![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Transcription Factors (1)
|
A protein that stimulates transcription of a eukaryotic gene by binding to a promoter or enhancer element.
|
- 2 types: general factors and gene specific factors (activators)
|
|
|
Preinitiation Complex (2)
|
The combination of RNA polymerase and general transcription factors assembled at a promoter just before transcription begins.
|
- Polymerase II preinitiation complex contains polymerase II and 6 general factors: TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF, and TFIIH
- bind in specific order to establish the preinitiation complex |
|
|
E: Assembly of Pre-Initiation Complex (4)
|
In vitro gel shifts and footprinting assays
|
- TFIID binds first to the DNA, at the TATA box, with the help of TFIIA, creating a footprint from position -42 to -17
- TFIIB binds next, at/near TATA box, making +10 MORE sensitive to DNase - TFIIF helps RNA polymerase bind to the complex downstream of the TATA box, extending the footprint to position +17 (F by itself does not bind DAB and RNA pol II without F cannot bind the complex - TFIIE binds next, followed by TFIIH, forming the DABPolFEH preinitiation complex |
|
|
Formation of DABPolF Complex
|
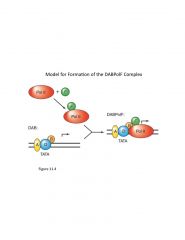
|
|
|
|
Structure of Function of TFIID (1)
|
A class II general transcription factor that binds first to TATA-box-containing promoters in vitro and serves as a nucleation site around which the preinitiation complex assembles. Contains TATA-box-binding protein (TBP) and TBP-associated factors (TAFIIs).
|
- contains a TATA-box-binding protein (TBP, 38 kD) and 8-10 TBP-associated factors (TAFs or TAFIIs)
|
|
|
TATA-box-binding protein (TBP) (3)
|
A subunit of SL1, TFIID, and TFIIB in class I, II, and III preinitiation complexes, respectively. Binds to the TATA box in class II promoters that have a TATA box.
|
- highly conserved, 80% aa identity among yeast, plants, humans
- yeast TBP can substitute for human protein in preinitation complex - carboxyl-terminal 180 aa highly basic. Truncated form of TBP containing only these aacan bind to TATA box |
|
|
E: TBP Binding to TATA Box (5)
|
Mobility Shift assay.
|
- measured binding of TFIID to new CICI box and original TATA box
- binds to minor groove of the TATA box DNA - all bases of TATA box were substituted so that major groove was changed but minor groove was not - inosine looks like adenine in minor groove but very different in major groove - similarly, cytosine was switched for thymine |
|
|
Nucelosides Viewed from Major and Minor Grooves
|
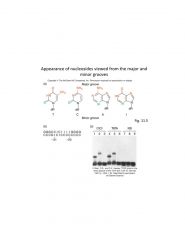
Pic2
|
|
|
|
TFIID Association with TATA Box Minor Groove (4)
|
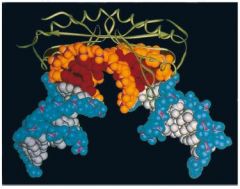
Pic3
|
- crystal structure of TBP and TATA box complex shows protein shaped like a saddle and this curvature forces the DNA to bend 80o
- during bending, minor groove is forced open, most pronounced at first and last basepairs of TATA box - at this point, 2 phenylalanine side chains of TBP insert between basepairs and cause the DNA to kink - opening DNA minor groove likely helps local DNA melting to form open promoter complex |
|
|
Universality of TBP (4)
|
Pic1
|
- functions with Pol II promoters with a TATA box
- also with Pol II promoters without TATA box - also TATA-less Pol III promoters - and TATA-less Pol I promoters |
|
|
TBP Associated Factors (2)
|
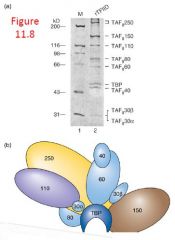
Pic4
|
- immunoprecipitation using antibody specific to TBP was used to identify 8 associated proteins in the fruit fly
- these are since cloned and can be expressed and assembled as the TFIID complex in vitro |
|
|
Function of TAFs
|
1) Interaction with promoter
2) Interaction with gene-specific transcription factors |
|
|
|
Extended Binding of TFIID (1)
|
Footprinting studies
|
- TAFs attached to TBP extend the binding of TFIID beyond the TATA box
|
|
|
