![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
150 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an atom? |
A tiny particle with electrons, protons and neutrons |
|
|
Element |
A substance made of one type of atom only |
|
|
Compund |
A substance made of 2 or more types of atoms |
|
|
What is chromatography? |
Chromatography can be used to separate mixtures of colored compounds |
|
|
What is distillation? |
Distillation is a method for separating liquid based on boiling point |
|
|
What is the proton/atomic number? |
The number of protons and elections in an atom |
|
|
What is the nucleon/mass number? |
The number of particles in the nucleus |
|
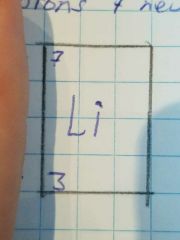
Which is the nucleon number and which is the proton number? |

|
|
|
What is diffusion? |
Diffusion is the spreading out of particles due to their random movement |
|
|
Speed = what? |

|
|
|
What is the outer layer of the tooth called? |
Enamel |
|
|
What is the 2nd layer of the tooth called? |
Dentin |
|
|
What is the inner layer of the tooth called? |
Pulp or nerve |
|
|
What happens to the teeth if food is left in your mouth? |
If food is left in your mouth bacteria will break it down. as they do this they produce acid |
|
|
What happens if you do not have good dental hygiene? |
The acid will begin to eat away the enamel and creates a cavity |
|
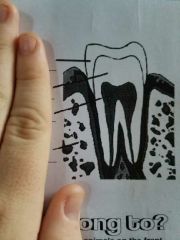
Name all the layers of a tooth |
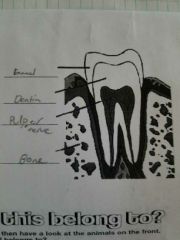
|
|
|
Where doess the alimentary canal begin? |
Mouth |
|
|
Where does it end? |
The anus |
|
|
Was the function of the teeth? |
Chewing and helps digestion |
|
|
What are the two functions of the tongue? |
Moving food to help chew |
|
|
Saliva is released by the salivary glands. What are the two functions of saliva? |
To remove germs and lubricate food |
|
|
What is the muscular tube between the mouth and the stomach called? |
The osophegas |
|
|
What two chemicals does the stomach secrete and what are their functions? |
Hydro chloric acid to dissolve food and food substance |
|
|
What is the purpose of stomach muscle contractions? |
To move food through the body |
|
|
What is chyme? |
What food turns into |
|
|
What chemical does the liver produce? |
Bile |
|
|
What is the function of bile? |
To filter and neutralize chyme |
|
|
Where is bile stored before entering the small intestine? |
Gallbladder |
|
|
What is the other function of the liver? |
Cleans blood |
|
|
Why is the pancreas important for digestion? |
Digestive enzymes |
|
|
Why does chyme need to be neutralized? |
Because it's bad for you |
|
|
Food is broken down by enzymes in the small intestine. what other process also occurs in the small intestine? |
Nutrients are absorbed here |
|
|
How is the wall of the small intestine adapted to speed up the nutrient absorption process? |
Muscle movement and absorption |
|
|
What are the two major roles of the large intestine? |
To absorb water and pass out waste |
|
|
Give 2 examples of what bacteria do in your gut |
Neutralize other bacteria and feed of you, produce gas |
|
|
The appendix is left over from our revolutionary past and is no longer needed to help digest the types of plant matter we used to eat. when can the appendix actually be useful? |
Against disease |
|
|
What is respiration? |
Respiration is the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy |
|
|
What are some properties that metals have that non-metals don't? |
- Shininess -Good conductors of heat and electricity -High density (heavy for their size) -Ductile (drawn out into thin wires) -Malleable (flexible but hard to break) -Can easily lose electrons |
|
|
What are some properties that non-metals have that metals don't? |
-Dull appearance -Poor conductor of heat and electricity - Low density -Low melting point -Brittle (breaks easily) -Not ductile or malleable -Tends to gain electrons |
|
|
What raw materials are used to extract iron using carbon in a blast furnace? |
Iron ore (haematite) and coke |
|
|
How does a blast furnace work to remove iron using carbon? |
Hot air is blown into the furnace causing the coke to burn, forming carbon dioxide and releasing heat energy. This reduces the iron oxide in the ore to molten iron, which flows to the bottom of the furnace |
|
|
What is electrolysis? |
Electrolysis is splitting up substances using electricity |
|
|
What is an electrolyte? |
The substance being broken down |
|
|
What is an anode? |
A positive electrode |
|
|
What is a cathode? |
A negative electrode |
|
|
What is an electrode? |
A rod which conducts electricity |
|
|
What is an electrolyte? |
Solution or liquid containing ions |
|

