![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Generalized seizure |
an abnormal electrical event that simultaneously involves both cerebral hemispheres and is accompanied by loss of consciousness |
|
|
Partial Seizure - Simple - Complex |
in partial seizures, abnormal activity is limited to part of one cerebral hemisphere only
- Simple: Cognition maintained
Typical features of simple partial seizures include focal clonic movements; paresthesias; visual, auditory, olfactory, or gustatory experiences; sweating and flushing; dysphasia; a sense of déjà vu; or a sense of unwarranted fear.
- Complex: Cognition impaired
Associated with automatisms and amnesia for event |
|
|
Cognition |
refers to involvement of at least two of five features—perception, attention, emotion, memory, and executive function |
|
|
Types of non-convulsive generalized seizures |
include absence, or petit mal, seizures; myoclonic seizures; tonic seizures; and atonic seizures.
Less typical to have a post-ictal period |
|
|
Status epilepticus |
defined as serial seizure activity without interictal recovery or prolonged, continuous seizure activity
Traditional definition: Seizure for 30 minutes
Operational definition: Seizure for >5 minutes or more more than 2 seizures without intervening return to conciousness |
|
|
Common Causes of Secondary seizures |
Metabolic Disturbances
|
|
|
Types of gestational seizures |
Gestational epilepsy: hormonal and metabolic changes exacerbate underlying epilepsy or adversely influence serum levels of anticonvulsants
Eclampsia |
|
|
Postictal/Todd's paralysis |
Focal motor deficit following generalized or complex partial seizure that may persist for 24 hours
High likelihood of underlying structural cause for siezure |
|
|
Indications for neuroimaging in adults with 1st seizure presentation |
First seizure Acute intracranial process suspected History of acute head trauma History of malignancy Immunocompromised status Fever Persistent headache History of anticoagulation New focal neurologic examination Age older than 40 years without epilepsy history Focal onset before generalization Persistently altered mental status |
|
|
Anti Convulstants that can ictogenic as supra-therapeutic levels |
carbamazepine phenytoin lamotrigine topiramate |
|
|
Recommended ED anti-convulsants for status epilepticus |
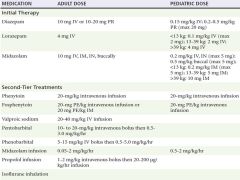
|
|
|
Factors increasing the risk of recurrence among 1st time ED seizure presentations |
partial (versus generalized) ictus status epilepticus history of intracranial surgery or trauma persistent neurologic abnormality 2nd seizure HIV |
|
|
Important adverse effects and interactions of AEDs |
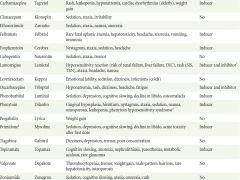
|
|
|
Seziure discharge instructions and safety |
|
|
|
Seizure mimics |
Syncope Panic attacks Pseudoseizure Complex migraine Movement disorder Vertebrobasilar CVA/TIA Sleep disorders (cataplexy, parasomnia) EPS of antipsychotics |
|
|
Effect of p450 enzyme inducers of oral contraceptives |
Reduced efficacy |