E: TFIID Activity with TBP (4-1)
|
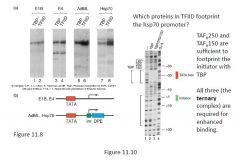
Pic5
- in vitro transcription with either TBP or TFIID and 2 different DNA templates a) DNA template containing only TATA box (adenovirus E1B and E4 promoters) b) DNA template containing TATA box, initiator and downstream element (adenovirus major late promoter and fly Hsp70 promoter) - RNA products assayed by primer extension |
- on promoters containing an initiator and a downstream promoter element, TFIID gave significantly greater activity than TBP
|
|
|
TATA-less Promoters
|
Achieve binding of TBP through the binding of its associated factors to other elements
|
- elements can be initiator or downstream elements to whichTAFII250 and TAFII150 bind and thereby secure the whole TFIID to the promoter
- also upstream elements that bind gene-specific factors that interact with one or more TAFs to secure TFIID -e.g. Sp1 binds to GC box and interacts with TAFII110 in Drosopholia. In this context, Sp1 can be classified as an activator and TAFII110 can be classified as a coactivator |
|
|
Interaction between TBP and Promoters
|
Pic6
|
|
|
|
TAFII Transcription Stimulation
|
Second function of TAFIIs is to participate in transcription stimulation by interactions with gene-specific transcription factors (activators)
|
- by mixing TBP with different TAFs, can make complexes and test transcription from different promoters
- e.g. TFIID (with TAFIIs included) is sufficient to participate in activation by Sp1 but TBP is not - activation by Sp1 occurred when TAFII110 was present, in addition to TAFII250 and TAFII150. By affinity binding Sp1 to a GC box containing column, it was shown that Sp1 binds TAFII110, but not TAFII250 or TAFII150. Likewise, another activator, NTF-1, binds TAFII150 and TAFII60 but not TAFII250. So all activation requires TAFII250 without binding it directly, suggesting TAFII250 is a scaffold that orders the TFIID complex. |
|
|
Model of TAFII Action
|
Pic7
|
|
|
|
Enzymatic Properties of TAFII
|
e.g. TAFII250 has 2 functions
|
1) Histone acetyltransferase, which adds acetyl groups to lysines of histones. This acetylation is usually a transcription activating event/
2) Protein kinase, which can phosphorylate itself and TFIIF. May regulate efficiency of assembly of preinitiation complex |
|
|
Structure and Function of TFIIB
|
A class II general transcription factor that binds to a promoter after TFIID in vitro. Helps TFIIF plus RNA polymerase II bind to the promoter.
|
- 35 kD, single subunit that requires no associated factors
- essential for binding RNA polymerase, Pol-TFIIF complex will bind to DAB but not to DA - composed of 2 domains: The C-terminus for binding TBP, the N-terminus to bind to Pol-TFIIF. It therefore acts as a bridge between TBP and RNA polymerase to position it at the transcription start site |
|
|
Structure and Function of TFIIH
|
The last class II general transcription factor to bind to the preinitiation complex in vitro. Associated with protein kinase and DNA helicase activities.
|
- phosphorylates Pol II
a) IIA form - unphosphorylated, form that joins preinitiation complex, binds tightly to TBP b) IIO form - multi-phosphorylated at CTD, form that carries out elongation, binds less tightly to TBP - phosphorylation may be trigger that allows Pol II to elongation phase |
|
|
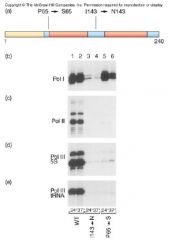
E: TFIIH Phosphorylates Pol II
|
Pic8
|
- incubated purified Pol IIA (unphosphorylated) with TFIIH and [gamma-32P]ATP
- the level of phosphorylation of Pol II by TFIIH was increased by addition of other factors |
|
|
E: Necessity of CTD of Pol II for Phosphorylation
|
Pic9
|
a) increasing amounts of Pol II incubated with transcription factors and [gamma-32P]ATP
b) cleaved CTD of Pol II with chymotrypsin. Remaining portion of polymerase was not labelled |
|
|
TFIIH Phosphorylation of Pol II
|
TFIIH phosphorylates Pol II only when it is bound.
