![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
tonic receptor definition and example
|
are always active
eye photoreceptors various receptors that monitor body position |
|
|
|
phasic receptors
|
when change happened they get activate
like touch and pressure in skin |
|
|
|
receptor classify simply to
|
extroreceptors
proproreceptors introreceptors |
|
|
|
propro receptor monitor
|
position of body
|
|
|
|
extroreceptor
|
external enviroment
|
|
|
|
interoreceptor
|
condition onside the body
|
|
|
|
nociceptor responsible for.. and locations
|
responsible for pain
location: skin , joint bone periostea, blood vessels,some viserae |
|
|
|
nociceptor receptor type
|
nerve free ending with large receptive field
|
|
|
|
three type of nociceptor receptor
|
1-receptor sensitive to mechanical damage
2-sensitive to extreme temperatures 3- sensitive to dissolve chemicals |
|
|
|
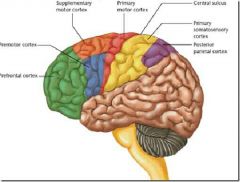
fast pain
where does it trigger ? rely to? |
stabing
triger somatic reflexes(affect muscle) relyed to primary sensory cortex and |
|
|
|
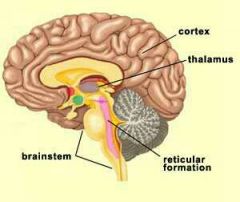
slow pain
|
aching
activates thalamus and reticular formation |
|
|
|
temoreceptor
location? |
location: skin dermis, skeletal muscle,liver,hypothalamus
|
|
|
|
thermoreceptor are tonic or phasy?
|
phasy receptor
quickly adapt to temapture |
|
|
|
pathway of thermoreceptor
|
same as nociceptor(pain) send to reticularbformation , thalamusband primary sensory cortex
free nerve ending |
|
|
|
mechanoreceptors types
|
1-tactile
2-baroreceptors 3-proprioceptors |
|
|
|
chemoreceptors
location? |
chemical compound
respiratory center(po2 and pH) carotid bodies ( pH/ po2/ pco2) arotic(pH/pco2/po2) water and liquid soluble |
|
|
|
tactile what sense?
location? |
pressure,touch , vibration
loc: skin |
|
|
|
fine touch receptors
|
free nerve ending
tactile discs root hair plexus |
|
|
|
root hair plexus respond to
|
initial contract with hair shaft
|
|
|
|
free nerve ending and tactile disc responded to
|
light contact with skin
|
|
|
|
pressure and vibration receptor
|
tactile corpuscle
lamellated corpuscle |
|
|
|
tactile corpuscle responded to
|
initiate contact and low frequency vibration
|
|
|
|
tactile corpuscle( meisser) responded to
|
initial contact ( deep) and high frequency vibration
|
|
|
|
deep pressure receptor
|
raffini corpuscle
|
|
|
|
raffini corpuscle responded to
|
stretching and distortion of dermis
|
|
|
|
lamellated corpuscle responded to
|
initial contact and deep high frequency
|
|
|
|
unencapsulated receptors are in:
|
papillary layer of dermis
|
|
|
|
unencapsulated receptors features
|
tonics, small receptive field
|
|
|
|
unencapsulated receptors measure
|
fine touch , pressure,movement
|
|
|
|
encapsulate Meissner's/ tactile corpuscle locations
|
eyelid
fingerprint lip nipple genitalia |
|
|
|
Meissner's shape
|
coiled interwoven dendirit covered by Schwann cells in a fibrouse capsule
|
|
|
|
raffini corpuscle location
|
dermis
|
|
|
|
raffini corpuscle features
|
interwoven with collagenous fober s extending into dermis
fast adaptation |
|
|
|
pacini / lamellated corpuscle location
|
dermis
finger breast genitalia viscera |
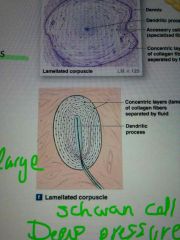
|
|
|
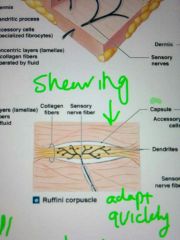
raffini corpuscle shape and feature
|
slowvadaptation
denderit shielding in concentric cell layers |
|
|
|
properioceptors
|
monitor the position of joint tendon ligaments muscle
|
|
|
|
muscle spindel are propioceptord that manitor
|
muscle length
|
|
|
|
Golgi tendon organ monitor the
|
tendon tension
|
|
|
|
baroreceptors located on
|
carotid sinus and aorotic sinus
lung colon digestive tract bladder |
|
|
|
sensory hununculus
|
primary sensory cortex map
|
|
|
|
how breathing is controlling?
