then there might be trouble with current relationship
-good relationship in pas, then good quality relationship now |
|
|
What are the different attachment styles?
|
secure
avoidant anxious-ambivalent dismissing |
|
|
What is secure attachment?
|
lower anxiety and avoidance
ex: it is easy for me to become emotionally close to others. I am comfortable depending on them and having them depend on me. I don't worry about being alone or having others not accept me |
|
|
What is avoidant attachment?
|
high anxiety and high avoidance
ex: I am uncomfortable getting close to others. I want emotionally close relationships but I find it difficult to trust others completely or depend on them. I worry that I will be hurt if I allow myself to become too close to others. |
|
|
What is anxious ambivalent?
|
-high anxiety and low avoidance
ex: I want to be completely emotinoally intimate with others, but I often find that others are reluctant to get as close as I would like. I am uncomfortable being without close relationships, but I sometimes worry that others don't value me as much as I value them. clingy |
|
|
What is Dismissing?
|
low anxiety and high avoidance
ex: I am comfortable without close emotional relationships. It is very important to me to feel independent and self-sufficient, and I prefer not to depend on others or have others depend on me. |
|
|
What was the results for the attachment study at the airport?
|
Higher on avoidance attachment:
-women-less care giving and contact seeking behaviors; more avoidance -not as warm to partners, less eye contact, not much distress -men: less sadness Higher on anxiety attachment style women: more self reported distress -but dont show it, just self reporting men: less contact maintenance and more avoidance -make sure not to show anxiety because they are a man |
|
|
What is attraction?
|
-the desire to approach
-we are attracted to those whose presence is rewarding (Directly or indirectly) -just by being in the vicinity -many factors contribute to who we find attractive--who we want to be our friends and romantic partners |
|
|
What is the relationship of proximity and propinquity among relationships?
|
-increases likelihood of meeting
-classic study of friendships in student housing at MIT -65% of friends lived in the same building -first have to meet them -just being there--> friends -friends with people said friends with 44% people next door than 22% 2 doors down down the hall 10% -stair well- likely to be friends with people on second floor -children had more friends with people whose last name is in same letter |
|
|
What is the mere exposure study?
|
-subliminal exposure
-chinese characters objects with no known association -repeated exposure=more liking -don't even need a positive interaction -negative interactions can increase as well 70% of people they dislike come from same building -at least if they didn't like them they could avoid them if they wanted to |
|
|
What is the bias of beautiful people?
|
-belief that what is beautiful is good
-describe people nicely when they are beautiful ex: kind, strong, outgoing, caring, sensitive, interesting, happier marriages etc. -cross cultural study -beautiful people recieve more praise -and beautiful people are skeptical when evaluator knew what they looked like than if they didn't and evaluated them |
|
|
How is beauty related to job?
|
-more likely to be hired at job and more pay
-better evaluation at work even when it is a controlled variable -more physical attraction, lower fine/smaller sentences |
|
|
What was the historical perspective early computer dance study?
|
-single students got free tickets to a dance
-rated on attractiveness by observers -randomly paired with a date -rated their date at intermission -only physical attractiveness predicted liking -only initial and short term, but doesn't hold true for long relationships -assume good characteristics |
|
|
What are some consistencies in physical attractiveness?
|
consistent in most cultures
women: large eyes, prominent cheekbones and small nose Neonate baby face features: large eyes, small nose sexual maturity features: -cheekbone prominence symmetry |
|
|
What are physical attractiveness traits in men?
|
-broad jaw and broad forehead
symmetry |
|
|
What was the study on baby-faced features?
|
-large eyes, small nose, round face and thin eyebrows
-correlated positively with perceptions of : -physical weakness -naivete -honesty -warmth (By men only) -rated more positive in woman than men in both gender observers |
|
|
What is attractive in women for body hip ratios?
|
waist to hip ratio of .70 for women and .90 for men
-consistent throughout different cultures |
|
|
What was the difference between buss and collegeagues and eagly and wood studies?
aka corss=cultural sex differences Evolution vs. Society? |
Buss:
-beauty= youth -youth in women: reproductive window -reproduction adaptive -men value attractiveness more Eagly and Wood -beauty= youth - youth in women: fewer resources -fewer resources means more likely to work inside the home -men value attractiveness more |
|
|
What is reciprocity?
|
we are attracted to people who are attracted to us and in "our league"
desirability= physical attractiveness x probability of acceptance -have to love you back |
|
|
What is the study with same or different movies playing at different cubicles?
|
attractive woman had the good movie
other cubicle, not interesting movie -75% went in the cubicle as the women if it was a good movie -25% if it was the same movie -has an excuse to sit in same cubicle |
|
|
How is similarity related to relationship satisfaction?
