![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
283 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the anatomical position in veterinary medicine?
|
Standing on 4 limbs
|
|
|
A structure closer to or further from the median plane is _______ or _______, respectively.
|
medial or lateral
|
|
|
A part is ______ if it is in front of another part or closer to the head.
|
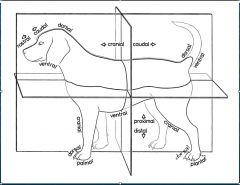
Cranial
|
|
|
What head term corresponds to "cranial" in the rest of the body?
|
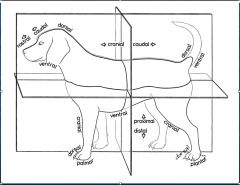
Rostral
|
|
|
What is the part closer to the tail or farther from the head?
|
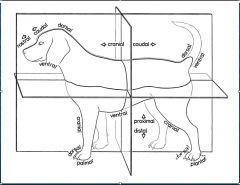
Caudal
|
|
|
For what is the term dorsal used?
|
The surface of the body away from the ground and below the proximal carpus and tarsus directed toward the head
|
|
|
What surface of the body faces the ground?
|
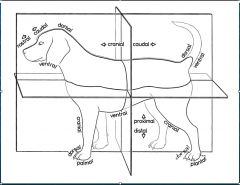
Ventral
|
|
|
What surface below the "top" of the carpus/ tarsus are directed toward the tail or ground?
|
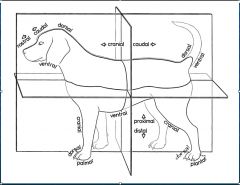
Palmar/ Plantar
|
|
|
What is the name of the surface opposite the palmar/ plantar surface?
|
Dorsal
|
|
|
What terms are used for a part distal from its point of origin or near the surface?
|
Peripheral
|
|
|
What terms are used for a part closer to or farther from a point of attachment or to the trunk, respectively?
|
Proximal or distal
|
|
|
What is the term for a structure closer to/ further from the longitudinal axis of a limb?
|
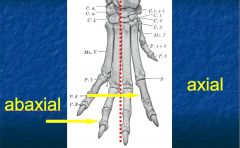
Axial and abaxial
|
|
|
Where is the axis of a limb in relationship to the digits?
|
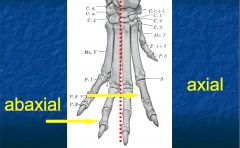
Between the 3rd and 4th digits
|
|
|
What is the term for being closer to the outer surface of a structure?
|
External
|
|
|
What is the term for being closer to the center of the structure?
|
Internal
|
|
|
What plane divides the body into unequal right and left portions?
|
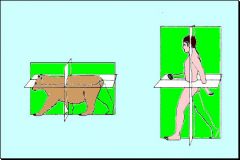
Sagittal plane
|
|
|
What sagittal section divides the body into equal right and left portions?
|
Median plane or mid-sagittal plane
|
|
|
What plane divides the body into cranial and caudal parts?
|
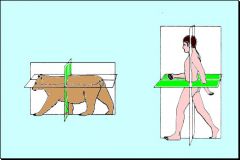
Transverse
|
|
|
The body is divided into the dorsal and ventral portions by a _____ plane.
|
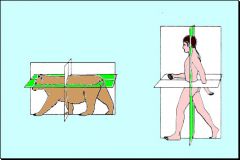
Frontal (Dorsal) plane
|
|
|
What are sections?
|
Cuts through the planes of the body
|
|
|
A _______ plane cuts an organ or limb at a right angle to its long axis. These are usually called_______ ________.
|
Transverse; cross section
|
|
|
What section cuts parallel to the long axis of an organ or limb?
|
Longitudinal section
|
|
|
What section cuts through a transverse plane?
|
Transverse section or cross section
|
|
|
The human term "anterior" corresponds with what veterinary term?
|
Cranial on limbs, rostral face and ventral body
|
|
|
Where are "superior" and "inferior" used in veterinary medicine?
|
For the eyes and some other head structures (replacing dorsal and ventral)
|
|
|
The human term "posterior" corresponds with ____ and _____.
|
Caudal (limbs and head);
Dorsal (body) |
|
|
The skeleton can be divided into _____ and ______ portions.
|
Axial and appendicular
|
|
|
Name the three parts of the axial skeleton.
|
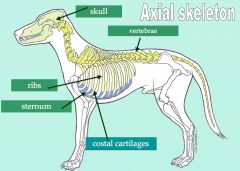
Skull, vertebral column, thorax
|
|
|
The vertebral column consists of what five regions?
|
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and caudal
|
|
|
Of what does the appendicular skeleton consist?
|
limb bones and bones connecting them to the axial skeleton
|
|
|
What connects the thoracic girdle to the axial skeleton?