|
PONS: monitor blood oxygenation and chemistry
medulla obliganda: respiratory rythmic centerDRG+VRG chemo and baroreceptors stretch receptors |
|
|
|
olfactory epitheli consist of
|
olfactory receptors
supporting cells basal cells (stem cells) |
|
|
|
olfactory organ consist of
|
cribirofo plate
lamina propria olfactory epithelium |
|
|
|
lamina propria contains:
|
1-olfactory glands ( bowmann's gland):produce pigmented mucus
2-blood vessels 3-nerves |
|
|
|
why the smell reminds emotions?
|
olfactory os only sensation that reach cerebral cortex with out firs synaps in thalamus
extensive lymbic and hypothalamic connection help |
|
|
|
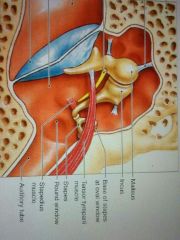
three bone in middle ear
|
malleus
incus stapes |
|
|
|
two small muscle protect eardrum in noisy condition
|
tensor tympani:stiffening tymanum
stapedius muscle: reduce movement |
|
|
|
the receptors are housed within a collection of fluid filled tubes and tubes named
|
membranous labyrinth
|
|
|
|
endolymph
|
the membranous labyrinth contain fluid called
|
|
|
|
perilymph
|
تتت
|
|
|
|
membranous complex divided to
|
vestibular complex
cochlear duct (hearing) |
|
|
|
vestibular complex include
|
semicircular ducts(rotation)
utricle and saccule( gravity and linear acceleration) |
|
|
|
outer wall of perilymph has two small area
|
round window( cochlear window)
oval window( base of stapes steak with annular ligaments) |
|
|
|
hair cell attached to the walk of ampulla from raised structure known as
|
cristae
|
|
|
|
cilium of hair cell in semicircular ducts
|
kinocilium
|
|
|
|
kinocilia and sterocilia of hair cells are embedded in gelatinous structure nemed
|
cupula
|
|
|
|
pathway of vestibular sensation
|
vestibular nerve viii go to vestibular nuclei between PONS and medulla obliganta
|
|
|
|
the information from vestibular nucleus rely to
|
1-rely to cerebellum
2-cerebral cortex--> conscious sense of position and movement 3-send commands to motor stem and spinal cord--> reflex commend to head eye neck |
|
|
|
low ferqency detect by
|
inside part of cochlear
|
|
|
|
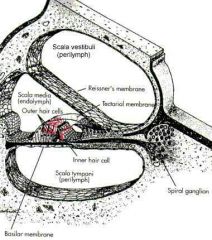
the irgab that separate tempanic duct from cochlear duct called
|
organ of corti or spiral organ
|
|
|
|
tectorial organ
|
the hair cell of cochlear are in contact with it
|
|
|
|
hair cell in cochlear
|
just stereocilia
lack of kinocilia |
|
|
|
round oval functions
|
relieved sound
|
|
|
|
cochlear turn is
|
2.5
|
|
|
|
cochlear in sectional view
|
|
|
|
|
sound wave frequencies
|
20-20,000hz domain
|
|
|
|
first order neuron of cochlear branch
|
exit spiral ganglion enter medulla
|
|
|
|
second order neuron of cochlear branch
|
some go to inferior colliculus of midbrain in oposide side
some inferior colliculus of same side some of them go to superior olivery nucleus for localizing sounds |
|
|
|
the inferior colliculus func
|
number of response reflex to muscular skeleton
|
|
|
|
helicotrema
|
apex of cochlear
|
|
|
|
palpebrate
|
eyelid
|
|
|
|
tarsal gland or meibomian
location |
inner margin of eye lid
|
|
|
|
tarsal glands
|
secret lipid rich product that keep eye lids from sticking togethor
|
|
|
|
muscles response to open and close eye lid
|
elevator palpebrae superior is muscle
oblicularis oculi |
|
|
|
eye muscles
|
superior rectus,
medial rectus, lateral rectus inferior rectus superior oblique(rotation) inferior oblique |
|
|
|
corneal lombus
|
border between cornea and sclera
|
|
|
|
white eye
|
sclera
|
|
|
|
cornea epithelium
|
stratified squmous non keratinised epithelium
|
|
|
|
cornea layers
|
epithelium
basement substantial propria descement's membrane endothelium(simple squmousq) |
|
|
|
choroid layers components
|
choroid, ciliary body, iris
|
|
|
|
choroid feature
|
highly pigmented, light absorbance
|
|
|
|
dilators of iris occurs by
|
sympathetic nerves
|
|
|
|
constrictors of iris occurred by
|
parasympathetic netve
|
|
|
|
iris muscles
|
pupilary dilator muscles(radial)
pupilary consyrictor muscle(sphincter) |
|

