![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Scientific Revolution |
the emergence of modern science and the questioning of traditional thought |
|

Nicolaus Copernicus |
Polish scientist who discovered the heliocentric model of the universe |
|
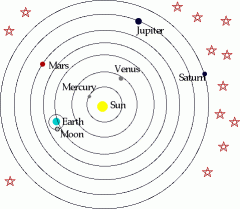
Heliocentric Model |
theory that the sun is at the center of the universe |
|

Galileo |
- Italian astronomer who confirmed Copernicus’ findings of the heliocentric model
- used an advanced telescope |
|

Isaac Newton |
English scientist who discovered gravity and developed 3 uniform laws of motion |
|
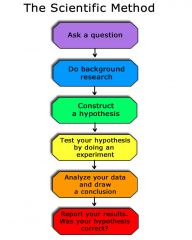
Scientific Method |
scientific approach based on experimentation and observation centered around a hypothesis |
|

The Enlightenment |
era in which human reason was used to create new ideas about government, power and law |
|

John Locke |
- English writer who believed all humans were born with natural rights
- wrote the Two Treaties of Government |
|

Natural Rights |
John Locke’s belief that everyone is born, regardless of social class, with the right to life, liberty and property |
|

Consent of the Governed |
John Locke's belief that a government should make decisions based on the will of the people |
|

Montesquieu |
French thinker who believed there should be 3 branches of government to provide a system of checks and balances |
|

Voltaire |
French thinker who encouraged people to do their own thinking instead of believing what they are told |
|

William Wilberforce |
English abolitionist who wanted to end all slavery |
|

Abolitionist |
a person who wants a complete ban on slavery |
|

Mary Wollstonecraft |
English women and writer who argued that women have the same natural rights as men |
|

Jean-Jacques Rousseau |
- believed that when people create a government the main goal should be for the majority of people to do what is best for everyone
- wrote The Social Contract |
|

Censorship |
A restriction on access to ideas and information |
|

Democracy |
a form of government in which the people are in charge and make decisions together |
|

Nationalism |
a love and pride in one’s country |
|

Enlightened Despots |
an absolute ruler who used his or her power to reform society and bring about political or social change |

