![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The senses |
Transduction Sensory receptors Adaption Encoding |
|
|
Transduction |
Cochlea and hair cells |
|
|
Sensory receptors |
Stimuli sensory receptors |
|
|
Adaption |
Trait current into functional role in the life of an organism |
|
|
Encoding |
Convert into a coded form |
|
|
Amplitude |
Height of wave |
|
|
Wavelength |
Distance to one peak to another |
|
|
Frequency |
The fastness of the wave |
|
|
Pinna |
External Part of the ear |
|
|
Tympanic membrane |
Forming part of the organ of hearing |
|
|
Malleus ,anvil stapes |
Tiny bones in middle ear |
|
|
Cochlea |
Fluid filled tube |
|
|
Basilar membrane |
Cochlea(fluid filled ) of the inner ear |
|
|
Auditory nerve |
Cochlear nerve is 1of 2 part of vestibular cochlear never |
|
|
Prosopagnosia |
Neurological disorder that impairs a person's ability to perceive or recognize faces face blindness |
|
|
Oliver Sacks |
Has prosopagnosia Face blindness |
|
|
Sensation |
The bottom up process by which our senses like Vision hearing and smell receive and relay outside stimuli |
|
|
Perception |
The top down when our brains organize and interpret that information and put it into context |
|
|
Absolute threshold |
The minimum stimulation needed to register a particular stimulus 50% of the time |
|
|
Signal detection Theory |
Model for predicting how and when a person will detect weak stimuli partly based on context |
|
|
Sensory adaptation |
Exposure to a constant stimulation which causes the senses to adjust |
|
|
Difference threshold |
Being able to tell the difference between two different stimuli the stars are different brightnesses |
|
|
Webers law |
Receive differences on a logarithmic not linear scale Not amount but percentage |
|
|
Perceptual set |
Mental predisposition to proceed one thing and not another |
|
|
Extrasensory perception (ESP) |
The controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input includes telepathy Clairvoyance and precognition |
|
|
Parapsychology |
The study of paranormal phenomena ESP and psychokinesis |
|
|
Pupil |
The adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters |
|
|
Iris |
The ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil |
|
|
Lens |
The transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help Focus images on the retina |
|
|
Retina |
The light-sensitive inner surface of the eye. containing rods and cones + layer of neurons that begin the processing of visual information |
|
|
Accommodation |
The process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina |
|
|
Rod |
Retinal receptors that detects black white and gray Necessary for peripheral and Twilight Vision when Cons don't respond |
|
|
Cones |
Retinal receptor cells near the center of the retina functions in daylight or well the conditions detect fine detail and color Sensations |
|
|
Optic nerve |
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain |
|
|
Blind spot |
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye creating a " blind spot" because no receptor cells are located there |
|
|
Fovea |
The central focal point in the rent them around the cones comes cluster |
|
|
Feature detectors |
The nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of the stimuli such as shape angle or movement |
|
|
Parallel Processing |
Processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously |
|
|
Young-Helmholtz trichromatic (three color) theory |
The theory that the retina contains three different color receptors( red green and blue) |
|
|
Opponent -process Theory |
The theory that opposing random processes enable color vision (red- green ,yellow -blue, white- black) |
|
|
Gestalt |

An organized whole. Gestalt psychologists emphasize our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful holes |
|
|
Figure - ground |

The organization of visual fields into objects ( the figures) that stand out from their surroundings (the ground). |
|
|
Grouping |
The perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups |
|
|
Proximity |
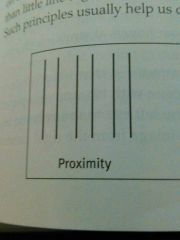
Regroup nearby figures together |
|
|
Continuity |
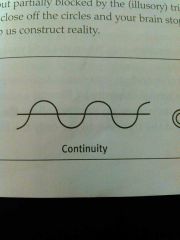
We perceive smooth continuous patterns rather than discontinued ones |
|
|
Closure |
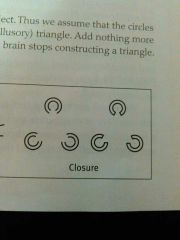
We fill in gaps to create a complete whole object |
|
|
Depth perception |
The ability to see objects in three dimensions although the picture that strike the retina are two dimensional allows us to judge distance |
|
|
Visual cliff |
A laboratory device for testing death perception in infants and young animals |
|
|
Binocular cues |
Depth cues such as retinal disparity that depend on the use of two eyes |
|
|
Retinal disparity |
Binocular cues for perceiving depth by comparing images on retina the brain computes distance |
|
|
Monocular cues |
Depth cues such as interposition and linear perspective available to either eye alone |
|
|
Phi phenomenon |

An illusion of movement created when two or more adjustment lights blink on and off in a quick succession |
|
|
Perceptual constancy |
Perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change |
|
|
Color consistency |
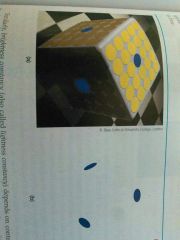
Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color, even it changing illumination alters the wavelengths reflected by the object. |
|
|
Perceptual adaptation |
in vision the ability to adjust to an artificially displaced or even inverted visual field. |
|
|
Pitch |
Tones experience highness or lowness depending on frequency |
|
|
Fusiform Gyrus |
Part of the brain that helps identify faces |
|
|
Inner ear |
The innermost part of the ear containing the cochlea ,semicircular canals and vestibular |
|
|
Sensorineural hearing loss |
Caused by damage to the cochlea receptor cells or to the auditory nerve |
|
|
Conducting hearing loss |
Hearing loss caused by damage to the molecular system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea |
|
|
Place theory |
In hearing the theory that links the pitch be here with a place where the cochlea membrane is stimulated |
|
|
Frequency theory |
The theory that the rate of nerve impulses travel up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of tone thus enabling us to sense its pitch |
|
|
Sensor interaction |
Principle that One sense Can influence the other |
|
|
Synesthesia |
The production of a sense compression relating to incense or part of the body by stimulation of another sense or part of body. Two sensation connecting. |
|
|
Kinesthesis |
The way your body senses its own movement and position |
|
|
Vestibular sense |
Monitors your head position and your balance |
|
|
Relative size and height |

Full grown dog |
|
|
Linear perspective |

Sharper angles equals greater distance |
|
|
Texture gradient |
You can see the closure one is more detailed but with distance become less detail |
|
|
Interposition |
Tells us when one object blocking something else we perceive it as being closer |
|
|
Motion perception |
The speed and direction of a moving object |

