![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
242 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the types of movement? |
Internal Movement, Locomotion |
|
|
|
Internal movements are always voluntary - Correct the sentence |
Internal movements are voluntary or involuntary |
|
|
|
Give Examples of types of muscles causing internal movements - Give example for each classifying voluntary/ involuntary |
1. Smooth muscles (involuntary) - Peristaltic movements, constriction and dilution of blood vessels etc 2. Cardiac muscles (involuntary) - Contraction and relaxation of heart 3. Striated muscles (voluntary) - Movements of limbs, head, eyeballs, etc. |
|
|
|
Types of movements |
1. Amoeboid 2. Ciliary 3. Whorling 4. Muscular 5. Tentacular |
|
|
|
Amoeboid movement is performed by _________________ using cytoplasmic elements like ________________ and _______________. |
Examples showing Amoeboid movement |
Leucocytes, Macrophages |
|
|
Examples showing ciliary movement |
Ciliated epithelium in trachea, oviduct, Paramoecium |
|
|
|
In Paramoecium, cilia help in _________________ and _______________. |
1. Movement of food through cytopharynx into food vacuole 2. Locomotion |
|
|
|
Whorling movement is caused by ________________ for example in _________. |
Flagella, sperm |
|
|
|
Hydra uses tentacles to ________________ and for _______________. |
Capture prey, locomotion |
|
|
|
Types of movements shown by human cells |
Amoeboid, ciliary, muscular |
|
|
|
Number of skeletal muscles in human body |
640 |
|
|
|
Body movements help to maintain _____________ against gravity. |
Equilibrium |
|
|
|
____________________ helps in the circulation of blood and respiration respectively. |
Rhythmic movement of heart and lungs |
|
|
|
_________________ from one place to another on its own is called Locomotion. |
Change in locus of whole body/ Act of displacing body |
|
|
|
Locomotion is the characteristic feature of _____________. |
Animals |
|
|
|
Locomotion requires a perfect coordinated activity of _____________ systems. |
Muscular, skeletal, neural |
|
|
|
What are limbs? |
Extensions from trunks |
|
|
|
What are the parameters found in limbs which bring about movement and locomotion? |
Supporting bones, joints and skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
During locomotion, __________ serve as lever, ___________ as fulcrum and the ____________ generate force. |
Bones, joints, skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
Locomotion helps in escaping from _______________. |
Predators |
|
|
|
Locomotion increases chances of _____________ and ____________. |
Survival and continuation of race |
|
|
|
About ________% of body weight in human adult is contributed by muscles |
40-50 |
|
|
|
Muscle is of ______________ origin. |
Mesodermal |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles are primarily involved in ___________ and __________. |
Locomotory actions and changes of body posture |
|
|
|
_______________ muscles show branching pattern. |
Cardiac |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles are also known as |
Voluntary/ Striated |
|
|
|
Smooth muscles are also known as |
Involuntary/ unstriated/ visceral |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles are attached to skeleton by means of ____________. |
Tendons |
|
|
|
Fascicles are held together by |
Common collagenous connective tissue layer called fascia |
|
|
|
Contractile structural and Functional units of muscles are ________________. |
Sarcomeres |
|
|
|
Names of muscle filaments with thickness - |
1. Actin - Thin 2. Myosin - Thick |
|
|
|
Specific names for the following for muscle fibres - 1. Plasma membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Endoplasmic reticulum |
