![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Kinesis |
Random movement in response to a stimulus |
|
|
Taxis |
Directional movement in response to a stimulus (positive =forward taxes,negative = backward taxes) |
|
|
Tropism |
Growth movement of part of a plant in response to a directional stimulus |
|
|
Phototropism |
+ve in leaves for photosynthesis -ve in roots to grow into soil |
|
|
Geotropism |
-ve in leaves to grow towards light +ve in roots to find more mineral ions and water (+ve hydrotropism) |
|
|
Reflex arc |
Stimulus --> Receptor --> Sensory Neurone --> Intermediate Neurone --> Motor Neurone --> Effector --> Response |
|
|
Nervous Organisation -CNS/PNS |
CNS- brain and spinal chord PNS- (peripheral nervous system) pairs of nerves that originate from the brain/spinal chord - split into: sensory neurones and motor neurones |
|
|
Spinal chord |
Column of nervous tissue, vertebrate for protection |
|
|
Reflex arc importance |
Involuntary - more complex responses so brain does not overload Protection - harmful stimuli Fast - one or two synapses (slowest section) |
|
|
Sympathetic nervous system |
Speeds up activity |
|
|
Parasympathetic pathway |
Slows down effectors, controlling activities and conserving energy |
|
|
Heart rate control - Chemoreceptors |
Stimulus: drop in blood pH Chemoreceptor in carotid artery and aorta walls detect. Frequency of impulses to the medulla oblongata increase. SAN increases heart rate via sympathetic pathway so CO2 is removed quicker. Chemoreceptors then reduce the frequency untill normal pH has returned |
|
|
Sympathetic nervous system |
Speeds up activity |
|
|
Parasympathetic pathway |
Slows down effectors, controlling activities and conserving energy |
|
|
Heart rate control - Chemoreceptors |
Stimulus: drop in blood pH Chemoreceptor in carotid artery and aorta walls detect. Frequency of impulses to the medulla oblongata increase. SAN increases heart rate via sympathetic pathway so CO2 is removed quicker. Chemoreceptors then reduce the frequency one normal pH has returned |
|
|
Heart rate control - Baroreceptors |
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE: Impulse sent to medulla oblongata decreases heart rate via parasympathetic pathway to the SAN
LOW BLOOD PRESSURE: Transmit impulse to oblongata along sympathetic pathway to SAN increasing heart rate |
|
|
Features of a Pacinian Corpuscle |
Specific stimulus - pressure only 'Transducers' - to create an action potential by translating a stimulus |
|
|
Features of a Pacinian Corpuscle |
Specific stimulus - pressure only 'Transducers' - to create an action potential by translating a stimulus |
|
|
Pacinian corpuscle structure |
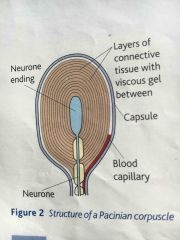
Single sensory neurone is in the centre surrounded by tissue seperate by gel |
|
|
Pacinian corpuscle function |
Pressure causes lamella (flattened Schwann cells by the sensory neurone) to change the shape of the stretch-mediated sodium channels causing sodium to diffuse in, depolarising the membrane and creating a generator potential then an action potential. |
|
|
Cone cells |
COLOUR IMAGES Found in central fovea where light intensity is highest (requires higher intensity to create a potential) No summation one single bipolar neurone to each cell Gives a high visual acuity |
|
|
Rod cells |
BLACK AND WHITE More frequent then cone cells One neurone to multiple rod cells - retinal convergence (summation) Respond to low light intensity Have a low visual acuity |

