![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are melanocytes?
|
They are responsible for skin pigmentation
They are derived from neural crest** |
|
|
What role does melanin play in the summer and sunlight?
|
Melanin protects us from UVB light by absorbing it
|
|
|
Where in the melanocyte is the melanin produce?
What happens to this organelle after? |
Melanin is made melanosomes using tyrosine as precursor.
The melanosome (organelle) is then passed up to the keratinocytes*** |
|
|
Where are melanocytes located?
What are they derived from (embryo)*** |
They are located in the basal layer
Derived from the neural crest*** |
|
|
Does Kobe Bryant have more melanin then Joe Flacco?
|
NO!
The difference in the skin is due to melasomes (NOT MELANIN) |
|
|
Vitiligo
|
Localized loss of skin pigmentation
autoimmune destruction of melanocytes (FOCALLY)** |
|

What does he have?
|
Vitiligo
(note: easy to see in dark skinned people. For whites, you might have to wait till summer or they go tanning) |
|
|
Albinism
MOA of disease |
Congenital lack of pigmentation
Enzyme defect (usually tyrosinase*) that impairs melanin production |
|
|
What enzyme is generally missing in albinism?*
(hint: what is the melanin precursor?) |
Tyrosinase*
the precursor to melanin is tyrosine |
|
|
What are you at an increased risk of if you have albinism?
|
Increased risk to be damaged by sunlight b/c melanin absorbs the UVB light
Increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and melanoma |
|
|
What other abnormalities may albinism pt. have?
|
Tend to have eye abnormalities
(eg. cross-eyed, vision problems, blindness, light sensitivity, rapid eye movements) |
|
|
Freckle (ephelis)
|
Small tan to brown macule
gets darker with sunlight Due to increased number of MELANOSOMES (not melanocytes) |
|
|
Melasma
|
hyperpigmentation of the cheeks
associated with pregnancy and oral contraceptives |
|
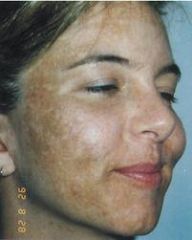
25 yr old pregnant pt. comes in for her weekly visit for her fetus
|
Melasma
|
|
|
Nevus (mole)
MOA of disease |
benign neoplasm of melanocytes
often associated with HAIR |
|
|
Mole
Congenital or acquired? |
Both
|
|
|
Where in the skin (dermis, epidermis, etc.) does the acquired nevus begin?
|
Dermal-epidermal junction
(junctional nevus) Most common mole in children |
|
|
Compound nevus
|
Nevus which extends to the dermis (from the epidermis-dermis junction)
note: grows down |
|
|
Intradermal nevus
|
Most common mole in adults
Since the mole extends down; eventually the junctional component is lost. |
|
|
Dysplastic nevus
|
precursor to melanoma
doesn't occur with all moles. |
|
|
Melanoma
MOA of disease |
Malignant neoplasm of melanocytes
|
|
|
What is the most common death from skin cancer?
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
What are the 3 malignant tumors of the skin?
Which ones have good prognosis? Which have bad prognosis? |
Squamous, basal, melanoma
Squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma = GOOD prognosis Melanoma = bad prognosis |
|
|
Risk factors for melanoma
|
DNA damage due to sunlight exposure
albinism xeroderma pigmentosum dysplastic nevus syndrome (genetic defect where dysplastic mole transfer to melanoma) |
|
|
ABCD of melanoma
|
Asymmetry
Borders are irregular Color is NOT uniform Diameter > 6mm |
|
|
How many growth phases does melanoma have?
Explain them |
2 growth phases
Radial growth horizontally along the epidermis-dermis junction Vertical growth into the deep dermis |
|
|
What is the most important prognostic factor in predicting metastasis of melanoma?
|
Depth of extension (Breslow thickness)**
Vertical growth into the dermis |
|
|
Which of the 2 phases of growth has low risk of metastasis? high risk?
|
Low risk: radial growth
High risk: vertical growth |
|
|
4 variants of melanoma
|
Superficial spreading
Lentigo maligna melanoma Nodular Acral Lentiginous |
|
|
4 variants of melanoma
Superficial spreading |
Most common subtype
dominant early radial growth good prognosis |
|
|
4 variants of melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma |
Lentiginous proliferation (radial growth)
good prognosis |
|
|
4 variants of melanoma
Nodular |
early vertical growth
poor prognosis |
|
|
4 variants of melanoma
Acral lentiginous** |
arises on the palms or soles
often in dark skinned individuals Not related to UV light exposure |