1. Sarcolemma 2. Sarcoplasm 3. Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
|
Important feature of sarcolemma |
Electrically charged |
|
|
|
Sarcoplasmic reticulum is a storehouse of __________. |
Calcium ions |
|
|
|
4 main properties of muscles |
1. Excitability 2. Contractility 3. Expandability 4. Elasticity |
|
|
|
Tendons are __________. |
Inelastic thick bands of white fibrous tissue |
|
|
|
Ligaments are ______________ (elastic/ inelastic) |
Elastic |
|
|
|
Myosin is anchored to _____________ in a ____________ manner |
M-line, straight |
|
|
|
Actin is anchored to _____________ in a ____________ manner |
Z-line, Alternate |
|
|
|
Actin and myosin are arranged ____________ to each other and to ____________. |
Longitudinal, myofibril axis |
|
|
|
Sarcomere is portion between two _________________. |
successive Z-lines |
|
|
|
Each actin filament is made up of |
1. Two F (filamentous) - actin chains helically interwoven 2. Two filaments of Tropomyosin running close to F-actin 3. Troponin - receptors on tropomyosin |
|
|
|
Tropomyosin and troponin are ________________. |
Proteins |
Biomolecular form |
|
|
Function of Troponin |
In resting state, it masks the the Myosin binding sites |
|
|
|
Each F-actin is a polymer of _________________. |
Monomeric G (globular) - actins |
|
|
|
Monomeric unit of myosin is _____________. |
Meromyosin |
|
|
|
Parts of meromyosin |
1. Heavy Meromyosin (HMM) - Globular head + short arm 2. Light Meromyosin (LMM) - Tail |
|
|
|
________________ projects outwards at regular distance from polymerised myosin filament and is known as ________________. |
HMM component, cross arm (Note: not cross bridge) |
|
|
|
Globular head of meromyosin contains __________ enzyme and has binding sites for ____________. |
ATPase, ATP and actin |
|
|
|
HMM in resting state is known as ____________ and in bound state as ____________. |
Cross arm, cross bridge |
|
|
|
Mechanism of muscle contraction is best explained by _______________. |
Sliding filament theory |
|
|
|
__________ slides over __________. |
Actin, myosin |
|
|
|
Sliding filament theory in short using keywords |
CNS - signal - motor neuron - neuromuscular junction - axon end - synaptic bulb - acetylcholine - sarcolemma - Action potential - T tubule - sarcoplasmic reticulum - calcium ions - Troponin receptor - Tropomyosin twisting - myosin binding sites exposed - In myosin - ATP at ATP binding sites - ATPase - ADP and inorganic Phosphate - cross bridge - another ATP - pulled inwards - actin sliding - Z-lines closer -Hzone disappear - contraction micro to macro |
|
|
|
Reaction time is (same/different) in different muscles |
Different |
|
|
|
Repeated activation of muscles leads to formation of _______________ due to ________________, causing ____________. |
Lactic acid, anaerobic breakdown of glycogen, fatigue |
|
|
|
Oxygen storing pigment in muscles is called ______________. |
Myoglobin |
|
|
|
If myoglobin content is more, it gives ________ appearance to muscles. Then muscles are called _____________. These are found in __________ people. |
Reddish, red muscles, physically active |
|
|
|
If myoglobin content is less, it gives ________ appearance to muscles. Then muscles are called _____________. These are found in __________ people. |
Relatively whitish, white muscles, lazy |
|
|
|
Red fibres have high amount of ____________ (other than myoglobin), so they are also called _____________. |
Mitochondria, aerobic fibres |
|
|
|
Muscle starting is at ___________ and known as __________. |
Fixed bones of joints, origin |
|
|
|
Muscle termination is at ___________ and known as __________. |
Movable bones, insertion |
|
|
|
