![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mannitol salts agar would be used for culturing which organism?
|
Staphylococci
|
|
|
What are the three species of Staphylococci associated with human diseases?
|
S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus
|
|
|
What molecules from gram positive bacteria are responsible for causing shock?
|
peptidoglycan fragments + lipoteichoic acids
|
|
|
What is the role of protein A in gram positive bacteria?
|
binds to Fc portion of IgG, creating anti-opsonin effect
|
|
|
What is the role of Fibronectin-binding protein in gram positive bacteria?
|
promotes binding to mucosal cells
|
|
|
What is the role of microcapsule in gram positive bacteria?
|
anti-phagocytic
|
|
|
___________ __________ causes clot formation by S. aureus in citrated rabbit plasma
|
free coagulase
|
|
|
Which staphylococci toxins act as superantigens?
|
toxic shock syndrome toxin, enterotoxins
|
|
|
What is the difference between a furuncle and a carbuncle?
|
furuncle is a single abscess, carbuncle is multiple furuncles that have coalesced
|
|
|
An infection of the umbilical cord resulting in scalded skin send is caused by the release of what?
|
epidermolytic toxins A and B
|
|
|
Food poisoning is caused by the release of what following the ingestion of S. aureus is caused by the release of what in the gut?
|
Enterotoxins A,B,C,D or G
|
|
|
Many S. aureus strains are now resistant to methicillin (true/false)
|
true
|
|
|
What are methicillin, nafcillin, and oxacillin?
|
penicillinase resistant penicillins
|
|
|
Which antibiotic would be used first in the treatment of minor skin infections with S. aureus?
|
tetracycline
|
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for penicillin resistance?
|
beta-lactamase
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of S. aureus resistance to methicillin?
|
Transpeptidase no longer binds methicillin
|
|
|
Which antibiotic is reserved for treatment of serious infections, including Hospital Acquired MRSA?
|
vancomycin
|
|
|
What is the first-line treatment for community acquired MRSA?
|
trimethoprim/sulfoxazole
|
|
|
MRSA is often transmitted by direct contact with an infected person (true/false)
|
true (wash your damn hands for Christ's sake!)
|
|
|
What species of staph is likely to be acquired through catheters?
|
S. epidermidis
|
|
|
What species of Staph is likely to be responsible for a UTI?
|
S. saprophyticus
|
|
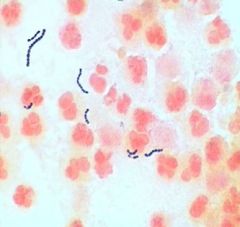
Identify the Organism
|
Streptococcus
|
|
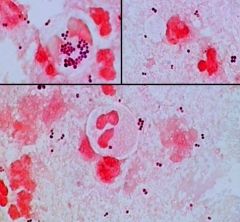
Identify the Organism
|
Staphylococcus
|
|
|
Which species of Streptococcus is classified by beta hemolysis, Lancefield group A and a Bacitracin S test?
|
S. pyogenes
|
|
|
Which species of Streptococcus is classified by beta hemolysis, Lancefield group B and a Hippurate hydrolisis test?
|
S. agalactiae
|
|
|
Which species of Streptococcus is classified by Gamma hemolysis, Lancefield group D and a Bile esculin test?
|
S. faecalis
|
|
|
Which species of Streptococcus is classified by alpha hemolysis, and a postive quelling test?
|
S. pneumoniae
|
|
|
__________ infections are abscesses, __________ infections are spreading
|
Staph, Strep
|
|
|
Which bacterial species is known to produce scarlet fever?
|
Grp A Streptococcus (pyogenes)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Streptococci infection?
|
penicillin
|
|
|
Which Strep is known to cause subacute endocarditis?
|
Viridans strep
|
|
|
What diseases are commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae?
|
pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis media
|
|
|
___________ ____________: oxidase positive, grow at 42 degrees C, colonies produce a fruity odor
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
What species produces exotoxin A? What does it do?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Causes ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 thereby inhibiting protein synthesis; Eschar formation w/ tissue necrosis (gangrene)
|
|
|
___________: Oxidase negative (aerobic), nonfermentative, nonmotile, pleomorphic organisms
|
Acinetobacter
|

