![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chylamydia: Causative organism
|

|
|
|
Give........... for 3 types of Chylamydial organism:
a. Species b. Serovar c. Natural host d. Human disease |
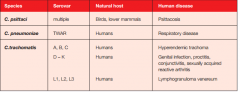
|
|
|
Problems of Chylamydial infection in pregnancy
|

|
|
|
Chylamydia: Clinical diagnosis ♂ & ♀
|

|
|
|
Chylamydia: Investigations
|

|
|
|
Chylamydia: Indications for testing
|

|
|
|
Chylamydia: Indications for Rx
|
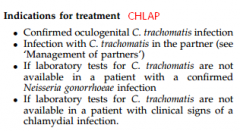
|
|
|
What mammals are riddled with Rx resistant Chylamydia?
|

|
|
|
Chylamydia: Rx
|
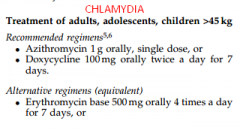
|
|
|
Chylamydia: Rx in pregnant ♀
|

|
|
|
Chlamydia Mx of partners
|
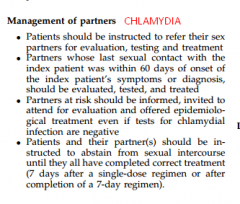
|
|
|
Chlamydia: Complications
|

|
|
|
Lymphogranuloma vereneum
|

+abdo pain
|
|
|
Herpes: Ix
|
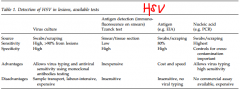
|
|
|
Herpes: Indications for Rx of 1st episode
|

|
|
|
Herpes: Mx 1st episode
|

|
|
|
Herpes: Additional Mx
|

|
|
|
Herpes: Mx complications
|

|
|
|
Herpes: Mx recurrent HSV
|

|
|
|
Gonorrhoea: Sx in ♂
|

|
|
|
Gonorrhoea: Sx in ♀
|

|
|
|
Gonorrhoea: Sx in ♂ ♀
Complications? |

|
|
|
Gonorrhoea: Dx
|

|
|
|
Gonorrhoea: Δ tests (2)
|

|
|
|
Rx Uncomplicated Gonorrhoea (4)
|

|
|
|
Gonorrhoea partner notification?
|

|
|
|
HIV at risk groups
|

|
|
|
Clinical indicator diseases for patients with HIV
|
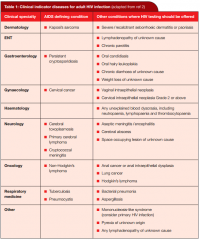
|
|
|
Define urethritis
|

|
|
|
Symptoms of urethritis
|

|
|
|
Causes of urethritis
|

|
|
|
Rx for uncomplicated Chlamydia & NSU
|

|
|
|
Rx for uncomplicated Gonorrhoea
|

|
|
|
Partner notification for:
a. Gonhorroea b. Chlamydia c. NSU |

|
|
|
Causes of abnormal vaginal discharge
|

|
|
|
Give..... for BV, Candidiasis & TV:
a. type of discharge b. odour c. associated Sx d. Typical signs e. vaginal pH |
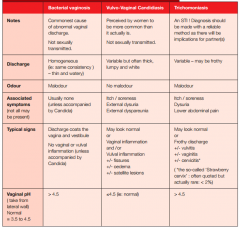
|
|
|
What is the normal vaginal pH?
What causes it to be acidic or alkalotic? How do you measure vaginal pH? |

|
|
|
Give treatment protocol for a woman with vaginal discharge
|
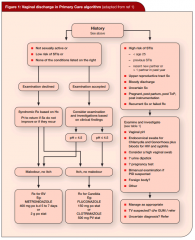
|
|
|
How useful are HSV?
|

|
|
|
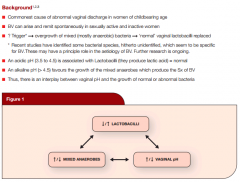
MCC abnormal vaginal discharge
Trigger/pathogenesis? |
|
|
|
BV 'associations'
Is BV a STI? Protective factors? |

|
|
|
BV: Sx & signs
|

|
|
|
BV: Complications
|

|
|
|
BV: Dx
|

|
|
|
BV: Sx and signs
|

|
|
|
BV: Complications
|

|
|
|
BV: Dx
|

|
|
|
BV: Rx
|

|
|
|
BV: Rx in pregnancy
|

|
|
|
BV: Rx for:
a. Breast feeding mothers b. if undergoing TOP c. recurrent BV Partner notification? Follow-up? |

|
|
|
Thrush: Aetiology organisms
Primary Vs Secondary |

|
|
|
Candida: Sx & signs
|

|
|
|
Candida: Complications
Can you determine type of species by Sx and signs? |

|
|
|
Candida: Rx for uncomplicated cases
Topical PO Follow-up? |

|
|
|
Candida: Rx in pregnancy
|

|
|
|
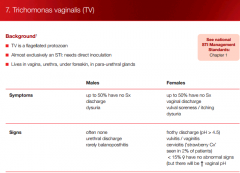
TV: Type of organism?
Is TV and STI? Sx and signs in ♂ & ♀ |
|
|
|
TV: Complications
|

|
|
|
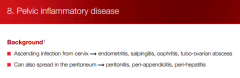
PID: definition
Where can infection spread to? |
|
|
|
PID: Sx
|