|
-we are attracted to people who are similar to us
-background -interests -tastes -personalities -spouses with similar personality are more satisfied -share same emotional responsibility -predictable -understand what you're going through opposites don't attract! -people become similar in their emotional reactions over time -coordinate thoughts and behaviors of relationship partners -incraeses their mutual understanding and foster their social cohesion |
|
|
What is gonzaga campos and bradbury's study on emotional convergence?
|
172 newly wed couples
-studied at 2 time points, 12 monts apart -personality -relationship satisfaction -emotional lab tasks -over 12 months prsonality became more simliar, world views similar -lab tasks reaction similar -increase in relationship satisfaction -increase in change, similarity and satisfaction |
|
|
What about opposites attract?
|
no
-old man and young woman? -increase similar over time or break up -arranged marriages- just as happy as non arranged -because parents arranging find people who have similar demographics and personality traits |
|
|
What is primacy effects?
|
forming first impressions
-envious, stubborn, critical, impulsive, industrious and intelligent -intelligent, industrious, impulsive, critical, stubborn and envious -first is more positive and preferred more even though same |
|
|
What is the Hanna study of forming impressions?
|
-showed a video of hannah and said if she was rich or poor
-showed her taking a test, and getting some wrong -when she was rich- people thought she had a higher level of ability poor: lower level -confirmation bias- prove they are correct then look for evidence that they are wrong |
|
|
What is transference?
|
need for closure (personality trait)
-people vary in their desire to reduce ambiguities in their lives -people with high need for closure do not like ambiguity -do not like to look at people in multiple ways -first info=crucial info for viewing them |
|
|
What is the study of transference?
|
Susan Andersen paradigm
SO= significant other -Participant’s list attributes of positive significant other (SO) and negative (SO) -Come back later for “another study” in which they will interact with stranger and given information about this stranger -list of stranger's traits -partial list of theirs or others' -confederate was same person in all -Partial list of one of their SO’s attributes OR given list from someone else’s SO -When given own SO they think the stranger also possesses the other attributes of SO that were not presented! -Influences their affect and cognitions about stranger -if participant's traits of SO were positive more likely for positive interaction with stranger if SO negative, less positive interaction and not develop friendly relationship -they filled gaps with knowledge assume they are similar -just like significant other even if you don't know |
|
|
What is overconfidence as relationship goes on?
|
-confidence increases with time, but accuracy does not
study: 1/2 year: accurately knew what partner had recorded 39% right longer- 90% confident, but still only 39% right increase in confidence about past but not always more accurate |
|
|
What is the study of estimates of relationship outcome?
|
-People in new relationships (1-11 months)
-Will you be in this relationship in 1 year? -Parent and roommate also asked -Re-contacted participants 1 year later -Correlations: prediction and actual outcome Participants = .21, not significant Roommates = .37, significant Parent = .35, significant Roommates and parents made better predictions than participants, roommates were best -Parents thought there were more challenges and hardships |
|
|
What is the study of " I love you more today than yesterday"
|
-101 dating couples followed for four years
-60 broke up, 41 stayed together -Provided 5 assessments: Current love, satisfaction, commitment -Estimations of how much feelings changed in last year, if at all (decreased, same, increased) -Actual change was not significant across any of the time points -Perceived change of intact couples: “increased” -Perceived change of breakup couples: “decreased” -Happier couples perceived more change than less happy couples |
|
|
What is positive illusions?
|
-Positive illusions of our partners that minimize their faults and accentuate their positives
-Partners are a mix between reality and our own ideal partners -We judge our partners more favorably than they judge themselves higher favorable view= -Increased commitment -Increased self-esteem of partner |
|
|
What is self-verification?
|
-Married people with low SE reported higher intimacy when spouse verified their self-views
-when given negative feedback not positive because it confirmed self views -Dating partners preferred those who enhanced their self-views -even when not positive -This change is called “the marriage shift” -feelings of closeness are enhanced with positive feedback or low self esteem -accurate feedback even negative is preferred, how serious, honest, and committed |
|
|
What is rejection sensitivity?
|
-to anxiously expect, readily perceive and overreact to rejection
-individual differences in RS: high RS= high concern low RS = low concern |
|
|
What are the functions of non-verbal behavior in communication?
|
-providing info
-knowing when to start/stop talking -regulating info may sit closer -defining info -see who is dominant/submissive -social control -purposely influence in someone else's behavior -presentation and display- give off an image ex: pretend to be happy to end fight -service tasks: taking them to dr's or airport |
|
|
What are the ways we use emotional facial expressions?
