![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

anemometer
|

An instrument used to measure wind SPEED.
|
|
|
wind chill factor
|

The increased cooling that a wind can cause.
|
|
|
local winds
|

winds that blow over short distances
|
|
|
land breeze
|
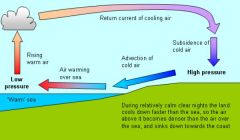
The flow of air from land to a body of water.
|
|
|
monsoons
|
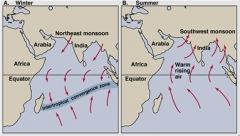
Sea and land breezes over a large region that change direction with the seasons.
|
|
|
sea breeze
|
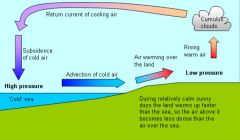
A wind that blows from an ocean or lake onto the land.
|
|
|
global winds
|
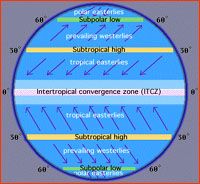
Winds that blow steadily from specific directions over long distances.
|
|
Coriolis effect
|
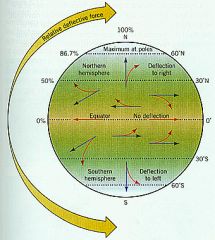
The way the Earth's rotation makes winds curve.
|
|
|
Monsoons happen in _______.
|
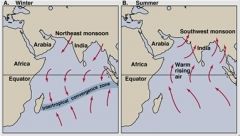
Monsoons happen in SOUTH AND SOUTHEAST ASIA
|
|
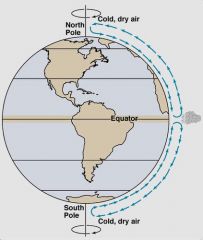
The movement of air between the equator and the poles produces?
|
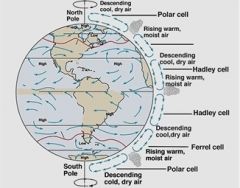
Global winds
|
|
|
wind vane
|

A device which determines wind DIRECTION.
|
|
|
The name of a wind tells you__________.
|
The name of a wind tells you the direction a wind IS COMING FROM.
|
|
|
Name the three major global wind belts.
|
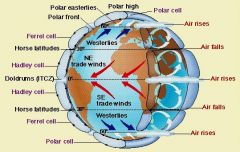
1. trade winds
2. prevailing westerlies 3. polar easterlies |
|
|
doldrums
|
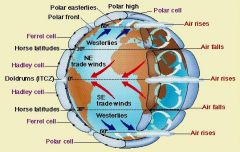
A calm area near the Equator where warm air rises. There is little or no wind.
(The trade winds meet at the doldrums) |
|

horse latitudes
|
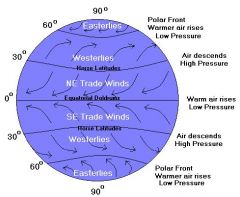
Belt of calm air at about 30 degrees north and south. Becalmed sailors ran out of food and threw their horses overboard here.
|
|
|
Trade winds
|
Belt of winds between 30 degrees N or S and the Equator. The winds blow towards the Equator and are turned west by the Coriolis effect.
|
|
|
prevailing westerlies
|
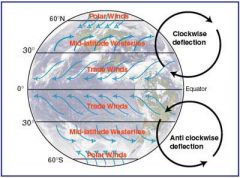
Belt of winds between 30 and 60 degrees N or S. The winds blow from the SW in the northern hemisphere and from the SW in the southern hemisphere.
|
|
|
Polar easterlies
|
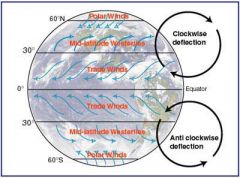
Belt of winds from the poles to 60 degrees N or S. Winds blow from the poles and and are turned by the Coriolis effect to the west.
|
|
|
polar front
|
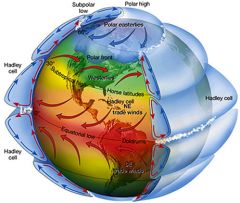
At 60 degrees N and S the polar easterlies meet the prevailing westerlies mixing warm and cold air. The polar front has a MAJOR effect on weather in the USA.
|
|
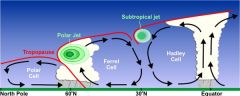
jet streams
|
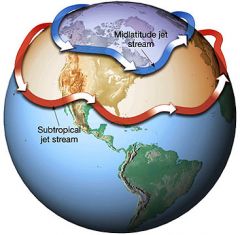
Global west winds found 10 kilometers above the Earth and only a few kilometers deep. They blow at 200 to 400 kilometers an hour.
|
|

How do jet streams effect airplanes?
|
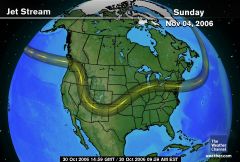
Airplanes flying east can be helped by flying in the jet stream, gaining speed and saving fuel. Airplanes flying west are slowed down.
|
|

What is the cause of local winds?
|
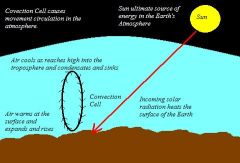
The unequal heating of Earth's surface within a small area.
|
|
|
All winds are caused by?
|
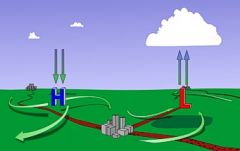
differences in air pressure
|

