![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
adaptation
|
current traits that play a functional role in the life history of an organism that maintained and evolved by means of natural selection
|
survive in different environments
|
|
|
natural selection
|
acts on organism phenotype which affects it's genotype.
|
Darwin (key method in evolution), fitness, genotype affect phenotype, & variety of N.S.
|
|
|
fitness
|
organism capacity to survive, mate, & reproduce.
|
ana+phsy+biochem+behavior=
"survival of the fittest" |
|
|
How do phenotypes affect genotypes
|
Because the strongest phenotype survive & mate with other strong & reproduce& make stronger&...
|
Can affected by drastic external condition( xtremclimate change
|
|
|
What are the 4 selective processes that cause evolutionary change or preserve existing adaptive traits?
|
Normalizing or Stabilizing selction
Directional Variation Disrupting/diversifying selection Balanced Selection |
Long time in same environment.
Enviroment favors genetic variant. Pop. confrntd wth new condtions &or prospr at expnsive of other. (Hybrid advantage) hetero is fitter than homozygote |
|
|
What temperature does water boil?
|
100°c, 212°f, 373.15°k
|
F=(c°)(1.8)+32
|
|
|
What is waters freezing point?
|
0°c, 32°, 273.15°
|
jordan
|
|
|
emigrated
|
move away, leave, exit current homeland, point of arrival
|
exit
|
|
|
immigrated
|
, move into, come into country to live, point of departure
|
enter
|
|
|
What are Cytosine, thymine & uracil together are?
|
pyrimidines
|
Triangle
|
|
|
What do purines consist of?
|
adenine & guanine
|
Rna ish.
|
|
|
What does a g / gram equivalent to?
|
1ml, 1cm3, 1cc
|
d=M÷V
|
|
|
What is the formula to get from grams to ml. ?
|
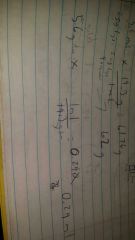
grams to ml.
|
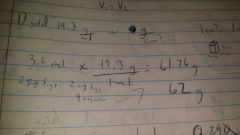
opposite of this
|
|
|
What does -3,-2,-1 after an atom?
|
Ion,Anion, wants those -e,needs that amount to reach -8 electrons in its valence shell,
|
inbalance
|
|
|
What is a +1,+2,+3 after an atom?
|
ion, cation, loose those extra, to reach valence shell at -8,
|
in balance
|
|
|
Which atoms like have + ions?
|
metals,
|
non metals -&+
|
|
|
mass of one mole of any element is?
|
MM,/molar mass, OR
6.02X10 to 23rd power X 1 |
Atomic #
|
|
|
octet is?
|
atom achieves 8 e.
|
valence e.
|
|
|
covalent compond?
covalent bond? |
share electrons
|
CH4,
|
|
|
ionic bound?
ionic compound? |
transfer electrons.
commonly metal+nonmetal |
NaCl
|
|
|
What are the masses of e, n,&p?
|

|
|
|
|
coulomb&/or electrostatic do what?
|
Keep electrons attracted to + charger nucleus
|
|
|
|
What is an isotope?
|
An atom with the same number of protons/electrons but different number of neutrons.
|

carbon-12, carbon-13, & carbon-14
|
|
|
What is an isotope symbol ?
|

|
superscript
|
|
|
What does A, Z, N in an atom signify?
|
mass, atomic # neutrons,
|
|
|
|
What is diatomic & give all examples?
|
exist naturally in pairs, same element
|
Have no fear of ice cold beer
ch, br |
|
|
How many elements are on the periodic table?
|
111
|
28 man made
|
|
|
What are groups/family?
|
columns, up&down, horizantal, 18 groups, periodicity.
|
group 1a=alkali metals
..2a=alkaline earth metals 7a=halogens 8a=inert gasses or noble gasses |
|
|
periods?
|
7, vertical,
|
|
|
|
lanthanides? Actinides?
|
manmade.
|
|
|

What 3 does this describe?
|

|

|
|
|
One way chemical reaction are characterized is?
|

combination/synthesis, decomposition, isomerization
|

|
|
|
anatomy?
|
structure
|
|
|
|
physiology?
|
function
|
|
|
|
animal tissue?
|

epithelial, muscle, bone, connective, blood, nerve, cartilage,
|
humans have 4 main tissues.
|
|
|
organ?
|
structure with 2 or more tissues that perform a specific function for the body
|
|
|
|
name the 11 organ systems?
|

|
c, i, s, m, n, e, l, r, d, u, r.s.
|
|
|
metabolism? catabolism? anabolism? cellular respiration?
|

|
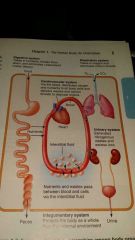
|
|
|
integumentary system?What are some examples? types of tissue? What are its functions?
|

|

|
|
|
Skeletal system?Ex.? tissue types? functions?
|

long, short, flat irregular bones.
|
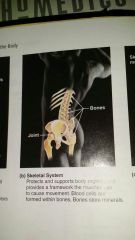
|
|
|
axial skeleton?
|
skull, sternum, ribs, veritable column(spine)
|
|
|
|
appendicular skeleton?
|
bones of the limbs, &shoulders&hips
|
|
|
|
muscular system?
|

smooth=involuntary, hollow organs, slow long contractions, single nuclei
skeletal=long, voluntary, cardiac=involuntary contractions, striations&branched, special connection between cells |

|
|
|
nervous tissue &system?
|

Central & peripheral nervous systems.
sympathetic=fight or flight parasympathetic=control basic body functions. |
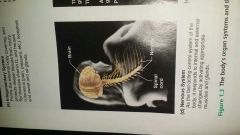
axion=send impulse or message
chemical synapse=point were meet. glial cells= structual support dendrites= receive signals, branched soma=contain nucleus & organelles myelin sheath= node of ranvier |
|
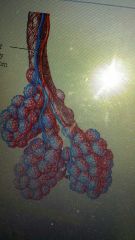
What are the parts of everything? blue, red?
|
b= pulmonary arteries
red=..... veins alveoli |
|
|
|
capillaries
|
smallest of blood vessels, oxygen& carbon are exchanged
|
|
|
|
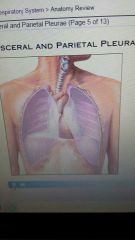
Visceral and parietal pleura
|
inner & outer, lines medaiastum, diaphram& inner thoratic wall.Surround lungs, cavity, fluid
|
|
|
|
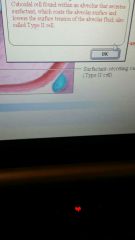
structure of an alveolious?
|
simple squamous epithelium, alveolar macrophages, surfactant-secreting cell.
|
|
|
|
respiratory membrane
|
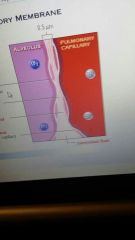
|
|
|
|
What are some hormones that are secreted my the endocrine system?
|
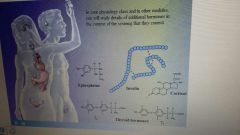
|
|
|

What are the all the glands in the endocrine system
|

|
|
|

pineal gland
|

|
|
|
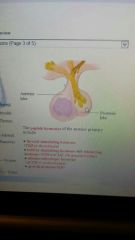
pituitary gland
postierlobe= pic |
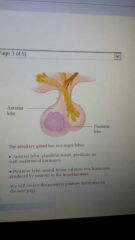
|
|
|
|
Who produces hormones?
|

|
|

