![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Solid |
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. |

|
|
|
Liquid |
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. |

|
|
|
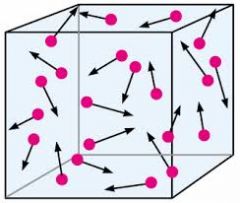
Gas |
an airlike fluid substance which expands freely to fill any space available, irrespective of its quantity. |
|
|
|
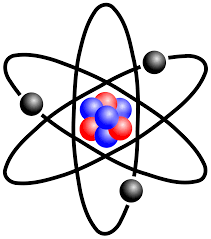
Atom |
the basic unit of a chemical element. |
|
|
|
property |
an attribute, quality, or characteristic of something. |
|
|
|
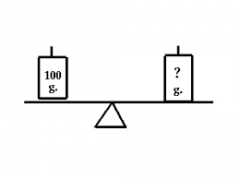
Mass |
In physics, mass is a property of a physical body which determines the strength of its mutual gravitational attraction to other bodies, its resistance to being accelerated by a force, and in the theory of relativity gives the mass–energy content of a system. The SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). |
|
|
|
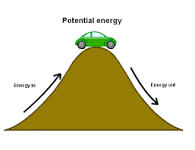
Potential energy |
This potential energy is a result of gravity pulling downwards. The gravitational constant, g, is the acceleration of an object due to gravity. This acceleration is about 9.8 meters per second on earth. The formula for potential energy due to gravity is PE = mgh. |
|
|
|
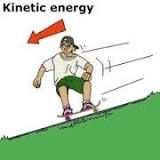
Kinetic energy |
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is theenergy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. |
|
|
|
Chemical energy |
Chemical Energy is energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds (atoms and molecules). It is released in a chemicalreaction, often producing heat as a by product (exothermic reaction). Batteries, biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and coal are examples of stored chemical energy. |

|
|
|
Force |
A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. Whenever there is an interaction between two objects, there is aforce upon each of the objects. When the interaction ceases, the two objects no longer experience theforce. |

|
|
|
Element |
A chemical element or element is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. |

|
|
|
Heat |
the quality of being hot; high temperature. |

|