|
basic emotions
-hard to control signals -often honest of how they feel Display rules -intensify, minimize, neutralize, and mask |
|
|
What is the social function of embarrassment?
|
-react when you don't want the whole world to know
-violation of social invention failed to do something study: -failed at personal achievement task, not on ideals, but others -embarass act- uninterested in having public behavior -judgment ridicule from group -allow quick repair to be accepted back in group |
|
|
What are the outcomes of embarrassment?
|
-reflect greater concern with others' evaluations
-if you show you are embarrassed, don't really care what others think, then not as social -better liked: if showed embarassment, less punishment from others -elicits help -less likely to be delinquent- adolescents show embarrassment will be less delinquent |
|
|
What are display rules?
|
Intensify: parents to show kids
minimize: try to minimize your expressions neutralize: withstand the feelings mask: replace with another emotion -show which are appropriate ex: runner up to contest |
|
|
What was the display rules study: Emotional labor?
|
-Managing emotions on the job (e.g., restaurant workers, hospital workers, bill collectors)
-99 participants, 21 years, 81% experience (service related jobs, deal with customers) -Randomly assigned to difficult customer Display rules: positive yes, negative no emotional exhaustion, r = .17** task errors, r = . 31** -record main errors-be happy/friendly -1st: ok 2nd problem: either had polite or hostile customer -more erros on hostile customers than polite -more emotionally exhausted and more cognitive and emotionl effort |
|
|
What are courtship displays, flirtation?
|
-nonverbal para-language plays a role
-different behaviors, vary by culture -courtship displays flirting women: look around room, move more with music, run fingers through hair men: women's attention drawn, need to notice them, take up lots of space, open posture, try to display high status and dominance if mutual--then patterns converge gaze more, touch partners, warmer and inviting -flirting by women does not mean sexual interest |
|
|
What are dominance displays?
|
-holding eye gaze
-shows interest in others, but can show dominance/submission -usually people look 60% when listening, 40% when talking dominant: 60% when talking 40% when listening -lets them know you're interested but it's supposed to be reversed dominance |
|
|
What are the different body movements women show?
|
-smile more
-hedge more (ex: umms, kinda) -submissive posturing catch-22 -women who engage in these behaviors are liked better -signs of lower status -inhibited work place progress -if equal status, differences disappear |
|
|
What do body movements show in our culture?
|
-dominance:
displayed more dominance, interpruted more space, in teacher student study -touched back side of person more ex: prisoner experiment Sexual orientation -evaluators were gay/lesbian and better at distinguishing what orientation they were Personality: -if shown slices of persons behavior, able to tell OCEAN ex: bad mood etc |
|
|
What was the tiedens and fragale's study on dominant submissive postures?
|
93 MBA students
-Takes turns with confederate describing Kandinsky paintings in information task -Confederate adopted dominant or submissive posture during task Dom: draped arm over chair, legs extended Sub: slouched, hands in lap, legs together -depends on the subjects -if confederate is complimentary style, they like them more than if they were the same style |
|
|
How is touch related to dominance or affection?
|
consented touch: conveys closeness, affection, can relieve stress
uninvited touch: implicit signal of dominance ex: putting one or both hands on shoulders |
|
|
What was the comfort of touch study?
|
16 couples
-Wife was to be shocked During random trials: Alone Could hold hand of stranger (experimenter) Could hold hand of husband -less stressed when could hold hand of husband |
|
|
In the U.S. what is the acceptable interpersonal space?
|
Intimate zone: 1 1/2 feet
-romantic partners Personal zone: 1 1/2 to 4 ft -friends, family members Social zone: 4 to 12 ft -work people if violated, feel uncomfy -unhappy spouses: larger personal space |
|
|
What is self disclosure theory?
|
-process of revealing personal information
-repciprocity- valance and intimacy Three aspects of self-disclosure -descriptive intimacy: the facts -evaluative intimacy: emotions and judgments -topical reciprocity: responsiveness -to be more intimate in relationship, there is a systematic change -don't say too much too soon -less liked when they talk about taboo topics -good overtime and mutual for both to be comfy -better relationship satisfaction -68% don't like talking about state of relationship -it's counter productive |
|
|
What is social penetration theory?
|
-early in the relationship it's narrow and shallow
-but as the relationship develops, it becomes broad and deep -more/less willing to talk about topics -disclose small amount of topic and limited depth -over time more able to talk about wider topics -gradual process |
|
|
What are the different paralanguage communications?