|
Muscle Attachments (synsarcosis)
|
|
|
The arm (brachium) possesses what bone?
|
Humerus
|
|
|
The radius and ulna form the skeleton of what area?
|
Forearm or antebrachium
|
|
|
Carpal bones make up what structure of the limb?
|
Carpus (human wrist)
|
|
|
The tarsus, metatarsus and digits make up the _______.
|
Pes (human foot)
|
|
|
What is the common name for the tarsus?
|
Hock
|
|
|
What makes up the hock or tarsus?
|
Tarsal hock
|
|
|
The pelvic girdle is made up of which two bones?
|
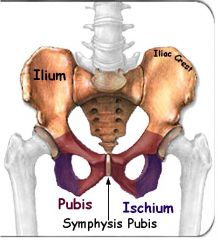
Illium, pubis, ischium
|
|
|
The femur is located in which region of the pelvic limb?
|
Thigh
|
|
|
List the 5 types of bones according to shape.
|
Short, flat, irregular, sesamoid, and long bones
|
|
|
Give an example of each type of bone according to the 5 shapes?
|
Short (carpals),
Long (Humerus, most bones), irregular (vertebral) Flat (Facial), Sesamoid (Patella) |
|
|
What is the smooth layer of hyaline cartilage over the joint ends of bones?
|
Articular cartilage
|
|
|
What are the parts of the long bone?
|
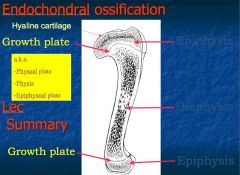
2 ends Epiphysis;
body: diaphysis |
|
|
What joins the diaphysis to the epiphysis in mature bones?
|
Metaphysis
|
|
|
In growing bone, where does lengthening take place?
|
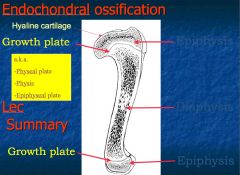
Epiphyseal/ growth plate or physis
|
|
|
Name the fibrous covering of bone not covered by articular cartilage.
|
Periosteum
|
|
|
What layer of bone is necessary for bone growth, repair, nutrition, and attachment of ligaments and tendons?
|
Periosteum
|
|
|
What do radiologist often call the epiphyseal plate?
|
Physis
|
|
|
The structure of the bone can be either ____ or ______.
|
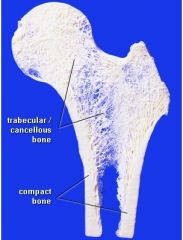
Compact or Spongy (cancellous)
|
|
|
What is the three dimentional lattice of bone spicules of spongy bone?
|
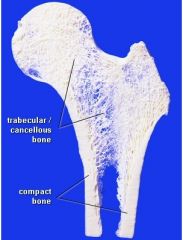
Trabeculae
|
|
|
What is the name of the process of bone formation?
|
Osteogenesis
|
|
|
What are the two possible methods of osteogenesis?
|
Intramembranous & endochondral
|
|
|
In the endochondral ossification, where are the centers of ossification located?
|
Diaphysis and 2 epiphyses
|
|
|
As the centers of ossification of long bones expand, they replace all the cartilaginous model, expect which parts?
|
Epiphyseal plates and the articular cartilage
|
|
|
Lengthening of long bones occurs in what area?
|
outer growth plate (epiphseal side of plate)
|
|
|
What does lengthening of long bones cease?
|
When cartilage cells cease to divide and physis is completely replaced by bone
|
|
|
What are the two different types of growth plates? Give an example of each?
|
Traction (calcaneous) and Compression (most of the rest)
|
|
|
What type of physes contributes the most to lengthening of a long bone?
|
Compression, not traction
|
|
|
What is any prominent, roughened projection from a bone?
|
Process
|
|
|
What is a large, knuckle-like articular prominence?
|
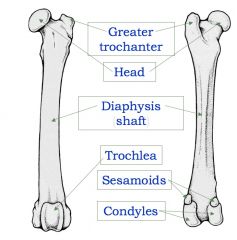
Condyle
|
|
|
A ______ is a tube-like canal through a bone.
|
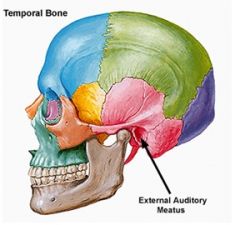
Meatus
|
|
|
What is the pulley-shaped structure of the femur?
|
Trochlea
|
|
|
What is a prominence above a condyle?
|
Epicondyle
|
|
|
A _______ is an opening through a bone.
|
Foreman
|
|
|
Structural classification groups joints according to their _______ _______.
