![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vertebrates |
Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone |
|
|
Invertebrates |
Invertebrates are animals that do not have a backbone |
|
|
Biology |
Biology is the study of living things |
|
|
Animal Cell and Plant Cell |
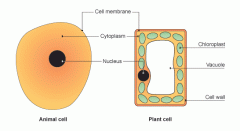
Cell |
|
|
Cell Membrane |
Cell Membrane is a skin that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane protects the cell and it controls the things that enter and leave the cell |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
A watery substance that contains many dissolved substances necessary for life. This is also where the chemical reactions necessary for life take place |
|
|
Nucleus |
The nucleus acts as the control centre of the cell. |
|
|
Large Vacuole |
Plant cells have large vacuoles. Vacuoles are spaces in the cytoplasm which store things and give support |
|
|
Chlorophasts |
They hold chlorophyll the green colour plants use to make food |
|
|
Cell Wall |
Plant cells have a cell wall outside the cell membrane. The cell wall gives shape and support |
|
|
Tissue |
A tissue is a group of similar cells with the same function |
|
|
Organ |
An organ is made of many different tissues working together |
|
|
System |
A system is a group of organs working together |
|
|
Growth |
Growth results from cells dividing |
|
|
Food is needed as |
a) Source of energy b) Material for growth and repair of cells |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Sugar Starch Fibre |
|
|
Sugar |
To Provide Energy. Found in Fruit, Honey, Milk |
|
|
Starch |
To Provide Energy. Found in potatoes, pasta and bread |
|
|
Protein |
For growth and repair of cells to make muscle and hair. Found in Lean Meat, egg white |
|
|
Fats |
To provide a store of energy For Insulation Found in Butter, Milk, Cheese |
|
|
Vitamin C |
For healthy skin and gums Lack of Vitamin C causes scurvy Found in Citrus fruits
|
|
|
Vitamin D |
To build strong bones and teeth Lack of Vitamin D causes rickets Found in Cheese, Milk, Yoghurt |
|
|
Iron |
Needed to make red blood cells Found in Red Meat, Liver, Cabbage |
|
|
Calcium |
Lack of iron causes anaemia For healthy bones and teeth Found in Milk, cheese, Tinned salmon |
|
|
Test For The Presence of Starch |
Iodine Solution Brown/yellow -> Blue/Black
|
|
|
Test for The Presence of Reducing Sugar (Glucose) |
Benedict's solution (+heat) Blue -> Brick Red |
|
|
Test for Protein |
Sodium Hydroxide Solution+Copper Sulfate Solution (Biuret) Blue -> Purple |
|
|
Test for Fat |
Brown Paper Translucent spot |
|
|
what is the energy in food measured in |
The energy in food is measured in Kilojoules |
|
|
A balanced diet depends on |
A balanced diet depends on a person's age, sex and activity level |
|
|
Water is needed |
Water is needed as a solvent and to transport substances |
|
|
Digestion |
Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small soluble food molecules |
|
|
Physical Digestion |
where the food is broken down by the teeth and the churning action of the muscles of the digestive system |
|
|
Chemical Digestion |
Where the food is broken down by special chemicals called enzymes |
|
|
Starch + Amylase = |
Maltose+ Amylase |
|
|
Enzymes |
Enzymes are biological catalysts |
|
|
Eating |
Food is taken into the mouth |
|
|
Digestion |
The food is broken down into smaller, soluble molecules |
|
|
Absorption |
The digested food is taken into the bloodstream and carried to the cells where it is used |
|
|
Excretion |
Getting rid of undigested waste as faeves |
|
|
Mouth |
Physical digestion by teeth Chemical digestion by enzymes |
|
|
Oesophagus |
carries food from mouth to stomach
|
|
|
Stomach |
Food is mixed with digestive enzymes and churned |
|
|
Liver |
Produces bile |
|
|
Pancreas |
Produces digestive enzymes |
|
|
Small Intestine |
Completes digestion digested food absorbed into the bloodstream |
|
|
Large Intestine |
Takes water back into bloodstream |
|
|
Incisor |
Cutting and biting the food |
|
|
Canine |
Tearing food |
|
|
Premolar |
crushing and grinding food |
|
|
Molar |
Crushing and grinding food |
|
|
All living things need |
All living things need energy |
|
|
Respiration |
Respiration is the release of energy from digested food |
|
|
Equation for Respiration |
Food(Glucose) + Oxygen = Energy + Carbon Dioxide + Water |
|
|
Larynx |
Voice Box, Responsible for making sounds |
|
|
Rings of cartilage |
keeps the air tubes open |
|
|
Lungs |
The breathing organ |
|
|
Diaphragm |
A sheet of muscle which moves up and down during breathing causing air to move in and out of the lungs |
|
|
Trachea |
allows air to pass in and out of the lungs |
|
|
Bronchus |
Tube which carries air from the trachea to the lungs |
|
|
Bronchioles |
thin tubes which carry air within the lungs |
|
|
Alveoli |
Tiny air sacs covered by a network of narrow blood vessels. Oxygen and carbon dioxides are exchanged in the alveoli |
|
|
Gaseous Exchange |
Gaseous Exchange occurs when oxygen from the air is swapped with carbon dioxide from the body. During gaseous exchange, oxygen in the air we breathe in, diffuses across the wall of the alveolus into the bloodstream. At the same time, Carbon Dioxide diffuses into the lungs from the bloodstream and is breathed out. |
|
|
Function of the Circulatory System |
The function of the circulatory system is transport |
|
|
The functions of blood |
1) Transport 2) Defense against diseases 3) Constant Body Temperature |
|
|
Function of Plasma |
The function of plasma is to transport substances and heat. |
|
|
Function of Red Blood Cells |
The function of Red Blood Cells is to transport oxygen. Red blood cells contain a red pigment called Haemoglobin |
|
|
Function of White Blood Cells |
The function of White Blood Cells is to defend against diseases. |
|
|
Function of Platelets |
The function of Platelets is to clot blood |
|
|
Arteries |
Thick wall and Small Lumen Blood is carried under high pressure from the heart No valves Carry blood away from heart Usually contain oxygen rich blood
|
|
|
Veins |
Thin wall with large lumen Blood flow not under pressure Have valves to prevent backflow of blood Carry blood to the heart Usually contain oxygen poor blood |
|
|
Capillary |
a
|