|
- various DNA templates were incubated with Pol II and TFIIH. TFIIH phosphorylated polymerase in the presence of TATA box or initiator, but not well with synthetic DNA (poly dl-dC)
- TFIIH phosphorylates S2 and S5 of the heptad repeat found in the PolII CTD. S5 phosphorylation is removed during elongation. Sometimes, S2 phosphorylation is also removed, which stalls the polymerase. This stalling can be removed by re-phosphorylation of S2 by P-TEFb in a cell-cycle dependent manner |
|
|
TFIIH Complexes
|
TFIIH contains 9 subunits divided into 2 complexes
|
1) Kinase - 4 subunits
2) Core - 5 subunits, with 2 separate DNA helicase/ATPase activities |
|
|
RAD25 Subunit
|
The subunit of yeast TFIIH that has DNA helicase activity
|
- essential for viability
- exhibits ATP dependent helicase activity which is necessary for transcription |
|
|
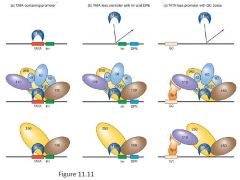
Model for Initiation, Promoter Clearance, and Elongation
|
Pic10
|
- TFIIH is required for full DNA melting at the promoter, but not abortive transcription. The helicase activity of TFIIH stimulates promoter clearance and elongation by unwinding DNA downstream of the start site to create the transcription bubble
- additional protein TEFb (transcriptional elongation factor b) further phosphorylates CTD of Pol II |
|
|
P-TEFb Regulation
|
Pic11
|
- P-TEFb is made up of 2 factors: the cyclin dependent kinase CDK9 and a cyclin T1, T2, or K
- P-TEFb is either free (active) or is held inactive in a regulatory complex called the 7SK RNP. - Components of the 7SK RNP include: a) the pol III transcript 7SK RNA b) La-related protein 7 (LARP7) c) HEXIM1 - loss of HEXIM1 or LARP7 results in breakdown of the 7SK RNP and constitutive P-TEFb release and activation - mutations of LARP7 leading loss of function and 7SK RNA degradation have been strongly implicated in human cancer |
|
|
TFIIS Elongation Stimulation
|
Pic12
TFIIS (IIS) stimulates elongation |
Shown by:
- incubating Pol II with DNA template and NTPs, allowing initiation to occur - adding heparin to block new initiation - adding either TFIIS or buffer - measuring rate of incorporation of labelled GMP into RNA |
|
|
Roles of TFIIS
|
A protein that stimulates transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II by limiting pausing at pause sites.
|
Two roles:
a) polymerases pause as they transcribe, and sometimes they arrest. TFIIS increases rate of elongation by minimizing transcription arrest. TFIIS stimulates RNase activity of backtracked Pol II, which cuts off extruded piece of RNA b) Pol II pauses at misincorporated nucleotide and backtracks, causing arrest. TFIIS promotes proofreading, again by stimulating the RNase activity of Pol II, allowing it to cleave off a misincorporated nucleotide |
|
|
Class I Transcription Factors
|
Preinitiation complexes on Class 1 promoters include only the polymerase I, and 2 factors: SL1 in humans (TIF-IB in others) and UBF (upstream binding factor in mammals, UAF in yeast)
|
- SL1 binds to core and UBF binds to upstream promoter element
- core binding factor, along with Pol I, is required for basal transcription. Core-binding factor is necessary and sufficient to recruit Pol I to the promoter (in most organisms) - UBF helps core-binding factor bind to the core promoter element - SL1 (human factor) can not by itself stimulate Pol I to bind to promoter, but needs UBF to assist its binding |
|
|
Structure and Function of SL1
|
A class I transcription factor that contains TBP and three TAFIs. Acts synergistically with UBF to stimulate polymerase I binding to DNA and transcription.