|
|
|
PID: Signs
|

|
|
|
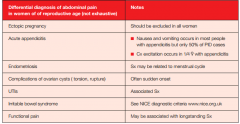
ΔΔ for abdo pain in ♀ of reproductive age (7)
|
|
|
|
PID: Aetiology
|

|
|
|
PID: Rf (6)
|

|
|
|
PID: 1st line Rx
Give 2 courses |
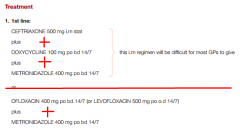
|
|
|
Epydidymo-orchitis: Def & Aetiology
|
![Viral: mumps orchitis is most common. Coxsackievirus A, varicella and echoviral infections are rare.[5][6]
Bacterial and pyogenic infections: E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species are unusual.[7]
Granulomat...](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/38/41/76/5384176_m.png)
Viral: mumps orchitis is most common. Coxsackievirus A, varicella and echoviral infections are rare.[5][6]
Bacterial and pyogenic infections: E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species are unusual.[7] Granulomatous: syphilis, TB, leprosy, Actinomyces spp. and fungal diseases are rare.[1][8][9] Trauma. Idiopathic. |
|
|
Epydidymo-orchitis: Sx & signs
|

|
|
|
Epydidymo-orchitis: ΔΔ
|

|
|
|
Epydidymo-orchitis: Rx for likely STI cause
|

|
|
|
Epydidymo-orchitis: Rx for:
a. ? UTI b. ? TB c. ? Mumps |

|
|
|
Epydidymo-orchitis: Complications
|
1. Infertility - the relationship between epididymo-orchitis and infertility is poorly understood. Men who present with obstructive azoospermia are usually found to have epididymal obstruction when explored for sperm retrieval, which may be a consequence of previous infection.
2. Mumps epididymo-orchitis can lead to testicular atrophy. Of those with bilateral orchitis, 13% will have reduced fertility. 3. Reactive hydrocele. 4. Abscess formation and infarction of the testicle (both are rare). |
|
|
Syphylis: Sx & Definition
|

Venereal syphilis is a contagious, systemic disease caused by Treponema pallidum. T. pallidum enters via abraded skin or intact mucous membrane and distributes via the bloodstream and lymphatics after an incubation period of around 3 weeks.
|
|
|
3° Syphilis manifestations (5)
|

General paralysis of the insane = neurosyphilis
|
|
|
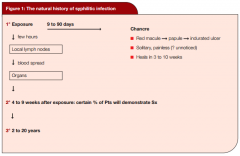
Syphylis: Natural Hx
What is a chancre? How is it formed? Is it painful? How does it spread? Over what time frame? |
|
|
|
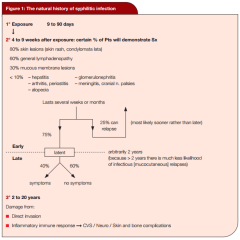
Syphylis: Sx
1° Vs 2° Vs 3°? |
|
|
|
Genital warts: Cause
Pathogenesis How many types ofthe virus? |

|
|
|
Give a summary of HPV type and the tpyes of skin leision they all cause
|

|
|
|
Genital warts: Pathogenesis
|

|
|
|
Genital warts: Sx
|

|
|
|
Genital warts: ΔΔ
|

|
|
|
Genital warts: Rx options and mechanism of action
|

|
|
|
Give the...... for Hep A, B & C:
a. Incidence b. Incubation period c. Infectious period d. chance of persistent infection e. contacts |
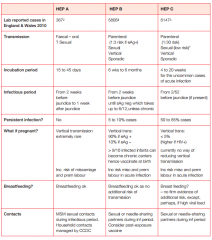
ABC... it's as simple as 123
|
|
|
Give the...... for Hep A, B & C:
a. risks of infection during pregnancy b. risks of breast-feeding |
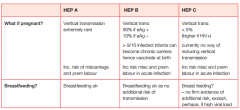
|
|
|
Give the...... for Hep A, B & C:
a. general advice b. follow-up c. diagnosis |
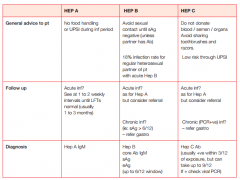
|
|
|
Genital Scabies: Mx
|

|
|
|
Genital Molluscum Contagiosum: Causative organism
Is it an STI? Transmission? ♂ : ♀? Risks of Mother to Child transmission? Facial MC...? |

|
|
|
Genital Molluscum Contagiosum: Sx and signs
|

|
|
|
Genital Molluscum Contagiosum: Complications
Impact in HIV+ve? |

|
|
|
Genital Molluscum Contagiosum: Mx
|

|
|
|
Balanitis: Definition & Aetiology
|

|
|
|
Balanitis: Give the Sx, Signs and Rx for:
a. Candida b. HSH c. Anaerobic Balanitis d. Staph/Strep e. Circinate Balanitis f. Plasma cell Balanitis g. Lichen sclerosis h. Carcinoma-in-situ |
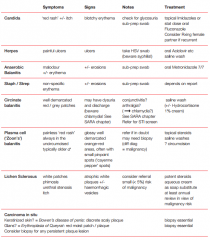
|
|
|
Balanitis:
a. Zoon's Balanitis? b. Bowen's disease of Penis? c. Erythroplasia of Queyrat |
a. Plasma cell balanitis
b. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ that is aka karetanising (PIN) III c. HPV related Penile Intraepithelial Neoplasia (PIN) III ie aka non-keratinising CIS |