|
Uniting medium
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of uniting medium
|
Fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial
|
|
|
What functional classifications of joints indicate the degree of motion?
|
Immovable, slightly movable and freely movable
|
|
|
A suture is what type of structural joint? Functional (movement)?
|
Fibrous (immovable)
|
|
|
Where are the symphyseal joints found?
|
Generally on the midline of the body
|
|
|
What is the configuration of the shoulder joint?
|
Ball and socket joint (spheroidal)
|
|
|
List the joints of the carpus.
|
Antebrachiocarpal joint,
Middle carpal joint, Carpometacarpal joint, Intercarpal joint |
|
|
What are the two joints between the phalanges of each main digit?
|
Proximal interdigital and Distal interdigital
|
|
|
With what do the proximal ends of the ribs articulate? Distal Ends?
|
Thoracic vertebrae; Sternum
|
|
|
Name the fibrocartilages between the bodies of adjacent vertebre.
|
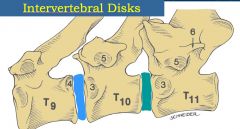
Intervertebral discs
|
|
|
What elastic connective tissue structure attaches the 1st thoracic spine to the spine of the axis (C2) in the dog?
|
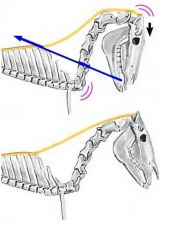
Nuchal ligament
|
|
|
What elastic tissue fills the dorsal space between the arches of adjacent vertebrae?
|
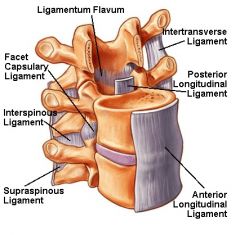
Ligamentum flavum,
Interarcuate, or yellow ligament |
|
|
What connects the heads of a pair of opposite ribs, crossing the dorsal part of the intervertebral discs?
|
Intercapital ligament
|
|
|
What is the relatively immovable joint between the sacrum and the ilium?
|
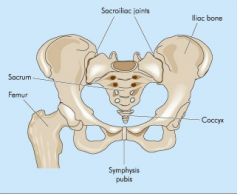
Sacroiliac joint
|
|
|
Name the ball and socket joint of the pelvic limb.
|
Hip joint or coxal joint
|
|
|
What is the compound condylar joint between the femur, patella, and the tibia?
|
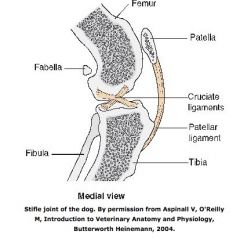
Stifle
|
|
|
What are the fibrocartilaginous discs between the condyles of the femur and the tibia?
|
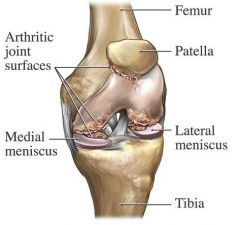
Medial and lateral menisci
|
|
|
How are the cruciate ligaments that attach the femur and tibia named?
|
For their attachment to the tibia
|
|
|
List the joints of the hock/ tarsus.
|
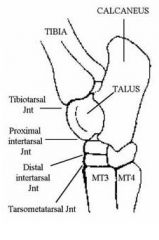
Proximal intertarsal joint,
Distal intertarsal joint, Tarsometatarsal joint |
|
|
What plate of fibrocartilage partically or completely divides the joint cavity of the stifle and temporomandibular joint?
|
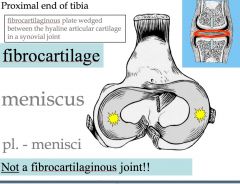
Meniscus
|
|
|
How are synovial joints classified by their number of articular surfaces?
|
Into simple and compound
|
|
|
A _______ or ________ joint allows flexion and extension.
|
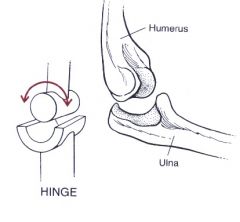
Ginglymus or hinge joint
|
|
|
What type of motion does a plane joint allow?
|
Simple gliding and sliding motion
|
|
|
What type of synovial joint allows universal movement?
|
Ball and Socket/ spheroidal
|
|
|
Most of the joints of the thoracic and pelvic limb have what type of ligament? Which joints don't?
|
Collateral ligaments; shoulder and hips
|
|
|
Define movement of abduction and adduction.
|
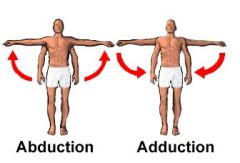
ADduction: towards (adds to) body; ABduction: takes away from body
|
|
|
Define supination and pronation.
|
Supination: palmar surface doral
Pronantion: Palmar surface ventral |
|
|
Rotation is movement of a part around its _______ axis.