Middle portion of muscle is _________. |
Belly |
|
|
|
Three main types of striated muscles - give examples with respect to flexion of elbow |
1. Prime movers - initial movement/ major contraction (Biceps) 2. Antagonists - opposite movement to prime (Triceps) 3. Synergists - Assist prime (Brachialis for biceps) |
|
|
|
What are antagonistic muscles? |
Muscles which on contraction produce opposite movement at same joint |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles are (neurogenic/myogenic). Give meaning |
Neurogenic - need repeated stimuli from CNS |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles are (neurogenic/myogenic). Give meaning |
Myogenic - stimulus by own node |
|
|
|
Meaning of following - 1. Flexion 2. Extension 3. Adduction 4. Abduction 5. Supination 6. Pronation 7. Levation 8. Depression 9. Constriction 10. Dilation 11. Protaction 12. Retractor |
1. Angle decrease 2. Angle increase 3. Towards midline 4. Away from midline 5. and 6. Prabhu pronates, student supinates 7. Lifted up 8. Lowered down 9. Opening reduces 10. Opening decreases 11. Move forwards 12. Move backwards |
|
|
|
Give one term for the following 1. Angle decrease 2. Angle increase 3. Towards midline 4. Away from midline 5. Rotate upwards 6. Rotate downwards 7. Lifted up 8. Lowered down 9. Opening reduces 10. Opening decreases 11. Move forwards 12. Move backwards |
1. Flexion 2. Extension 3. Adduction 4. Abduction 5. Supination 6. Pronation 7. Levation 8. Depression 9. Constriction 10. Dilation 11. Protaction 12. Retractor |
|
|
|
2 Examples of flexor and extensor pair |
1. Elbow movement - biceps and Triceps 2. Knee movement - Quadriceps and hamstrings |
|
|
|
In a meromyosin, what is the relative position on head of an ATP binding site and an actin binding site? |
Actin BS - Up ATP BS - Down |
|
|
|
Example of adductor-abductor pair and location |
Adductor - Latissimus dosti Abductor - Deltoid Shoulder |
|
|
|
Contraction and dilation are types of ____________ action. |
Sphinctor |
|
|
|
Give the types (Neurogenic/ myogenic), (Striated/ Non- striated) 1. Voluntary 2. Involuntary 3. Cardiac |
1. Neurogenic, Striated 2. Neurogenic, Non-striated 3. Myogenic, Striated |
|
|
|
Which muscles do not get fatigued? Why? |
Involuntary and Cardiac. Because Contractions are slow and for longer period |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles shows __________ striations. |
Faint |
|
|
|
Visceral muscles are arranged in _________ and _________ layers. |
Inner circular, Outer Longitudinal |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles are found in ___________ . |
Middle wall of heart i.e. myocardium |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles show ___________ with _________. (Structure key points) |
Syncytium, branching pattern |
|
|
|
Characteristic feature of cardiac muscles is _____________. |
Intercalated discs |
|
|
|
Physical Principles of locomotion |
Density, Forces, Machines, Friction, Upthrust (5) |
|
|
|
Study of bones is known as ________________. |
Osteology |
|
|
|
Which of the following do humans have? - Exoskeleton/ Endoskeleton |
Both |
|
|
|
Human Endoskeleton is made up of _________. |
Bones and cartilages |
|
|
|
Adult human skeleton is made up of _____________ bones while that of a kid is made up of ___________ bones. |
206, 213 |
|
|
|
Bone marrow manufactures blood cells. What is the process called? |
Haemopoiesis/ Hematopoiesis |
|
|
|
Bones in middle ear called ______________ transmit ____________ and help in ____________. |
Ear ossicles, sound waves, hearing |
|
|
|
Difference in fore limb and hind limb w.r.t bones |
