![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A region where the particles are close together in a sound wave is called a... |
compression |
|
|
Describe how vibrations are passed through the ear to the auditory nerve. |
The Pinna collects the sound waves which then travels through the ear canal. They vibrate against the eardrum. The vibrations are passed to the ossicles which amplify the sound. The movement is then passed to the Cochlea where the hairs will turn the movement into electrical signals. The electrical signals are transmitted through the auditory nerve which is connected to the brain. |
|
|
The loudness of a sound is measured in... |
decibels |
|
|
When people get older, they find it most difficult to hear... |
high pitched sounds |
|
|
Describe what a longitudinal wave is. |
A longitudinal wave is a wave where the oscillation is parallel to the direction of the wave. |
|
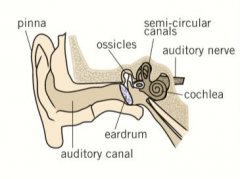
Label the parts without looking at the names. |
(blank) |
|
|
The wave of a louder sound has a bigger... |
amplitude |
|
|
A region where the particles are far apart in a sound wave is called a... |
Rarefaction |
|
|
Sound cannot travel in space because... |
There is no material to vibrate |
|
|
The higher pitched a sound is, the higher the... |
frequency |
|
|
A guitar string is plucked. As the string is tightened, the sound will get... |
higher |
|
|
The distance from one point on a wave to the same point on the next wave is called the... |
wavelength |
|
|
Waves can also superpose. Describe what happens when waves superpose. |
Waves add up or cancel each other. |
|
|
Explain why sound travels faster in solids than liquids or gasses, and why it cannot travel in a vacuum. |
Sound travels faster in solids as the particles are denser. The particles in liquids and gasses are not as dense as they freely roam around. Sound cannot travel in a vacuum as there is no medium to vibrate or to move back and forth very quickly. |
|
|
The point on the top of the wave is called... |
peak/crest |
|
|
The word for the distance from the middle to the top or the middle to the bottom. |
Amplitude. |
|
|
Lower frequency means there are... |
less waves |
|
|
When a sound gets louder, the waves look... |
the peak/crest gets higher and the trough gets lower. |
|
|
If a sound is high-pitched, there are... |
more waves |
|
|
Describe what a transverse wave is. |
In a Transverse wave, the oscillation is at 90 degrees to the direction of the wave. |
|
|
What is sound? |
vibrations traveling through the air as sound waves |
|
|
Definition of ultrasound: |
Sound with a frequency about 20,000 Hz |
|
|
Name of the two waves when it comes into the barrier and bounces off. |
Incident wave (into barrier), reflected wave (bounces off) |
|
|
State the speeds of sound, |
340 m/s in air, 1500 m/s in liquids, 5000 m/s in solids |
|
|
Why does light travel faster than sound? |
Sound can only travel through matter, which will slow the waves down. Light can travel through a vacuum and doesn't need matter to travel through. |
|
|
humans can hear a range of frequencies called the... |
audible range |
|
|
frequencies below 20 Hz is called... |
infrasound |
|
|
Name 4 ways you can damage your hearing |
1. sharp objects that could make a hole in your ear drum 2. build-up of ear wax 3. very loud sounds (permanent) 4. head injuries (permanent) |
|
|
What happens when you sing into a microphone? |
sound waves hits a flexible plate called a diaphragm. |
|
|
How does a diaphragm work? |
The diaphragm vibrates, like your ear drum. It produces an electrical signal like your cochlea. The signal carries the information that the sound wave carried. |
|
|
What produces an echo? |
Sound that reflects off a surface. There is a time delay between making a sound and hearing an echo. |
|
|
How do you reduce echoes? |
By covering the walls with soft material and putting carpet on the floor. |
|
|
State a use of ultrasound in pregnant women |
To make images of unborn babies, the ultrasound wave travels through the woman and reflects off the fetus. The machine detects the echo. It uses the time taken for the echo to build up an image of the fetus. |
|
|
State a use of ultrasound in ships |
A transmitter under the ship sends out a beam of ultrasound which travels through the water and reflects off the seabed. A receiver detects the reflection and uses the time work out the depth of the water. |
|
|
State the use of ultrasound in physiotherapy. |