|
Longitudinal axis
|
|
|
What is the movement of an extremity in a plane describing the surface of a cone?
|
Circumduction
|
|
|
What motion moves a part forward? Backward?
|
Protraction; Retraction
|
|
|
What is the bending of the spinal column dorsally or ventrally?
|
Dorsal or ventral flexion
|
|
|
Superficial fascia is another name often used for the _______.
|
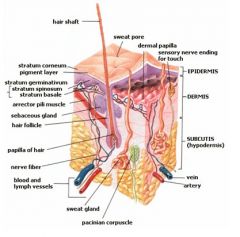
Subcutis
|
|
|
What structural type of joint is characterized by its mobility?
|
Synovial
|
|
|
What characterizes a synovial joint?
|
Mobility, articular cartilage, joint capsule (synovial membrane and Fibrous capsule), synovial fluid, joint cavity
|
|
|
Of what does the joint capsule of a synovial joint consist?
|
Outer fibrous layer & inner synovial layer (membrane)
|
|
|
What covers the articular ends of the bones?
|
Articular cartilage, usually hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
What are the strong bands of white fibrous tissue uniting bones?
|
ligaments
|
|
|
What saclike structure is found between different tissues?
|
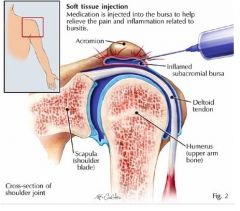
Bursa
|
|
|
What is the function of a bursa?
|
Reduce friction between structures
|
|
|
What is the function of a synovial sheath?
|
Reduces friction on a tendon as it crosses a number of joints
|
|
|
The skin consists of what 2 layers?
|
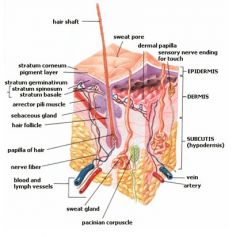
Epidermis and dermis
|
|
|
The two layers of skin (dermis and epidermis) lie on the _________.
|
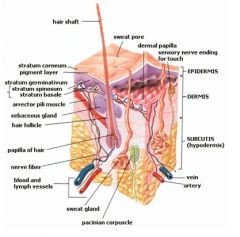
Subcutaneous layer, superficial fascia, subcutis; hypodermis, SQ or SC
|
|
|
The ______ consists of collagenous and elastic connective tissue containing blood vessels, nerve fibers, glands, and hair follicles.
|
Dermis
|
|
|
How does the epidermis receive nutrition?
|
Blood vessels in the dermis
|
|
|
What is the modified epidermis enclosing the dog's ungual process?
|
Claw
|
|
|
Name the toughest skin of carnivores.
|
Pads
|
|
|
Name a pathological, fluid-filled space between the epidermis and dermis.
|
Blister
|
|
|
What are the different types of muscles?
|
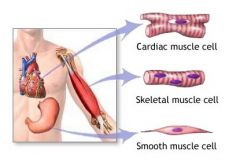
Striated (skeletal & cardiac),
unstriated (smooth) muscle |
|
|
What muscle types are involuntary?
|
Smooth & cardiac muscles
|
|
|
What type of muscles are voluntary?
|
Skeletal
|
|
|
What are the two attachments of skeletal muscles?
|
Origin & insertion
|
|
|
What are the flat attachments of flat muscles (ex. abdomenal muscles)?
|
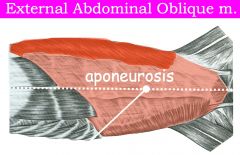
Aponeuroses
|
|
|
What attaches of muscle to a bone?
|
Tendon running through the entire muscles
|
|
|
What structure attaches two bones?
|
Ligament
|
|
|
What do muscles actions depend upon?
|
How they cross a joint, number of joints crossed & shape of joint
|
|
|
What is the fascia deep to the superficial fascia surrounding and compartmentalizing the muscles?
|
Deep fascia
|
|
|
What is the loose irregular connective tissue deep to the skin?
|
Superficial fascia, SQ tissue, subcutis
|
|
|
What local thickening of the deep fascia hold tendons in place?
|
Retinaculum
|
|
|
What is the proper name of the arm pit?
|
Axilla
|
|
|
What is the proper name of the arm?
|
Brachium
|
|
|
What is the proper name for the forearm?
|
Antebrachium
|
|
|
What structure does the carpus, metacarpus, and digits compose?
|
Manus
|
|
|
What is the area between the back legs on the stomach?
|
Inguinal region
|
|
|
Where would you find the tibia and fibula?
|
Crus or true leg (gaskin)
|
|
|
What is the distal part of the hindlimb consisting of the tarus, metatarsus and digits called? What does it correspond to in humans?