Fore limbs do not have patella like structure (1 in hind limbs) This deficit is balanced by 1 extra carpel (8 carpels in fore limb but 7 tarsals in hind limb) Thus the no. Of bones = 60 for each limb is balanced |
|
|
|
Axial skeleton constitutes _____________ of body. It is formed of _______ bones. These include ________________. |
Upright axis; 80; skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. |
|
|
|
Human skull is formed of _______ bones. It is ___________ part of axial skeleton. |
29, anterior |
|
|
|
Skull bones are connected to each other by ________ joints except _________. |
Immovable, mandible |
|
|
|
Mandible helps in ___________ |
Opening and closing of mouth |
|
|
|
Skull is made up of __________ (description - 3) bones. |
Flat, compact, irregular |
|
|
|
____________ forms hard protective covering for brain. |
Cranium |
|
|
|
____________ skeleton forms front part of skull and provides _____________. |
Facial; sockets for ear, nasal chamber, eyes |
|
|
|
Types of Ear bones with short description (relative position, shape, size) |
1. Malleus - Outermost, Hammer shaped, Largest among ear ossicles 2. Incus - Middle, Anvil shaped 3. Stapes - Innermost, Stirrup shaped, smallest in the entire skeleton |
|
|
|
Path of sound (signals) |
Pinna - Tympanic membrane - malleus - incus - stapes - oval window - cochlea |
|
|
|
Classify as Monocondylar or dicondylar Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia |
A, A (Amphibia, Aves) - Monocondylar Reptilia, Mammalia -Dicondylar |
|
|
|
Meaning of dicondylar |
2 occipital condyles at base of skull |
|
|
|
Meaning of condyle |
Surface of attachment of vertebral column to skull Note: not be said as skull to V.C. |
|
|
|
Vertebral column is made up of ________ small ring like ________ bones called ____________. |
33, irregular, vertebrae |
|
|
|
Names of vertebrae with location and number |
Cervical Vertebrae - neck - 7 Thoracic/ Dorsal Vertebrae - back - 12 Lumbar Vertebrae - back - 5 Sacral Vertebrae - hip - 5 - fused to from 1 sacrum bone Coccygeal Vertebrae - end of V.C. - 5 - fused to from 1 coccyx bone |
|
|
|
7 cervical vertebrae are found in almost all - (choose correct option) 1. Primates only 2. Mammals only 3. Chordates only 4. Humans only |
2 |
|
|
|
The 1st cervical vertebra is called _______ which articulates with ___________ |
Atlas/ C1, occipital condyles of skull |
|
|
|
Vertebral column encloses a cavity called _______________ within which ___________ lies protected. |
Neural canal, spinal cord |
|
|
|
The vertebral column shows _______ curvatures. Name them and classify as concave or convex |
Four 1.Cervical and 3.lumbar - concave posterior 2.Thoracic and 4. sacral - convex posterior |
|
|
|
Uses of curvatures of vertebral column |
Strength, Elasticity, Flexibility, Balance (erect posture) .... (4) |
|
|
|
Fracture of coccyx is known as ___________. |
Coccydynia |
|
|
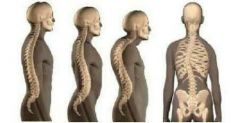
Identify Normal and spinal abnormalities |
Left to right : Normal, Lordosis, Kyphosis, Scolosis |
|
|
|
Hyoid bone is also known as _____________. |
Tongue bone |
|
|
|
Location of hyoid bone |
It is a median bone inside soft tissue below mandible and above larynx |
|
|
|
Hyoid bone is small _________________ bone. (Strength and shape) |
Fragile U- shaped |
|
|
|
Parts of thoracic cage |
1. Ventromedian sternum 2. 12 pairs of ribs 3. 12 pairs of mid-dorsal thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
|
Sternum is also known as ___________. |
Breastbone |
|
|
|
Structure of sternum |
Long, flat, narrow bone |
|
|
|
Length of sternum |
15-17 cm |
|
|
|
Parts of sternum |
Manubrium, body, Xiphoid process |
|
|
|
Articulation of ribs |
Dorsally with 12 thoracic vertebrae Ventrally with sternum |
|
|
|
Human ribs are ____cephalic. |
Bi |
|
|
|