|
off-record markers- sarcasm, rhetorical questions
-verbal communication should be direct, honest, focused, hints etc shouldn't be used Baby-talk: communicates closeness Hedges- umms- how serious/certain about what is being said, not as serious boosters- absolutely , certainly, undoubtedly : dominant sounding, definitely believe what htey are saying, have to do what they say Pet names- nicknames- communicates closeness with them Idioms: verbal nonverbal, in jokes, phrase unique to this group |
|
|
What is teasing?
|
-teasing observed in many societies
-satisfied couples use teasing and humor to resolve conflicts -socially skilled individuals tease more effectively -had to get message across when using non literate communication |
|
|
What is the relationship between culture and teasing?
|
Hypothesis: Members of cultures that emphasize interdependence will find being the target of a tease to be more pleasurable than members of cultures that emphasize independence
1) Attribute more affiliative motives to teasers -tease them to be closer rather than dominance 2) Report more positive emotion Independent: european americans interdependence: asian americans 24- asian 26-european videotaped nickname teasing task -coded judgments of tease behaviors: hostile or off record signals -emotion ratings: positive or negative -tease already used in relationships -tease behaviors did not differ but -target positive emotion differed -asians: teasing brings people together for closeness -european: if not hostile, it's ok, but later, not happy about it, attack on independent self |
|
|
How do you communicate sympathy for loss?
|
-mention the loss
-stop at expressing sympathy do not: -offer advice -say something cheery about things looking up -suggest that person will get over it -wonder aloud how outcome could have been avoided |
|
|
What are precarious couples?
|
-critical disinhibited women pairing with inhibited men
ex: deborah and raymond -can amplify communication -men in situation withdraw -partner feels they are drifting -if say why don't you talking to me, men withdraw further |
|
|
What is the Negative affect reciprocity?
|
-quick to display negative affect
-escalate conflict -mutual rise in blood pressure -not in happier couples |
|
|
What are communication deficits?
|
-unhappy marriages
-kitchen sink/ cross complaining -jump to many topics of complaining -internal attributions for negative behavior -assume it's always like this -literal, harsh criticism -rather than gentle persecution, assume they mean something devious -contempt: hostile humor -defensiveness: don't solve problem -stonewalling- withdraw in silence, think they are not escalating situation, but make other person mad by not responding to the problem, not solved -belligerence -interruption |
|
|
What is communication gone right?
|
-active listening
-clarity -keep an open eye for your biases -responsiveness-both listening -validation- validate their concerns, understand why they have that perspective -express feelings clearly and with specifics -this specific statements make me feel "blank" -defuse negative affect reciprocity, don't escalate it -humor |
|
|
What is the social exchange theory?
|
-aka interdependence theory
-economic theory of interpersonal relationships rewards: desirable, brings enjoyment costs: undesirable, punishing Outcome= rewards-costs Comparison Level: CL -perceived value of outcomes we expect/think we deserve Comparison level for alternatives: -perceived value of outcomes we would receive if we left our current relationship Satisfaction=Outcomes-CL -if your outcomes exceed your comparison level, you will be satisfied, if not you will be dissatisfied Dependence= Outcomes- CL alt -if your outcomes exceeds the comparison level of your alternatives, you will be dependent on the relationship -if not you will be independent of the relationship |
|
|
What is the investment model?
|
-commitment: the intention to continue the relationship
investments: the "things" you would lose if you left the relationship determined by: satsifaction level, quality of alternatives, investment size |
|
|
What is the predicting stay/leave in abusive relationship?
|
100 women sought refuge at shelter
-interviewed to determine commitment, alternatives, investment, and satisfaction -phoned 3, 6, and 12 months after leaving shelter to determine status 36%returned to husbands within 3 months 31% 12 months only 1/3 didnt go back -if feel that they have a large investment, decide to stay more perception is more important |
|
|
What constitutes commitment?
|
-personal commitment
strongest determinant -constraint commitment too costly to leave? financial? -moral commitment obligations, marriage |
|
|
What are correlates of commitment?
|
-accomodative behavior
does not fight back -willingness to sacrifice sacrifice self interest -perceived superiority of own relationship fewer costs of other people, positive illusions maintains relationship in tough periods |
|
|
What is communal and exchange relationships?
|
-exchange relationships: governed by expectation of immediate payment for rewards given
-standard economic model -Communal relationship: governed by expectation of mutual responsiveness |
|
|
Differences between communal and exchange relationships
|
Communal Orientation Scale Items:
It bothers me when other people neglect my needs. When making a decision, I take other people’s feelings into account. Exchange Orientation Scale Items: It is best to make sure things are always kept even between two people. When someone buys me a gift, I try to buy that person a gift as comparable as possible. |
|
|
What is the difference between exchange and communal relationships
|
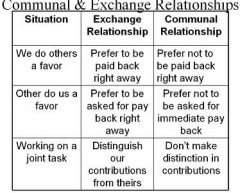
|
|
|
What is Equity Theory?