|
Pes, the human foot
|
|
|
What is the common name for the tarsus (ankle in humans)?
|
Hock
|
|
|
What makes the point of the shoulder?
|
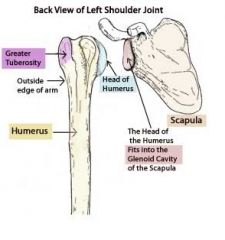
Greater tubercle
|
|
|
What forms the point of the elbow?
|
Olecranon
|
|
|
What forms the point of the hock?
|
Calcaneus bone
|
|
|
What part of the body closes the pelvic outlet and is around the terminal parts of the urogenital and digestive tracts?
|
Perineum
|
|
|
What are whirls of hair in certain areas called?
|

Vortices "cowlick"
|
|
|
What are the long course hairs sensory to touch called?
|
Tactile hair or vibrissae
|
|
|
What is another name for eyelids?
|
Palpebrae
|
|
|
What is the upper and lower eyelids called, respectively?
|
Superior and inferior palpebrum
|
|
|
What is the flap of skin inside the medial part of the eyelids?
|
Third eyelid (nictitating membrane)
|
|
|
How can you get the third eyelid to cross the eye for examination?
|
Open the palpebral fissure & press the eyeball through the upper lid
|
|
|
What is the general structure rostral to the eye called?
|
Muzzle
|
|
|
What is capillary refill time?
|
Time for the mucous membrane to regain its color after being pressed.
|
|
|
What remains of the entrance of the umbilical cord?
|
Umbilicus or belly button (faint scar)
|
|
|
Of what does the bony thorax consist?
|
Thoracic vertebrae, ribs & sternum
|
|
|
What is the opening into the thorax?
|
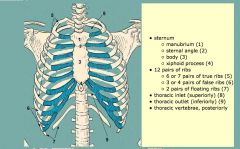
Thoracic inlet (1st thoracic vertebra, right and left ribs and sternum)
|
|
|
Where is the heart located in the thoracic cavity?
|
(2nd) 3rd to (5th) 6th intercostal space in the bottom 2/3rds of the cavity
|
|
|
What is the name of the space between two adjacent ribs?
|
intercostal space
|
|
|
What do the costal cartilages of the ribs caudal to the sternum form?
|
Costal arch
|
|
|
Name the crainal most sternebrae.
|
Manubrium
|
|
|
What is the caudal end of the sternum which is made of cartilage.
|
Xiphoid process
|
|
|
What tough, thickened common integument does a dog walk on?
|
Foot pads
|
|
|
What is the very large, single, triangular-shaped pad palmar to the metacarpo/ metatarsophalangeal junction?
|
metacarpals/ metatarsal pad
|
|
|
Name the rudimentary first digits on the fore- and sometimes hindlimbs.
|

Dew claws
|
|
|
What is the flap of cartilage and skin of the visible part of the ear?
|
Pinna
|
|
|
What are the two parts of the external ear canal?
|
Vertical and horizontal parts
|
|
|
What is the pocket of skin in the caudal edge of the ear?
|
Cutaneous pouch
|
|
|
What is the sac-like appendage housing the testicles?
|
Scrotum
|
|
|
What is one or both testicles not descending into the scrotum called?
|
Cryptorchidism
|
|
|
What is the sheath of skin covering the penius?
|
Prepuce
|
|
|
What is the external genitalia of the female?
|
Vuvla (labia plus clitoris)
|
|
|
What is the female counterpart to the scrotum?
|
Labia
|
|
|
Where is the clitoris found?
|
In the ventral commissure of the labia
|
|
|
What covers the trachea in the cranial neck?
|
Only strap muscles
|
|
|
List the lobes of the dog's lungs.
|
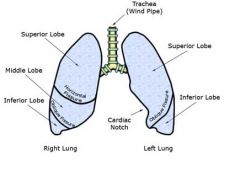
Left (2): cranial & caudal lobes
Right (4): cranial, middle, caudal, & accessory |
|
|
Name the fibroserous sac enclosing the heart.
|
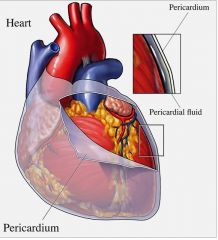
Pericardium
|
|
|
What is the term for ventricular contraction?
|
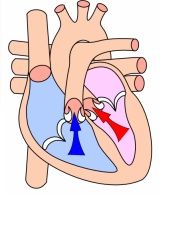
Ventricular systole
|
|
|
What is ventricular diastole?
|
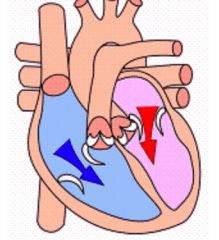
When the ventricles relax & fill with blood.
