![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
homeostasis |
is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. |

|
|
|
tissue |
Human body tissue makes up organs and other body parts. There are four main types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, connective and nervous. Each is made of specialized cells that are grouped together according to structure and function. |
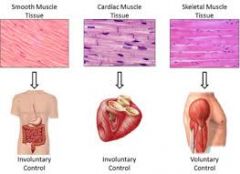
|
|
|
organ |
An organ is a part of your body that performs a specific function: like your brain, lungs, or skin. You might not use the word organ often, but you use organs every second — imagine getting through a day without your heart or skin. |
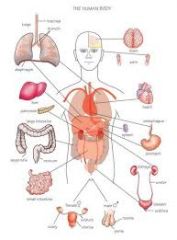
|
|
|
organ system |
The 11 organ systems of the body are the integumentary, muscular, skeletal, nervous, circulatory, lymphatic, respiratory, endocrine, urinary/excretory, reproductive and digestive. Although each of your 11 organ systems has a unique function, each organ system also depends, directly or indirectly, on all the others. |
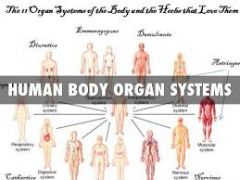
|
|
|
epithelial cell |
Epithelia are formed of cells that line the cavities in the body and also cover flat surfaces. Of the four major tissue types found in the human body (Figure 1), epithelial cells are by far the most prolific. |
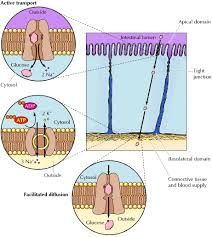
|
|
|
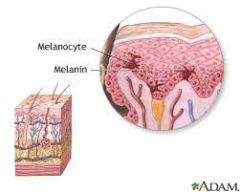
melanin |
Melanin is a complex polymer derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Melanin is responsible for determining skin and hair colour and is present in the skin to varying degrees, depending on how much a population has been exposed to the sun historically. |
|
|
|
epidermis |
the outer layer of cells covering an organism, in particular. |

|
|
|
dermis |
The dermis is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that consists of connective tissue and cushions |

|
|
|
follicle |
a small secretory cavity, sac, or gland, in particular. |

|
|
|
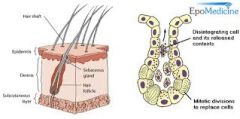
sebaceous gland |
a small gland in the skin which secretes a lubricating oily matter (sebum) into the hair follicles to lubricate the skin and hair. |
|