|
proportional justice:
your outcomes/your contributions= your partner's outcomes/ your partner's contributions -ration to be same -same outcome both sharing, so positive -gets out more but puts in more so ok -not equal even though better outcome |
|
|
What are the limitations to equity theory?
|
-predicts that inequity leads to distress for both the over and under benefited
-limitations and caveats -individual differences in how much equity is valued -more important in some domains (ex: housework and parenting) -may only be an issue when dissatisfied -if fair and satisfied then ok, only when dissatisfied becomes problem |
|
|
What are the positve and negative processes?
|
no relationship is exclusively rewarding or punishing
-rewards and costs have separate effects on relationship well being -appetitive motivations (desirable outcomes) -aversive motivations (avoid negative outcomes) -independent processes |
|
|
What are rewards and costs?
|
-when relationship begins:
-successful and unsuccessful relationships equally rewarding as they develop: -successful relationship become more rewarding; costs lower unsuccessful- less rewarding, lower costs -marriage satisfaction declines over time -parenthood exacerbates decrease |
|
|
What is the rewards ration study?
|
Married couples revisiting their last argument
Warmth/Anger Collaboration/Defensiveness/Criticism Compromise/Contempt 5 to 1 ratio in satisfied marriages positive to negative exchanges -more likely to be satisfied down the road -if positive outweighs the negative |
|
|
What was the Marriage and expectations study?
|
82 newlywed couples in first 6 months of marriage
-Videotaped discussing area of difficulty -Coded for positive and negative behavior -Questionnaires every 6 months -Marital satisfaction -Expectations and predictions for future -4 year follow up people expected positive relationship and it didn't happen had the largest decline in marital satisfaction high expectations and it happened, less decline in marital satisfaction -lower expectations had less decline |
|
|
What is sternberg's triangular theory of love?
|
-intimacy: feelings of warmth and closeness (emotional component)
-passion: physical arousal and desire (motivational component) -commitment: decision to stay in relationship and work to maintain it (cognitive component) =consumate |
|
|
What is nonlove according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
low intimacy
low passion low commitment |
|
|
What is liking according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
high intimacy
low passion low commitment |
|
|
What is infatuated love according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
low intimacy
high passion low commitment |
|
|
What is empty love according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
low intimacy
low passion high commitment |
|
|
What is romantic love according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
high intimacy
high passion low commitment |
|
|
What is companionate love according to types of relationships? (sternberg)
|
high intimacy
low passion high commitment |
|
|
What is fatuous love according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
low intimacy
high passion high commitment |
|
|
What is consumate love according to types of relationship? (sternberg)
|
high intimacy
high passion high commitment |
|
|
What happens to love over time?
|
-romantic love declines over time
-fantasy, novelty, and arousal decline -companionate love more stable over time -strong and steady companionate love in the first two years of marriage is negatively correlated with divorce |
|
|
What about love promotes commitment?
|
-the experience of love promotes commitment to an existing relationship
-signal of genuine commitment -positive internal experience -emotional expression -motivates us to reject alternatives -how do we stay in commitment if other potentially attractive people? |
|
|
Does love have an emotional expression?
|
affiliation cues:
-duchenne smiles -gesticulation -head nods -leaning towards the partner |
|
|
Does love motivate us to reject alternatives?
|
-love says how strong you feel about it
-desire is negatively correlated |
|
|
Do feelings of love last?
|
-arousal and excitement diminish, but we see this is not a required element of love
-engaging in novel, arousing activities increases feelings of love -do everydya moments of love hlep us stay in long lasting, satisfying relationships? -if you continue to have new activities of love, will love each other more |
|
|
What are some cultural love patterns? Traditional vs. westernized?
|
Love: decrease love over time, although maybe happy
arrangement: increase in love over time -level of love may be increased in arranged marriage but patterns differ -stability, consequences -marriage that makes it over time have feelings of love, intimacy, commitment, improved -but many aren't stable |
|
|
What are the different romantic love types?
|
Eros:eager in intimacy and strong physical attraction
Ludus: playful, play the field, men are higher in this storge- slowly developing attachment, lasting commitment pragma: certain demographic factors (logical good match) mania- possessive and demanding, fantasy agape: unconditionally without receiving anything in return |
|
|
What are the different types of attachment according to bartholomew?
