![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
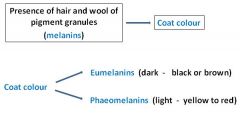
Coat colour inheritance |
|
|
|
Melanocytes
|
Dermal melanin is produced by melanocytes, specialized skin cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis. Melanocytes insert granules of melanin into specialized cellular vesicles, or organelles, called melanosomes. |
|
|
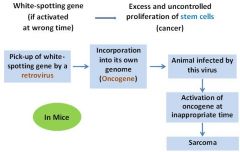
Dominant white spotting |
2 characteristic features White fur - usually on the belly or ventral surfaces rather than on the back or dorsal surfaces |
|
|
White spotting allele Explanation |
During embryonic development – melanocyte precursor cells migrate from neural crest down either side of the body – eventually meeting at the center of the belly. |
|
|
White-spotting gene and cancer |
|
|
|
Graying gene in horse |
Normal pigmentation at birth (Black or gray) Gene responsible: syntaxin-17 (STX17) |
|
|
Carpet wool gene |
solid unpigmneted wool fibers having a hollow core (medulla) running down the center of the fiber.
|
|
|
Use of Carpet wool gene |
Fleece from (Nd Nd) sheep Therefore, the number of (Nd Nd) and (Nd n) sheep increased |
|
|
Other carpet wool sheep |
Romaney Sheep Drysdale All breeds are the result based on Romney breed |
|
|
Polledness
|
Two alleles – autosomal, polled (P) dominant to horned (p)
Horns difficult to handle and cause injury, farmers prefer polled (horneless) livestock |
|
|
Muscular hypertrophy |
Also called double muscling Advantages of: |
|
|
Genes for sexing day old chickens |
genetically determined sex differences |
|
|
Methods of Pedigree checking |
Conventional (based on Mendelian inheritance - not powerful) - coat color patterns of the breed |