|
- composed of TBP and three TAFs
|
|
|
E: Co-Purification of SL1 and TBP
|
Pic13
|
- was purified by several different procedures and assayed for transcriptional stimulation by S1 method
- immunoblot for TBP showed that TBP co-purifies with SL1 - it should be possible to inhibit SL1 activity with an anti-TBP antibody - addition of SL1 restored activity - transcriptional activation not restored by adding back TBP |
|
|
E: TAFs in SL1
|
Pic14
SDS-PAGE of immunoprecipitate TAFIs and TAFIIs can compete with each other for binding to TBP Binding of TAFs is mutually exclusive |
- showed 3 proteins, TAFI110, TAFI63 and TAFI48
- SL1 activity could be reconstituted with TBP and the three TAFs Overall results: a) Pol I and Pol II rely on transcription factors SL1 and TFIID, respectively b) each factor is composed of TBP and associated TAFs c) the TBP is identical but the TAFs are completely different |
|
|
Class III Transcription Factors
|
Transcription of all Class III genes requires TFIIIB and TFIIIC
|
- TFIIIA is needed by 5S rRNA genes
a) binds to internal promoter of 5S rRNA gene b) has 9 zinc fingers in a row, they insert into major groove of DNA - zinc finger: a) characteristic of a DNA-binding protein b) finger shaped protein domain containing 4 amino acids that bind 1 zinc ion. Usually 2 cysteinses, 2 hystidines |
|
|
E: Antibody Effect Against TFIIIA
|
Pic14
Halts production of 5S rRNA but not tRNA synthesis 5SRNA and tRNA genes added to a) oocyte extract or b) somatic cell extract plus labelled nucleotide and Lane 1) no antibody Lane 2) irrelevant antibody Lane 3) anti-TFIIIA |
- TFIIIA required for transcription of 5S rRNA but not pre-tRNAs
|
|
|
E: TFIIIB and TFIIIC
|
Pic16
Footprinting assay to show effect of transcription on binding between tRNA gene and transcription factors a) Pol III, TFIIIB, TFIIIC b) Pol III, TFIIIB, TFIIIC, ATP/CTP/UTP (permits pol III to proceed until first G to be incorporated, +17) c) No proteins |
b) Shows downstream shift of protected region as polymerase migrates, but upstream region remains protected
|
|
|
TFIII Information
|
Pic17
Repeated footprinting assays with individually added transcription factors |
1) TFIIIC alone binds to internal promoter, especially box B. Does not bind to upstream region
2) TFIIIB alone does not bind to any region of DNA 3) TFIIIC and TFIIIB, upstream region protected along with box B. Binding of TFIIIB is dependent on TFIIIC. TFIIIB remains bound, even when polymerase has migrated and TFIIIC is released 4) TFIIIB recruits pol III and can promote further rounds of transcription |
|
|
TFIIIB Importance
|
A general transcription factor that activates genes transcribed by RNA Polymerase III by binding to a region just upstream of the gene
|
- only TFIIIB is required to initiate transcription by Pol III, but TFIIIC (and TFIIIA, in the case of 5S rRNA) are required to recruit TFIIIB to pol III promoters
- TFIIIB contains TBP along with 2 TAFIIIs - nonclassical Pol III genes have a TATA box without A and B boxes. TFIIIC would therefore not bind but TBP could bind to TATA box and anchor TFIIIB to the DNA - classical Pol III genes have no TATA box but have A and B boxes. TFIIIC binds to boxes, allowing TFIIIB to bind, which promotes Pol III binding |
|
|
Model of Preinitiation Complexes on TATA-less Promoters
|
Pic18
|
- an assembly factor binds, attracting another factor along with TBP, which recruits polymerase for transcription. Class II promoters also need general factors along with polymerase.
|
|
|
Unifying Principles
|
1) Assembly of preinitiation complex starts with transcription factor that binds to particular region of promoter. This protein then recruits other components.
2) TBP plays an organizing role, it helps bring remaining factors and polymerase, to the complex. 3) Specificity of TBP is governed by the TAFs; TBP associates with different TAFs when it binds to different promoters |
|