Ultrasound reduces the pain and swelling of a damaged tendon and could also look for cancer. |
|
|
Definition of reverberation. |
when lots of echoes join together to produce a long sound. |
|
|
How do you find the apparent depth of water? |
0.75 X real depth |
|
|
Word for: Does not give out light |
non-luminous |
|
|
The image is formed in the... |
retina |
|
|
Word for: Description of an image that is upside down. |
inverted |
|
|
Definition of a light year |
How far light travels in a year |
|
|
When you look at a mirror, the image is... |
a virtual image |
|
|
Definition of angle of incidence? |
Angle between normal and incident ray |
|
|
Word for: does not give out light |
non-luminous |
|
|
refracts light rays and focuses a clear image: |
lens |
|
|
Describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection |
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals to the angle of reflection |
|
|
Light is (blank) off of the stone |
reflected |
|
|
The stone appears to be (blank) where it really is. |
above |
|
|
Word: does not allow light to travel through it |
Opaque |
|
|
Put in order from the least amount of light it shows at the top: |
1. Opaque 2. Translucent 3. Transparent |
|
|
Controls the amount of light entering the eye: |
iris |
|
|
How does the eye work? |
1. Light from the object travels to our eyes 2. light passes through the len 3. light forms an image on the retina 4. our brain interprets the image telling us what we are looking at |
|
|
As light travels out of the water into the air the light is (blank) |
refracted |
|
|
Describe refraction using the words: density, speed, and normal |
The ray goes straight across the normal but bends towards it as the speed of air and solid (glass) is different. The speed of light slows down as it gets into a denser material. |
|
|
Light (blank) as it leaves the water. |
speeds up |
|
|
When light enters into a solid from a gas, the angle between the normal and a ray of the light (blank) |
decreases |
|
|
Reflection from a smooth surface (in light) is called |
specular reflection |
|
|
Describe what a lens does to light |
It focuses the light and enables you to see. |
|
|
The point where the rays cross in a lens is called.. |
focus or focal point |
|
|
cornea and lens does what to light? |
focus the light onto the retina |
|
|
which part of the eye does reflected light goes through? |
pupil |
|
|
reflection from a rough surface is called... |
diffuse scattering |
|
|
Definition of photoreceptors |
cells in the retina that respond to light |
|
|
What does a prism do to light? |
split white light into a spectrum |
|
|
there are two types of photoreceptors called the: |
rods and cones |
|
|
what are the rods and cones sensitive to? |
RODS: sensitive to movement and dim light CONES: sensitive to bright light and color |
|
|
Definition of dispersion: |
the separation of light into colors by refraction or diffraction with formation of a spectrum |
|
|
white light is made up of? |
seven different colors of light. |
|
|
definition of spectrum? |
the group of colors that a ray of light can be separated into including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet |
|
|
Spectrum of white light is (blank). There are no (blank) spaces. |
continuous, blank |
|
|
Why does dispersion happen? |
different colors of light are refracted by different amounts. |
|
|
the color that is refracted the most and the least. |
MOST: violet Least: Red |
|
|
What causes certain colors to be refracted more than others? |
Light with a higher frequency is refracted more than light with a lower frequency. |
|
|
What are the three primary colors? |
red, blue, and green. You can make all colors of light with these colors. |
|
|
What are the secondary colors? |
cyan, yellow, and magenta. They're created when you mix two primary colors. |
|
|
How do you achieve white light? |
Mix cyan, yellow, and magenta. |
|
|
What does a red filter do to colors? |
subtracts colors from white light. It transmits red light and absorbs the rest. |
|
|
What do ALL filters do? |
transmits the colors that they are and absorb the rest. |
|
|
Why are objects different colors? |
Objects reflect off light of their color into our eyes. When white light from the sun hits the object, it absorbs all the colors except it's own color. |
|
|
Black objects absorbs (blank) the colors. |
all |
|
|
white objects absorbs (blank) colors and (blank) all the light |
no, reflect |