Ribs are also known as ___________. |
Costa |
|
|
|
Ribs are attached to sternum by _______________ |
Hyaline costal cartilage |
|
|
|
Types of ribs with no. and explanation |
1. True/ vertebrasternal - 1 to 7 - Directly attached to sternum 2. False/ Vertebra-chondral - 8, 9, 10 - Indirectly attached through costal cartilage of 7th 3. Floating - 11, 12 - Not attached |
|
|
|
All the ribs are interconnected by ________________. |
Intercostal muscles |
|
|
|
Which part of thoracic cage is movable and why? |
Ventral part because it is cartilaginous |
|
|
|
Which parts together produce breathing effect? |
Ribs, intercostal muscles, diaphragm |
|
|
|
Give the entire skeleton system with no. of bones through a flow chart |
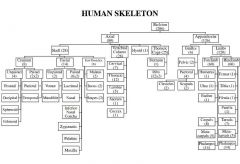
|
|
|
|
The 2nd cervical vertebra is called _________ and shows __________ process. |
Axis/ C2, odontoid |
|
|
|
Odontoid process is a feature of ______________ which fits into __________________. |
Axis (2nd cervical vertebra), anterior chamber of neural canal of Atlas (1st cervical vertebra) |
|
|
|
Bones and structures involving No movement |
Odontoid process of axis fits into anterior chamber of neural canal of atlas (C1 and C2) |
|
|
|
Smallest rib is |
12th |
|
|
|
Two types of girdles with location |
1. Pelvic - waist 2. Pectoral - chest |
|
|
|
What is the use of girdles? |
Articulation of appendicular skeleton with axial skeleton |
|
|
|
Pectoral girdle has two bones namely - (with alternate names) |
1. Clavicle/ S/ collar/ beauty bone 2. Scapula/ shoulder bone |
|
|
|
Three features (structures) of scapula with short description |
1. Acromion process - Articulation with clavicle 2. Coracoid process - Origin of biceps 3. Glenoid cavity - Articulation with head of humerus |
|
|
|
Shape and structure of 1. Scapula 2. Clavicle |
1. Large triangular flat 2. S/curved shaped fragile |
|
|
|
Clavicle shows _____ curvatures |
2 |
|
|
|
Location of 1. Scapula 2. Clavicle |
1. Dorsal part of thoracic between second and seventh ribs 2. Horizontally on front of neck |
|
|
|
Scapula has a slightly elevated ridge called _____________ which projects as a flat expanded process called _____________. |
Spine, acromion |
|
|
|
Shoulder joint formed at _________________ which is a _________________. |
Glenoid cavity, ball and socket joint |
|
|
|
The _________ cervical vertebra is seen on body surface as a point. |
Seventh |
|
|
|
Anatomy which can be studied from outside the body is called ___________. |
Surface anatomy |
|
|
|
Clavicle starts from near __________. |
Sternum |
|
|
|
Comment on the nutritional status based on visibility of clavicle from outside |
1. Seen - OK 2. Not seen - over nourished 3. Clearly seen deep on both sides - Malnourished |
|
|
|
The lowest part of scapula is called ______________. |
Apex |
|
|
|
Pelvic girdle is also known as - |
Hip bones, innominate bone, osso coxae, coxal, os-innominate, os-coxal bones |
|
|
|
Each innominate bone is fomed by _______________ (process) of ________ (number) bones - (names) |
Fusion (ossification); three; ilium, ischium, pubis |
|
|
|
Each innominate bone is fomed by _______________ (process) of ________ (number) bones - (names) |
Fusion (ossification); three; ilium, ischium, pubis |
|
|
|
The bone on which we sit is |
Ischium |
|
|
|
Give meaning of 1. Ossification 2. Mineralisation |
1. Fusion by adding calcium 2. Deposition of minerals |
|
|
|
In pelvic girdle, At the point of fusion of three bones - __________, ____________ and __________, a ________ shaped depression known as __________ is present into which _________ fits. |
Ilium, Ischium, Pubis, cup, acetabulum, femur |
|
|
|
Function of hyoid bone |
Attachment of muscles of tongue |