|
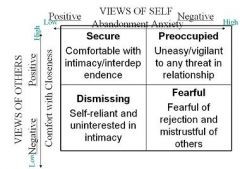
|
|
|
What does attachment styles affect in relationship?
|
-beliefs, expectations, and memories
-communication -coping and care giving -sexual behavior -personal well-being -relationship satisfaction if you're secure: trustworthy, accepting, emotionally available, more open, more supportive in times of need |
|
|
How are attachment styles and emotions related?
|
-secures have love experience that is higher in intimacy, passion, and commitment
-anxious are more prone to jealousy -distress(physical) during stressful task when partner absent and when partner returned in anxious/ambivalents and avoidants -needs lots of support from partner -secure and avoidants both sought out support in low stress but only secures sought support in high stress -no support in avoidants |
|
|
How does age affect relationship?
|
less romantic, more companionate
|
|
|
What gender differences are there in love?
|
-more similar than different
-men: "fall in love" more readily -women: are more likely to send unsatisfying relationships |
|
|
Do love and lust go together?
|
they can be separated into two systems:
-distinct subjective experiences -distinct neurobiology -sexual desire evolved in the context of sexual mating; romantic love--or pair bonding--originally evolved int he context of infant-caregiver attachment |
|
|
What are sexual attitudes toward premarital sex?
|
"it is always wrong"
1972: 46% 1998: 35% younger people least likely to say its wrong |
|
|
What are the attitudes toward casual sex?
|
-"permissiveness with affection" standard
-only ok if they have strong affection, not just desire -men slightly more permissive than women, especially regarding casual premarital sex |
|
|
What are the attitudes on extramarital sex?
|
-most americans strongly disapprove
4% say not wrong at all |
|
|
What are sexual attitudes toward homosexuality?
|
-attitudes becoming less negative
|
|
|
Should homosexuals have equal rights?
|
1977: No= 33% Yes 56%
2001: No=11% Yes= 85% |
|
|
Should homosexuality be considered an acceptable alternative lifestyle?
|
1982: No= 51% Yes=34%
2001: No= 43% Yes= 52% |
|
|
What are cultural differences in attitudes?
|
Americans have sexually conservative attitudes relative to other Western cultures
Canada versus U.S. “This type of sex is always wrong.”(1998) Sex before Marriage: CAN: 12% USA: 29% Homosexual Sex: CAN: 39% USA: 70% More liberal countries: Sweden, Netherlands, and Germany (West) Americans have sexually liberal attitudes relative to non-Western cultures U.S. vs Philippines “This type of sex is always wrong.”(1998) Sex before Marriage: PHI: 60 USA: 29 Homosexual Sex: PHI: 84 USA: 70 More conservative countries: China, India, Iran, Ireland, Philippines, Poland |
|
|
How often do couples have sex?
|
-average frequency of sex varies by
-status of relationship -dating, cohabiting, married -age and length of relationship -sexual orientation -the less they've been together, the more they have sex -gays have more sex than lesbians -cohabitants have the most sex |
|
|
What are the gender and sexuality differences in sexual desire?
|
-men have stronger sex drive:
-more frequent desire for sex -more intense sexual desires (fantasies) -more motivated to engage in sex -more likely to buy sex toys and porn -more likely to masturbate -want sex sooner in relationships -less satisfied with amount of sex |
|
|
Who is most likely to have extra-relationship sex?
|
-men are more likely than women
-gay men are more likely than straight men -if relationship is unequal, they cheat more |
|
|
What is sociosexuality orientation?
|
measures individual differences in whether sex requires commitment
-restricted: sex only in committed relationships -unrestricted: less commitment needed for sex -sex without love is ok -i can imagine myself being comfortable and enjoying " casual" sex with different partners |
|
|
What was the sociosexuality orientation and behavior study?
|
Heterosexuals in dating relationships
Evaluation of computer dating video w/attractive opposite sex After evaluation, participants given opportunity to win a free date with video person (card w/name and phone number) If they won, how willing to engage in sex? Unrestricted sociosexuality: 36% Restricted sociosexuality: 4% |
|
|
What affects relationships and sexual satisfaction?
|
-positive correlation between sexual satisfaction and relationship satisfaction
--but its not the frequency of sex per se -when actual frequency is close to desired frequency -when ratio of sex to arguments is high (as long as you don't argue that much then you dont need as much sex) -sex is one of many other positive activities |
|
|
Who is more assertive in sexuality?
|
men report taking the lead in beginning of a relationship on touching and sexual intimacy
|
|
|
What kind of sexual communication is a problem?