|
|
|
What is a serosa (serous membrane)?
|
A thin, continuous membrane lining a closed cavity & covering the cavity's organs
|
|
|
What serosa covers walls of a cavity?
|
Parietal serosa
|
|
|
What serosa covers an organ?
|
Visceral serosa
|
|
|
What connects parietal and visceral with visceral serosa?
|
Connecting serosa
|
|
|
What are the serous membranes of the pericardial cavity, thorax, abdomen, spermatic cord called, respectively?
|
Pericardial: Pericardium
Thorax: Pleura Abdomen: Peritoneum Spermatic Cord: Vaginal tunics |
|
|
What are the two parts of the central nervous system?
|
Brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the parts of the peripheral nervous system?
|
Cranial & spinal nerves & ganglia
|
|
|
What are the two impulses of the nervous system?
|
Sensory (afferent) & motor (efferent)
|
|
|
Name the four divisions of the spinal cord.
|
cervical, thoracic, lumbar & sacral
|
|
|
Where does the spinal cord end in the dogs?
|
Dog L6 (6-7)
|
|
|
What are the two types of neurons of the somatic motor nervous system?
|
UMN (upper motor neuron) & LMN (lower motor neuron)
|
|
|
What are carried in the ascending and descending tracts of the spinal cord?
|
Ascending: sensory
Descending: motor |
|
|
Functionally what does the somatic nervous system do?
|
Carries voluntary information from the CNS to the skeletal muscles
|
|
|
Which functional division of the NS keeps the body in balance with its external and internal environment, respectively?
|
External: somatic
Internal: autonomic (ANS) |
|
|
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) work?
|
Carries involuntary information to and from the CNS to smooth and cardiac muscle and glands
|
|
|
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) work?
|
Without conscious effect
|
|
|
What structures does the ANS (autonomic nervous system) regulate?
|
Smooth & cardiac muscles and glands
|
|
|
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
|
Parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions
|
|
|
What is the function of each division of the ANS?
|
Parasympathetic: energy conserving ("couch potato")
Sympathetic: energy expending ("flight or fight") |
|
|
What is the "flight or fight" division of the ANS?
|
Sympathetic
|
|
|
The visceral effectors of the ANS usually have a _________ innervation.
|
Dual
|
|
|
The actions of the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions usually have ______ effects on their visceral effectors.
|
Opposite
|
|
|
How does the ANS differ structurally from the somatic nervous system?
|
Two motor (efferent) fibers instead of one
|
|
|
What is the parasympathetic innervation to the thorax and most of the abdomen?
|
Vagus
|
|
|
What is the sympathetic innervation to the pelvis? Parasympathetic?
|
Hypogastric nn.; Pelvic nerve
|
|
|
Name the cranial nerves.
|
Olfactory (1),
Optic (2), Oculomotor (3), Trochlear (4), Trigeminal (5), Abducens (6), Facial (7), Vestibulocochlear (8), Glossopharyngeal (9), Vagus (10), Accessory (11), Hypoglossal (12) |
|
|
What cranial nerve is entirely sensory, dealing with vision?
|
Optic nerve (2)
|
|
|
What cranial nerve innervates the majority of the skin of the head?
|
Trigeminal (5)
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the muscles of facial expression?
|
Facial (7)
|
|
|
What are the most important functions of the facial nerve clinically?
|
Motor to obicularis oculi muscle & lacrimal gland (dry eye)
|
|
|
What type of nerve is the hypoglossal (12)? What does it innervate?
|
Motor nerve (somatic);
Tongue |
|
|
How do the spinal nerves leave the vertebral column?
|
Through intervertebral foramen
|
|
|
Ventral branches of spinal nerves interlace to form________.
|
Plexuses
|
|
|
What vessels travel toward the heart?
|
Vein
|
|
|
What vessels travel away from the heart?
|
Arteries
|
|
|
What vein returns blood from the head, neck, thoracic limb and cranial part of the thoracic cavity walls of the right atrium?
|
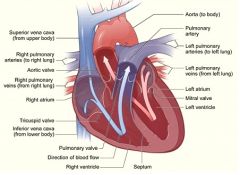
Cranial vena cava
|
|
|
What vein returns blood to the heart from the abdomen, pelvis and pelvic limb?
|
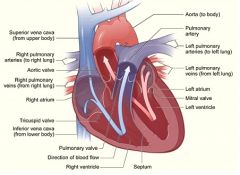
Caudal vena cava
|
|
|
What are the chambers of the heart in the order they receive blood?
|
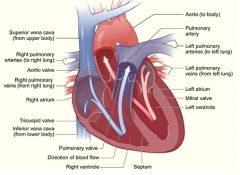
Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left atrium
|
|
|
What side of the heart is part of the pulmonic circulation?