|
|
|
Forelimb Bones with alternate names and number |
Humerus (bone of upper arm) - 1 Radio-ulna (Radius and Ulna: Bones of fore arm) - 2 Bones of hand- Carpals (wrist bones) - 8 Metacarpals (bones of palm) - 5 Phalanges (bones of digits) - 14 |
|
|
|
Hindlimb Bones with alternate names and number |
Femur (Thigh bone) - 1 Tibio-fibula (Tibia and Fibula: Shank bones) - 2Bones of hand- Patella (knee cap) - 1Tarsals (ankle bones) - 7 Metatarsals (bones of foot) - 5 Phalanges (bones of digits) - 14 |
|
|
|
Few features of tibia |
Strongest, Central front part known as shin |
|
|
|
Few features of tibia |
Feeble Doesn't form knee joint Outer Covered by muscles |
|
|
|
How to identify 1 .radius and ulna 2. Tibia and fibula |
1. In the line of thumb is Ulna 2. Outer is Fibula, centre is Tibia |
|
|
|
What is the standard position of human body taken conventional for study called? |
Human anatomical position |
|
|
|
According to human anatomical position, for the naming of digits 1. Which digit is given no.1? 2. Digit tip bones are called ________ 3. Phalanges attached to metacarpals/ metatarsals are called ____________ 4. The other phalanges are called ____________ |
1. Thumb 2. Distal 3. Proximal 4. Middle |
|
|
|
Define joint |
A joint is defined as a place where two or more bones get articulated with one another. |
|
|
|
Study of joints is called ____________. |
Arthrology |
|
|
|
Joints avoid __________ during movements of bones by packing. |
Friction |
|
|
|
Joints are protective because they act as ______________. |
Shock absorbers |
|
|
|
Classify the types of joints (with all alternative names) |
A. Immovable/ Fibrous Joints/ Synarthroses 1. Sutures/ Serrate sutures 2. Syndesmosis 3. Gomphosis/ Peg and socket joints
B. Slightly movable/ Cartilaginous joints/ Amphiarthroses 1. Synchondroses 2. Symphysis 3. Inter-vertebratal joints
C. Freely movable/ Synovial joints/ Diarthrosis 1. Ball and Socket 2. Hinge 3. Gliding 4. Condyloid joint 5. Saddle 6. Pivot |
|
|
|
Define fibrous joints |
The joints in which a thin or dense layer of white fibrous inelastic tissue is placed between two articulating bones, not allowing any movement of bones to take place |
|
|
|
White fibres of fibrous joints are made up of ______________. |
Collagen |
|
|
|
In a fibrous joint, the line of fusion at joint is called a ____________. |
Suture |
|
|
|
Fixed joints are primarily meant for ___________ and may permit __________ during ___________. |
Growth, moulding, childbirth |
|
|
|
Suture are also called ___________ joints because - |
Serrate, articulating surfaces of bones show serrated margins |
|
|
|
In sutures, bones are held together by _____________. |
Interlocking arrangement |
|
|
|
Examples of sutures |
Joints between cranial bones |
|
|
|
Prominent sutures are - |
1. Coronal suture - Between frontal and parietal bones 2. Sagittal suture - Between two parietal bones 3. Lambdoidal suture - Between parietal and occipital bone 4. Lateral suture - Between temporal and parietal bones |
|
|
|
In young or newborn, the sutures leave about ________ gaps called _________________. |
Six, fontanelles |
|
|
|
Use of fontanelles |
They permit flexibility for parturition and brain growth |
|
|
|
Parturition means _______________. |
Child birth/ Delivery |
|
|
|
At about ______ years of age, the fontanelles are closed by __________. |
2, ossification |
|
|
|
In which fibrous joint, fibrous tissue is not replaced by bone? |
Syndesmosis |
|
|
|
Examples of Syndesmosis |
1. Lower ends of Radius and Ulna 2. Lower ends of Tibia and Fibula |
|
|
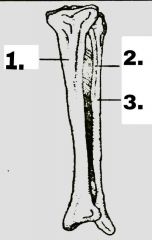
Label 1 to 3, name the joint and the part of body with view |