|
-ambiguous communication is open to misunderstanding
-genders read information differently -women: think it's friendliness men: think it's sexual |
|
|
What are friendships?
|
Friendships: trust, caring, affection, enjoy company, depend on them, shares
-Voluntary, personal relationship, provide intimacy and assistance, where 2 parties like each other and seek each others company -Deep structure reciprocity, giving and taking and returning -Different from romantic relationships b/c romantic relationships are more exclusive and involve higher loyalty |
|
|
What are three key facets of friendships?
|
Affective: self- disclosure, express appreciation and affection
-Provide encouragement and self worth Communal: participate in common activities -Have similar interests, instrumental support Sociability: sources of fun and recreation |
|
|
What are characteristics of high-quality friendships?
|
Respect
Trust Responsiveness Capitalization Social Support |
|
|
Why is depression problematic for maintaining friendships?
|
Depressed individuals have issues maintaining friendships because:
-sad mood hard to be around -speak slowly, longer to respond, pessimistic -too much in their life, so don't pay attention to friends -need excessive attention (real friendship is mutual) |
|
|
What are rules of friendships?
|
Volunteer help in time of need
Trust and confide in each other Stand up for the other person in his/her absence Don’t criticize each other in public Give emotional support to make him/her happy while in each others company Don’t be jealous/critical of each others success Ask for personal advice Don’t nag |
|
|
What is friendship like in childhood?
|
related to their cognitive development
-Egocentric-> complex -take friend's point of view -conflicts resolved when both friends benefit -fair cooperation -limited temporal perspective (if conflicts aren't resolved when occurred, think friendship is over) |
|
|
What is sullivan's view of friendship in childhood?
|
Children: based on companionships and compeers
-compeers:first when enter school Preadolescents: more intimacy, chumpships w/same sex peers -chumpships: consensual validation of personal warmth, care about others welfare Adolescents: intimacy w/ opposite sex peers |
|
|
What are the different peer groups in children?
|
Popular: liked by many of their peers
Neglected: neither liked nor disliked, shy -shy children: slower to establish adult roles Rejected: disliked by peers, victimized, aggressive -more likely to experience negative outcomes (dropping out of school, criminal behavior, poor psychological adjustment--more for boys) -more likely to experience rejections over childhood |
|
|
What are adolescent friendships like?
|
-Involve support, conflict, peer pressure
-family time: decreases 35% in 5th grade to 14% in 12th grade -cultural differences in time spent with family vs. friends -friends meet our attachment needs -but in India, 40% of seniors still spent time with family in HS |
|
|
What are the different stages in adolescent friendship?
|
Social network
stage1: interact in same sex cliques stage 2: group interaction in boy and girl cliques stage 3: sexes mix into cliques, pairs, loose groups -but securely attached adolescents still rely on parents for secure base |
|
|
What is friendship like in adulthood?
|
Dyadic withdrawal:
-withdrawal from friendship when become more involved with romantic partner -marriage-> increase in social network, but increase due partly to kin/ext family Friends after college: friends from home replaced by newer friends -people shuffle their social networks through college -after graduation, spend less time with same sex friends and friend groups |
|
|
What is friendship like in older adulthood?
|
-drop in sociability with increased age because have more barriers:
ex: -mandatory retirement -transportation -death of friends -discrimination friendships in older age-> fewer disabilities and decreased mortality -faster recovery from disabilities -feel healthier -not based on # of friends, but frequent contact with closer friends |
|
|
What are the theories behind drop in friends for older adulthood?
|
-disengagement: decline in natural and advantageous opportunities
socioemotional selectivity: -become more selective partners with whom they prefer to interact with -causing them to spend more time with the few people who offer the greatest emotional rewards |
|
|
What is the socioemotional model?
|
-based on interpersonal needs of children at different stages of development
-identifies need, competencies, possible problems, and main emotions experienced at each stage -as people age, they become more selective about the social partners with whom they prefer to interact -leading them to spend time with fewer partners who offer the greatest |
|
|
What are the causes and consequences of being rejected during childhood?
|
Rejected causes:
-aggressive behavior, disliked by peers, victimized Rejected (consequences): -more likely to experience negative outcomes (dropping out of school, criminal behavior, poor psychological adjustment--more for boys) |
|
|
What happens to number of friendships during old age?
|
-older people have fewer but closer friendships
|
|
|
Discuss gender differences in friendships
|
women: more emotional, sharing and self disclosure
men: more shared activities and active fun differences socialized and not found in middle east |
|
|
Discuss the aron and aron inclusion of other in self study
|
Inclusion of Other in Self Study (IOS):
-more motivated to enter and maintain close relationships by including resources, perspectives, characteristics of the other in their own self concept -Cognitive overlap of perceptions of others with perceptions of self -Lord’s Task: well established findings that words are remembered better when we imagine another person interacting w/ that object (rather than self interacting w/the object) -Study shows that the same pattern for mother and self in Lord’s task -We are slower to make trait “me/not me” decisions when the trait is different in spouse/romantic partner -Similar effects with best friends, but variable between individuals |
|
|
What are assumed bonds?
|
characteristics based on genetic relatedness
|
|
|
Discuss the Neyer and Lang family and closeness study
|
is human kinship orientation related to closeness, social support, and proximity?
