![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Abiotic? |
A non living thing |
|
|
What is biotic |
A living thing |
|
|
Give an example of 3 abiotic organisms |
1.Sand 2.Computer 3.Air |
|
|
give an example of 3 biotic organisms |
1.fish (animals) 2.Flower (plant) 3.people |
|
|
What are the 3 components of cell theory? |
1. all living organisms are composed of cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. cells arise from pre-existing cells |
|
|
Who were the 3 people to come up with the cell theory? |
1.Mat Thais Schleiden 2. Theodore Schwann 3. Rudolf Virchow |
|
|
What did Mat Thais Schleiden do for the cell theory? |
Schlseiden studied the plant-based part of the cell theory. He realized that all plants are made up of cells. |
|
|
What did Theodore Schwann do for the cell theory? |
Schwann came to the conclusion that all animals were made up of cells |
|
|
What did Rudolf Virchow do for the cell theory? |
Virchow proved that all existing cells arise from pre-existing cells. |
|

Label the microscope |
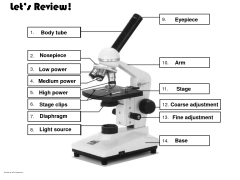
|
|
|
when would you use a dry mount? |
when you are working with inanimate objects or things that do not need water to live. |
|
|
when would you use a wet mount? |
when you are working with live cells, it lets the cells become hydrated, keeping them alive longer, therefore making them be able to move. |
|
|
name the 9 parts to an animal cell |
1. cell membrane 2. cyptoplasm 3. ribosomes 4.golgi apparatus 5. endoplasmic reticulum 6. mitochondria 7. nucleus 8. vacuoles 9. lysosomes |
|
|
name the 10 parts to a plant cell |
1. cell membrane 2. cyptoplasm 3. ribosomes 4.golgi apparatus 5. endoplasmic reticulum 6. mitochondria 7. nucleus 8. vacuole 9. chloroplasts 10. cell wall |
|
|
what is the cell membrane? |
The cell membrane surrounds and holds the cell contents together; controls movement into and out of the cell |
|
|
what is the nucleus? |
The nucleus is the control centre of the cell surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
|
|
what are the vacuoles (animal cell) |
storage compartments for the cell that stores water, nutrients, waste, and other substances. |
|
|
what is the cyptoplasm? |
Jelly like material that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. food and oxygen move through the cytoplasm to get to the organelles. |
|
|
what are ribosomes? |
ribosomes are tiny organelles that help make proteins. There are many in the cyptoplasm. |
|
|
what is the endoplasmic reticulum? |
a folded organelle that makes proteins |
|
|
what is the golgi apparatus? |
a folded organelle that combines proteins made by the endoplasmic reticulum and delivers them to the rest of the cell and outside the cell |
|
|
what are mitochondria's? |
the powerhouses of the cell. these organelles break down food particles and release their stored energy. the cell uses its energy to fuel all of its activities. |
|
|
what is a vacuole?? (plant cell) |
a large, sac-like organelle that stores excess food, waste, and other substances. |
|
|
what are chloroplasts? (plant cell) |
membrane-bound organelles that contain a green substance (pigment) called chlorophyll. |
|
|
what is the cell wall? (plant cells) |
the rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane. it provides the cell with strength and support. materials pass in or out through pores in the cell wall. |
|
|
what are lysosomes? |
organelles that break down food and digest wastes. |
|
|
whats a micrograph? |
A micrograph is a photo taken by means of a microscope |
|
|
what does permeable mean? |
allowing fluids to pass through |
|
|
what does impermeable mean? |
not allowing liquids to add through |
|
|
what does selective permeability mean? |
selective permeability is when some particles, ions, or water can cross the membrane. |
|
|
give an example of selective permeability |
1. coffee filters let the water go through but not the coffee ground 2. window screens let air and liquids in, but not solid things such as bugs and birds |
|
|
give an example of an impermeable thing |
1. plastic 2. tin foil 3. metal |
|
|
give an example of a permeable thing |
1. cotton 2. net/mesh 3. polyester |
|
|
what are the 2 types of cellular transport? |
1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis |
|
|
what is diffusion? |
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
|
|
What is a concentration gradient? |
the difference in concentration between two areas |
|
|
Give an example of diffusion |
1. Coloured food dye drops dropped into a bottle of water 2. A tea bag placed into a cup of water 3. oxygen diffuses from the blood cells into the blood stream into muscles |
|
|
what is osmosis? |
the movement of water from an area of high concentration to low concentration across a selectively permeable membrane |
|
|
what does hypertonic mean? |
higher concentration of solutes lower concentration of solvents |
|
|
what does hypotonic mean? |
lower concentration of solutes higher concentration of solvents |
|
|
what does isotonic mean? |
equal concentration |
|
|
Give an example of osmosis |
1. Pure water in an Iv bag and red blood cells 2. Salt water fish in fresh water |