1 - Tibia, 2- Interosseous membrane, 3 - Fibula Joint - Syndesmose Part of body - Left leg (Fibula is always outer) View - Anterior (since tibia is at front) |
|
|
|
Gomphosis is a characteristic of _____________ teeth. |
Thecodont |
|
|
|
Explain gomphosis |
Small projections are formed in one bone which fit into the sockets or depression of another bone |
|
|
|
The fibrous connections in gomphosis are many _____________. |
Periodontal ligaments |
|
|
|
Example of gomphosis |
Roots of teeth fitted into alveoli (sockets) mandible and maxilla |
|
|
|
Why are Cartilaginous joints called Amphiarthroses? |
Because the joint is neither immovable nor freely movable but is slightly movable |
|
|
|
Cartilaginous joints show some movement in response to _____________. |
Compression, tension, twisting |
|
|
|
In a Cartilaginous joint, the line of fusion at joint is called a ____________. |
Synchondrosis or symphysis |
|
|
|
The joint between rib and sternum is a ______________ joint. |
Cartilaginous |
|
|
|
Which cartilaginous joint is a temporarily joint? |
Synchondroses |
|
|
|
Synchondroses ia temporarily joint found as _______________ between two ends of ________________. |
Hyaline cartilage, long growing bones |
|
|
|
Comment on the strength of synchondrosis |
It is very soft and elastic with minimum strength |
|
|
|
Synchondrosis is later converted into ____________ by ______________ |
Synostosis, ossification |
|
|
|
Sychondrosis is found in ____________. |
Children |
|
|
|
Examples of synchondrosis-synostosis |
Metaphysis between epiphysis and diaphysis of long bones |
|
|
|
In symphysis, two bones are connected by _______________. |
Fibrous cartilage |
|
|
|
Shape of pubic symphysis |
Disc |
|
|
|
Example of symphysis |
Pubic symphysis between two innominate bones |
|
|
|
Which sex has More flexible pubic symphysis? What is the need? What causes the movement? |
Females Needed during parturition for increase in size of birth canal Female hormones from brain, body and ovaries |
|
|
|
Inter-vertebral discs are __________ joints between ____________ having ______________ cartilage. |
Slightly movable, two vertebrae, fibrous |
|
|
|
Inter- vertebral joints are not found between _____________ joints |
C1 and C2 |
|
|
|
Use of inter- vertebral discs |
Helps in shock absorption and protecting spinal cord from mechanical injuries |
|
|
|
Freely movable/Synovial joints/ Diarthrosis are also called ___________ joints due to _____________. |
Perfect, Presence of all well developed structures needed for free movement |
|
|
|
_____________ joints are most evolved. |
Freely movable/Synovial joints/ Diarthrosis |
|
|
|
A synovial joint is enclosed in a tough ___________ ligaments called __________ or ___________. |
Fibrous, capsule, bursa |
|
|
|
What is an articulating surface? |
Surface of bone participating in joint |
|
|
|
The ends of articulating surfaces are covered by ___________. |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
|
The function of hyaline cartilage is _______________. |
To avoid direct contact or Friction between the bones |
|
|
|
The hyaline cartilage is separated by a cavity called ____________ which is lined by a smooth thin membrane called _____________. |
Synovial cavity, synovial membrane |
|
|
|
In a synovial capsule, __________ secretes a fluid called ____________. |
Synovial membrane, synovial fluid |
|
|
|
Features of synovial fluid |
Clear, yellowish, slimy and viscous fluid containing mucus, albumin, fats, phagocytes and mineral salts |
|
|
|
Viscosity of synovial fluid is due to ________________. |
Hyaluronic acid |
|
|
|
The synovial membrane contains ______________ cells which may form ________________ forming ___________ to the joint. |
Fat cells, fat pads, cushions |
