![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a gene pool? |
a pool of combined genetic information (genes and alleles) of all the members in a particular population. |
|
|
If a scientist was interested in in hair color and black is dominant to brown, brown is dominant to red) which alleles would be in the gene pool? |
all of them: brown, black, red |
|
|
what is an allele frequency? |
the amount of times an allele appears in a gene pool |
|
|
if there is a change in the allele frequency what process happened? |
evolution |
|
|
if 20% of mice are grey, 20% are white and 30% are black what is the allele frequency for white and black alleles? |
50% |
|
|
What is the main thing that offspring inheiret from their parents? |
Genes |
|
|
Where do most variation in DNA come from? |
mutations and gene shuffling |
|
|
what is the difference between a single gene and a polygenic trait? |
single trait- a trait that is controlled by a single gene that has two alleles polygenic trait- a trait that is controlled by two or more genes |
|
|
What is genetic drift? When is it most powerful? |
genetic drift- a random change in allele frequency most common in a smaller population |
|
|
What is the founder effect? |
when a small group from the original population breaks away from the original population and over time develop different allele frequencies. |
|
|
How many phenotypes are possible for a single gene trait? Polygenic? |
Single- 2 Polygenic- 2 or more |
|
|
what does the graph for a polygenic trait look like? |
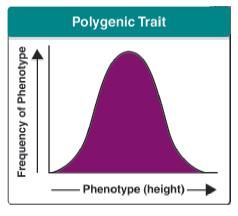
|
|
|
what does the graph for a single gene trait look like? |
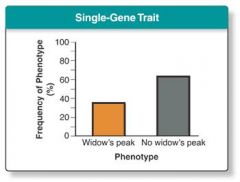
|
|
|
does natural selection act on genotypes or phenotypes? why? |
Phenotypes! Because phenotype is a physical chaecteristic and a genotype is DNA |
|
|
Directional Selection what does it select for? what does it select against? |
For: One of the extreme traits Against: the average or other extreme trait |
|
|
Stabilizing Selection
what does it select for? what does it select against? |
For: Average trait Against: the extreme traits |
|
|
Disruptive Selection
what does it select for? what does it select against? |
For: Either Extreme trait Against: The Average trait |
|
|
What does the Hardy weinberberg equation calculate? |
the frequency of certain genotypes |
|
|
What is genetic equilibrium? |
the situation in which allele frequencies remain constant, no evolution occurs |
|
|
what is the opposite of genetic equilibrium? |
Evolution |
|
|
What are the 5 points of genetic equilibrium? |
1. random mating 2. large population 3.no mutations 4.no natural selection 5.no movement into or out of a population |
|
|
What are the 5 points of evolution? hint: opposite of genetic equilibrium |
1. planned mating 2.small population 3.mutations 4.natural selection 5. movement into or out of a population |
|
|
What is geographic isolation? |
a physical barrier |
|
|
what is behavioral isolation? |
different mating rituals |
|
|
what is temporal isolation? |
different mating seasons or hours of awakeness |
|
|
what percent of species are now extinct? |
99% |
|
|
what was open for species that did survive a mass extintion? |
The ability for adaptive radiation since they didnt have anymore competition |
|
|
how are darwins finches an example of adaptive radiation? |
they evolved to be better fitted to their surroundings to become a different species and to live in different ways. |
|
|
what is convergent evolution? |
unrelated organisms that live in different ways but look similar |
|
|
what color did the oceans change from when oxygen started to be produced? |
brown-----> blue green through iron formation |
|
|
did life begin as single or multi celled organisms? eurkaryotic or prokaryotic? |
single celled and prokaryotic |
|
|
what happened to life on earth when oxygen became abundunt? |
some species died while others adapted to live in more efficient ways. |
|
|
why are proteinoid microspheres scientists best clue to the primitive cell? |
they are very similar to living cells ad systems |
|
|
which animals are common during the paleozoic? |
marine life |
|
|
which animals are common during the mesozoic?
|
dinosaurs |
|
|
which animals are common during the cenozoic?
|
mammals |
|
|
what did darwin learn from huttons work? |
earth is old |
|
|
what did hutton do? |
studied rock layers and helped darwin realize how old earth is |
|
|
what did lamark do? |
thought an animals traits were based on use and disuse of organs |
|
|
define darwins fitness |
the ability for an animal to survive and reproduce in its environment |
|
|
name 2 species that were important to darwins studies on the galapagous islands? |
finches giant tortuises |
|
|
what are vestigal structures? |
organs that serve no purpose or useful function |
|
|
what is a homologous structure? |
Homologous structures are parts of the body that are similar in structure to other species' comparative parts |
|
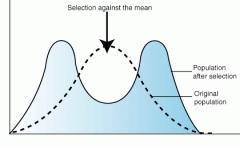
which type of selection graph is this? |
disruptive selection |
|
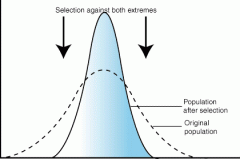
which type of selection graph is this?
|
stabilizing selection |
|
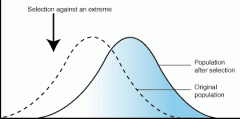
which type of selection graph is this?
|
directional selction |