|
Right side
|
|
|
What side of the heart is part of the systemic circulation?
|
Left side
|
|
|
What carries blood from the right heart to the lungs?
|
Pulmonary trunk & Pulmonary artery
|
|
|
What returns blood from the lungs to the left side of the heart?
|
Pulmonary veins
|
|
|
What is the outflow of the heart (left side) to the body?
|
Aorta
|
|
|
In the carnivores, what are the branches of the aortic arch?
|
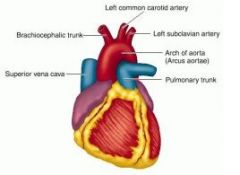
Brachiocephalic & left subclavian
|
|
|
What arteries travel up the neck to supply the head and face?
|
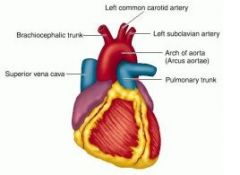
Common carotid aa.
|
|
|
What vein returns blood from the head and neck?
|
External jugular
|
|
|
What part of the aorta is divided into thoracic and abdominal parts?
|
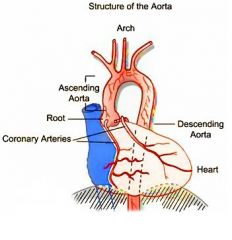
descending aorta
|
|
|
What is the main artery in the brachium (arm)?
|
Brachial artery
|
|
|
Where is the cephalic vein located?
|
On the cranial surface of the forearm
|
|
|
Name the three unpaired branches to the abdominal viscera of the abdominal aorta?
|
Celiac, cranial, & caudal mesenteric aa.
|
|
|
Name the main branches of the terminal aorta.
|
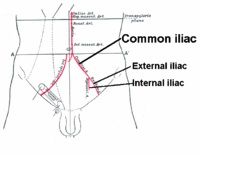
External iliac, internal iliac & median sacral
|
|
|
What terminal branch of the aorta supplies the pelvic viscera and part of the hip and thigh?
|
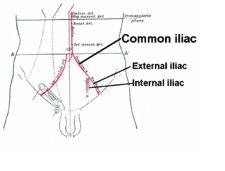
Internal iliac a.
|
|
|
What are the terminal branches of the internal iliac artery?
|
Internal pudendal & caudal gluteal aa.
|
|
|
What is the main branch to the pelvic viscera? And specifically to the uterus?
|
Vaginal or prostatic artery;
Uterine artery off vaginal |
|
|
What is arthritis?
|
inflammation of a joint
|
|
|
What is an osseous (bony) outgrowth seen radiographically?
|
Osteophyte
|
|
|
What is the term for an increase in the density of a bone?
|
Sclerosis
|
|
|
What is immobility and consolidation of a joint due to disease, injury or surgical procedure?
|
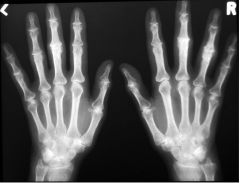
Ankylosis
|
|
|
What is destruction of a bone, seen as reduced density (blacker)?
|
Lysis
|
|
|
What is a luxation or a dislocation?
|
Complete loss of contact between the articular surface of a joint
|
|
|
Define a subluxation
|
Partial loss of contact between articular surfaces of a joint
|
|
|
Why can a broken neck result in respiratory paralysis?
|
Phrenic nerve to the diaphragm arises from the brachial plexus.
|
|
|
What is the panniculus (cutaneous trunci) response?
|
Contraction of the cutaneous trunci muscle in response to a pin prick of the trunk
|
|
|
What is the reflex arch for the panniculus response?
|
Sensation from the skin of the trunk over the thoracic & lumbar spinal n. to the spinal cord, up cord to the lateral thoracic n., out to the cutaneous trunci m.
|
|
|
Clinically what is the panniculus response used to evaluate?
|
Level of the thoracic spinal cord damage.
|
|
|
The __________ consists of collagenous and elastic connective tissue containing blood vessels, nerve fibers, glands and hair follicles.
|
Dermis
|
|
|
How does the epidermis receive nutrition?
|
Blood vessels in the dermis.
|
|
|
Name the modified epidermis enclosing the ungual process in carnivores.
|
Claw.
|
|
|
Name the toughest skin of carnivores.
|
Pads.
|
|
|
Define paralysis.
|
Complete loss of motor activity.
|
|
|
Define paresis.
|
Weakness, partial loss of voluntary motor activity
|
|
|
What is the definition of proprioception.
|
Sensing movements & position of body parts.
|
|
|
What does contralateral and ipsilateral mean?
|
Contralateral - opposite side.