|
|
|
Synovial fluid also contains phagocytes which removes ________________ and ________________. |
Microorganisms and cellular debris |
|
|
|
Synovial fluid is similar to ___________. |
Lymph |
|
|
|
Functions of synovial fluid |
1. Lubrication of joints allowing free movement 2. Avoids friction 3. Nourishes hyaline cartilage |
|
|
|
Deficiency of synovial fluid causes ________________ which is an ___________ disease. |
Arthrosclerosis, old age |
|
|
|
_____________________ causes Arthrosclerosis. |
Deficiency of synovial fluid |
|
|
|
Synovial joints are provided with _____________ ligaments and numerous _____________ ligaments. |
Capsular, accessory |
|
|
|
Synovial accessory ligaments may be __________ or _________. |
Intra or extra capsular |
|
|
|
Ligaments avoid _____________ of bones and make joints ____________ |
Dislocation, stronger |
|
|
|
Gymnasts, acrobats and yogis make the ____________ stronger for free movement. |
Ligaments |
|
|
|
Difference between Ilium and Ileum |
Ilium - Part of innominate bone Ileum - Part of small intestine |
|
|
|
What is the fundamental of ball and socket joint? |
Articular surfaces include a globular head fitting into a cup shaped socket |
|
|
|
Given movements are shown by which joints? 1.Multi axial 2. Transverse Uniaxial 3. Non axial 4. Biaxial 5. Vertical Uniaxial |
1. Ball and socket 2. Hinge joint 3. Plane or gliding 4. Condyloid or Ellipsoid/ Saddle 5. Pivotal or rotatory |
|
|
|
Axis of Ball and socket joint have _________ centre (number) |
One |
|
|
|
Examples of ball and socket joint with explanation. Tell which of them is easily dislocable or fracture |
1. Shoulder joint - head of humerus fits into glenoid cavity of scapula - Dislocation 2. Hip joint - Head of femur fits into acetabulum of pelvic girdle - Fracture |
|
|
|
In hinge joints, articular surfaces are _______________ shaped. |
Pulley |
|
|
|
In hinge joints, there are _______________ ligaments. |
Strong collateral |
|
|
|
Hinge joints resist _________________. |
Dislocation |
|
|
|
Explain elbow joint |
It is hinge joint between humerus and radio-ulna. Ulna has olecranon process which fits into cavity of humerus. Here Ulna works as hinges so only forward movement is possible |
|
|
|
Explain knee joint |
It is hinge joint between femur and tibia. Here patella works as hinges so only forward movement is possible |
|
|
|
Odontoid process is also known as _________. |
Dens |
|
|
|
In plane or gliding joint, articular surfaces are _______________ (structure) |
More or less flat, convex |
|
|
|
Movements by plane joint are _____________. |
Irregular |
|
|
|
In gliding joint, articulating surface is convex. What's the use? |
Friction is avoided |
|
|
|
Examples of Plane or Gliding joints |
Intercarpal, Intertarsal joints |
|
|
|
Fundamental of Ellipsoid joint |
Oval articular surface of one bone fits into a complementary elliptical concavity of another |
|
|
|
Examples of Ellipsoid joints |
1. Radio-carpal (wrist) joint 2. Metacarpo-phalangeal (proximal) joints |
|
|
|
Which joint is a modified condyloid joint? |
Saddle joint |
|
|
|
In saddle joints, articulating surfaces are _______________. (Shape) |
Reciprocal concave-convex |
|
|
|
Which is the most flexible joint in joint? |
Saddle |
|
|
|
Which joint has evolutionary significance in human evolution? |
Saddle |
|
|
|
Saddle joint increases ___________ and helps in __________. |
Grasping power of fingers, Skillful work |
|
|
|
Order of organization in muscles |
Muscles - fascicles ( bundles) - muscle fibres (cells) - myofibrils - myofilaments - actin and myosin |
|
|
|
Amount of _____________ is high in white fibres. |
Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|

