![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ossicles |
Malleus, Incus, Stapes. Their function is to transfer sound from the outer ear to the inner ear. |
|
|
What is the required amount of Decibels needed in order to damaged the Stereocilia? |
80 dB |
|
|
Myopia (near sightedness) |
-Having difficulty seeing objects that are farther away from your eyes. -Caused by Ciliary muscles that are too strong or an eyeball that is too long. |
|
|
If a person were to have trouble seeing near objects, what eye condition would they have? |
Hyperopia (far sightedness) |
|
|
Astigmatism |
Altered shape of the cornea, alters focus of light |
|
|
In the brain, which hemisphere is responsible for interpreting the left visual field? |
The Right Hemisphere |
|
|
Cornea |
Lets light into the eye |
|
|
Choroid |
supplies all of the layers in the eye with blood. |
|
|
Lens |
focus's light received from Cornea and projects it onto the retina |
|
|
Retina |
loaded with photo-receptors and convert light energy into electrical signals that the brain recieves |
|
|
Cones |
detect fine detail and color |
|
|
Rods |
control the peripheral vision and may only detect white and grey colors |
|
|
Frequency |
-The number of waves that pass a certain point in a given time frame -High pitched noises are the result of a shorter wave length -Low pitched noises are the result of a longer wavelength |
|
|
Amplitude |
-The difference between the high and low pressures created in the air by that sound wave |
|
|
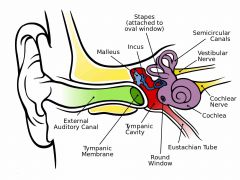
External Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear |
External and Middle Ear are only involved with hearing, while the Inner Ear is key to both hearing and maintaining your equilibrium |
|
|
Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) |
Amplifies sound waves so they are stronger when they enter the inner ear and that the sounds waves are strong enough to move the fluid in the Inner Ear. |
|
|
Auricle |
To enhance and collect sound vibrations and to pass them along deeper into the ear
|
|
|
External Auditory Canal |
amplifies and carries sound to the tympanic membrane, use hair and earwax for protection |
|
|
Tympanic Membrane (eardrum) |
Round, elastic structure that vibrates with sound waves and is connected to the Ossicles (Maleus, Incus and Stapes) |
|
|
Ossicles |
amplifies and transfers sounds from outer ear to the inner ear (from Tympanic Membrane to the Oval Window) Stapes causes Oval Window to vibrate. |
|
|
Oval Window |
beginning of inner ear and takes amplified vibrations and transfers them to the fluid filled Cochlea (organ of sound) |
|
|
Eustachian Tube |
Connects middle ear to the throat and allows pressure equalization in the middle ear with the outer ear. |
|
|
Cochlea |
used for hearing as well as converting mechanical energy (vibrations) into electrochemical impulses. The Cochlea contains the organ of hearing= the organ of Corti (stereocilia) |
|
|
Round Window |
membrane covered opening at the end of the Cochlea, finishes a sound wave |
|
|
Vestibule |
responsible for static or gravitational equilibrium and is comprised of the fluid filled utricle and saccule. |
|
|
Semicircular Canals |
arranged in three different planes (X,Y,Z) and is responsible for rotational or dynamic balance |
|
|
Vestibular Branch |
responsible for static and rotational equilibrium |
|
|
Cochlear Branch |
responsible for sound and hearing |
|
|
Pathway of sound through the Ear (in order) |
|