Ipsilateral - same side |
|
|
Why is paralysis of the obiscularis oculi and loss of lacrimation the most vital results of facial nerve paralysis?
|
Drying of the eye, animals not vain (facial paralysis)
|
|
|
What is the air in the thorax called?
|
Pneumothorax
|
|
|
What is the surgical opening of the trachea to the outside?
|
Tracheostomy
|
|
|
Where does blood back up into when the right heart is damaged?
|
Body (venae cavae - ascites, jugular pulse)
|
|
|
Where does blood back up into in left heart failure?
|
lungs
|
|
|
Where is the heart located in relationship to the intercostal spaces?
|
Between 2(3)-5(6) intercostal space
|
|
|
How does the olecranon and the intercostal space relate when standing?
|
Olecranon roughly at the 5th intercostal space or 5th rib
|
|
|
What is a memory aid for the heart valve's point of maximum intensity?
|
PaM 345, rt. AV: low 5th rt
|
|
|
What is the easiest vein to use for venipuncture?
|
Cephalic vein
|
|
|
How do you raise the cephalic vein on a restrained dog?
|
Crus of thumb behind elbow & index finger over cranial elbow & pull slightly lateral to straighten out vein
|
|
|
What superficial vein used for venipuncture, travels up the lateral side of the hind limb to disappear behind the stifle?
|
Lateral saphenous vein
|
|
|
What vein in the head can be punctured during surgery when other vessels are not accessible?
|
Lingual vein
|
|
|
What vessels supply the ventral abdominal wall? Where do they run?
|
Cranial & caudal epigastric aa.;
On the ventral abdomen, on either side of the midline |
|
|
What termination branch of the aorta is the main supply to the pelvic limb?
|
External iliac artery
|
|
|
What is the direct continuation of the external iliac artery out of the abdominal cavity to the pelvic limb for which it is the main supply?
|
Femoral artery
|
|
|
What are the superficial veins of the pelvic limb?
|
Medial & lateral saphenous vv.
|
|
|
What vein is on either side of the ventral surface of the tongue?
|
Lingual vein, sublingual vein on the floor of the mouth
|
|
|
Where are the growing long bones prone to fracture?
|
Physis
|
|
|
How are physeal fractures classified? Why?
|
Salter-Harris fractures;
Prognosis |
|
|
What does DJD stand for?
|
Degenerative joint disease
|
|
|
What is valgus and varus? How do you remember which is which?
|
vaLgus: lateral deviation of bones past joint
varus: medial deviation of bones past joint |
|
|
Name three of four common sources to harvest cancellous bone?
|
Tibial tuberosity, greater tubercle of the humerus, greater trochanter of the femur, wing of the ileum
|
|
|
Broken bones are called?
|
Fractures
|
|
|
What fractures do and do not penetrate through the skin?
|
Simple don't
Compound - do |
|
|
What fracture is pushed inward?
|
Depressed
|
|
|
Name a fracture where the bone is splintered into many fragments
|
Comminuted
|
|
|
Healing of a fracture begins with the formation of a ______.
|
Callus
|
|
|
What is infection of a bone called?
|
Osteomyelitis
|
|
|
What is an unhealed fracture, having all structures of a synovial joint?
|
false joint
|
|
|
What is an articular separation called?
|
Luxation, subluxation, or dislocation
|
|
|
Inflammation of a bursa is called __________.
|
Bursitis
|
|
|
What is a disturbance of endochondral ossification of articular cartilage?
|
Osteochondrosis
|
|
|
What is the most common site of osteochondrosis in dog
|
Shoulder - head of the humerus
|
|
|
What is the composition of most long bones at birth
|
Bone capped with articular cartilage, the 2 cartilage discs between diaphysis, and the 2 epiphyses
|
|
|
During growth how does the physis appear radiographically?
|
As a radiolucent line (dark line)
|
|
|
What should not be mistaken for fractures radiographically?
|
Phseal lines or sesamoid bones
|
|
|
The different views _____________ different sides of the bones.
|
Silhouette/highlight
|
|
|
What does the lateral view silhouette?
|
Cranial & Caudal surfaces of bone
|
|
|
Since cartilage can't be seen radiographically, how is it evaluated?
|
Check subchondral bone
|
|
|
What is the space between bones seen in a radiograph?
|
Joint space & articular cartilage
|
|
|
Is cartilage seen radiographically?
|
No, only inferred
|
|
|
What is osteochondrosis?
|
Defect in endochondral ossification which causes the deeper layers of articular cartilage to die.
|
|
|
List the joints affected by osteochondrosis in the dog.
|
Shoulder (caudal head), Elbow (medial condyle of the humerus), Stifle (medial or lateral femoral condyl), tarsus (medial trochlea or talus)
|