-samples: 20-40 young 45-65 middle aged >65 older adults greater closeness to kin than friends, but not closer than partners |
|
|
What is the nature of communication between family members, relative to friends or strangers?
|
Family:
-less polite and considerate study: problem solving task with strangers or spouse results: more polite with strangers, and take benefits for granted Study: new mothers reported on help received, most helpful members of their social network -results: biggest types of help from kin ex: down payments, furniture, clothes, regular babysitting -women reported that friends who occasionally babysat for them were most helpful members of social network Key finding: unbalanced relationships with kin more tolerated than unbalanced relationships with non kin -maybe because of this, we can be less considerate, polite and forgetful of benefits received |
|
|
Why are our interactions with family members different than our interactions with friends or romantic partners?
|
our interactions with family members are different than our interactions with friends or romantic partners because we can be less considerate, polite and forgetful of the benefits we receive because since there is genetic relatedness, we are more inclined to forgive each other
-parents said it was easier to forgive their child than each other -families of higher acceptance forgave more easily |
|
|
Do we have similar personality to our siblings?
|
No, siblings only share 50% of our genes
-no more alike than random strangers -though the family attributes newborn features to likeliness with parents, esp. father -family attributes personality of children to kin |
|
|
Discuss the non-shared environment of siblings
|
Environmental niches
-Eldest child gets to choose own niche -Youngest wants to choose a different niche Personality differences -Eldest: most conservative, defends status quo -Youngest: more open to new ideas, more creative Identical twins who live apart are more similar than those who live in the same household |
|
|
What is the relation between family disputes and later conflict management?
|
Mothers/siblings with no argument style (Because I told you so)
-leads to children having child aggression and conflicts Parents/siblings with good reasoning for doing things -teaches child to take different perspectives and points of view |
|
|
What are the effects of family during adulthood?
|
During adulthood family serves as an important base:
-college students frequently stay in contact with family -50% kin important sources of relational closeness -more young people move back home to save money (adultolescence) |
|
|
Discuss routines and rituals
|
routines:
-instrumental communication about matters that need to be taken care of Automatic (ex:dinner, bedtime, scheduled phone calls) Rituals: symoblic communication that instills sense of family identity "it's who we are" ex: birthdays, christmas, thanksgiving, sunday dinners, family reunions |
|
|
Be able to discuss cross-cultural variation in family interactions
|
The extent we value family and our willingness to sacrifice on their behalf
-Higher in members of collectivist cultures ex: latin america, asians -2 cultures characterize by stronger values and expectations regarding duty to assist, respect, and support family (relative to european americans Latinos in particular report family members sources of relational closeness and emotional support |
|
|
Discuss the fuglini et al. cross cultural study of family relationships
|
Participants:
-800 10th graders in US -Filipino, Chinese, Mexican, South & Central American, & European background -1st, 2nd & >3rd generation represented Measured: -Quality of family and peer relationships -Academic motivation -Academic achievement Results: -Asian and Latino 10th grader higher on values of family respect and future obligations (Filipino highest) than European -Family values: more emotionally close family and peer relationships -More academic motivation -No academic achievement differences |
|
|
What are the short term and long-term consequences of being raised in a risky family?
|
short term:
-infant: lack emotional processing -preschool: lack social competence Long term: -adolescence: substance abuse -Adult: mental and physical health problems |
|
|
What are the effects of early stress on later functioning?
|
Study:
-assessed harsh parenting, maternal depression, home environment, poverty status Key factor: cortisol levels at age 15 Early stress based on how much of secure base you got from parents |
|
|
What are the effects of attachment style on morning cortisol levels?
|
Early cortisol levels: related to morning cortisol levels
-Highest cortisol levels in the morning so you are prepared to respond to stress -Securely attached: higher cortisol levels b/c more prime to deal w/stress and responds correctly to stress -Stress and secure attachment: negatively related Non-securely attached: not typical cortisol pattern -Less able to respond to stress -Chronic stress flattens cortisol response to specific stressor |