Where are the anode, cathode, electrode and electrolyte located? |
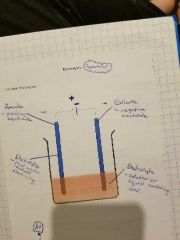
|
|
|
Do metals form at the anode or cathode? |
Cathode |
|
|
Why are electrodes often made from graphite? |
Cheap and conducts electricity |
|
|
What are the different types of electro magnetic waves? |
- Radio waves - Microwaves - Infrared waves - Visible light waves - Ultraviolet - X-rays - Gamma rays |
|
|
What is the function of root hair cells? |
To absorb water and mineral ions across the root hair cell |
|
|
What is transpiration? |
The loss of water vapour from a plant as it evaporates from leaves |
|
|
What does blood carry? |
Oxygen |
|
|
Where does the blood go to get oxygenated? |
The lungs |
|
|
Which side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs? |
The right side does this |
|
|
Where does water enter in a plant? |
The xylem vessels |
|
|
Where is water taken through to the plant? |
The stem |
|
|
The xylem cells branch into leaves where ?? |
Water enters the palisade and spongy cells where it is used for photosynthesis |
|
|
The water vapour from the plant evaporates out of the leaf through the stomata by diffusion. What is this loss of water called? |
Transpiration |
|
|
What speeds transportation? |
Heat Wind Low humidity Light |
|
|
What three things are used to help the heart pump blood through the body? |
Arteries, veins and capillaries |
|
|
What are the differences between arteries and veins? |
Arteries carry blood away from the hear and veins carry blood back to the heart |
|
|
What is the purpose of capillaries? |
To swap gasses. For example, they swap carbon dioxide into oxygen |
|
|
What do muscles take in and then waste? |
They take in oxygen and waste it as carbon dioxide |
|
|
What are the 4 chambers of the heart? |
The 2 atria and the 2 ventricles |
|
|
What are valves in the heart used for? |
To stop blood from splashing back and going the wrong way instead of the right way (like a door) |
|
|
Why does the blood return to the heart? |
To get pumped back to the lungs where it is oxygenated again |
|
|
What does the blood do as it travels around the body? |
Diffuses and exchanges gas and blood |
|
|
What blood vessels are oxgenated and which are not? |
Arteries - oxygenated Veins - deoxygenated Capillaries - both |
|
|
What direction do the blood vessels go in? |
Arteries - Away from the heart Veins - To the heart Capillaries - Both directions |
|
|
What is the pressure like in all these blood vessels? |
Arteries - high Veins - low Capillaries - low |
|
|
What blood vessels have valves? |
Arteries - no Veins - yes Capillaries - no |
|
|
What is a pulse rate? |
BPM - Beats Per Minute The number of times your heart beats per minute |
|
|
Why don't enzymes work if they change shape? |

As the first part states. Changing shape means it's molecule will no longer fit |
|
|
What do enzymes break down? |
A sugar called sucrose which is broken down into glucose and fructose |
|
|
Distance = ? |
Distance = speed multiplied by time |
|
|
What is an enzyme? |
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms |
|
|
What happens to enzymes when they overheat or when pH changes? |
Enzyme can change into a different shape and will no longer work (denature) |
|
|
What is the optimal temperature for human enzymes? |
37 degrees Celsius |
|
|
All enzymes only have one what? |
A shape of molecule to lock itself onto the enzyme active site or a certain spot that has been formed for that specific molecule |
|
|
What do enzymes break up? |
Enzymes breakup sucrose (a sugar) into glucose and fructose |
|
|
Speed = ? |
Speed = distance divided by time |
|
|
Time = ? |
Time = distance divided by speed |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
Multiple atoms sharing the same pairs of electrons with each other |
|
|
What do phloem tubes do in a plant? |
Transport food made in the leaves to other parts of the plant |
|
|
What is the journey that water takes to enter a plant? |
Water moves across the root and then enters the xylem vessels, up the stem then into the leaves |
|
|
What is water used for in the leaves? |
It is used for photosynthesis and leaves the leaf as water vapour out holes called stomata |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
Osmosis is the movement of water through a plasma membrane from a region of low solute concentration to high solute concentration |
|
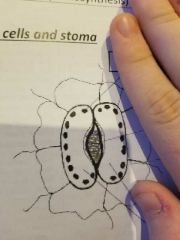
Where are the chloroplasts, stoma and guard cells? |
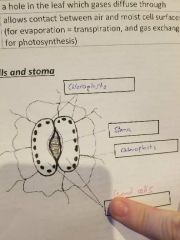
|
|
|
How many times does the blood pass through the heart during one conplete circulation of the body? |
Twice |
|
|
What do white blood cells do? |
Defend against disease. White blood cells are one of the main defenders in the immune system |
|
|
What is plasma? |
Plasma is a yellow liquid which transports nutrients and enzymes through the body. It also transports proteins and hormones |
|
|
What is cytoplasm? |
Cytoplasm is the jelly part of a cell surrounded by a thin lining |
|
|
What is the thin lining around a cytoplasm? |
The membrane |
|
|
What is the dark area inside of a cell? |
The nucleus |
|
|
What type of cells always have cell walls? |
Plant cells |
|
|
Do animal cells have cell walls? |
No |
|
|
What makes a plant look green? |
A substance called chlorophyll which are inside chloroplasts |
|
|
Most plants also contain a large fluid-filled area called a what? |
Vacuole |
|
|
What are transverse waves? |
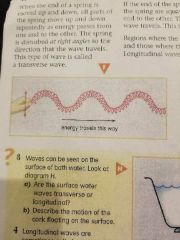
|
|
|
What are longitudinal waves? |

|
|
|
What is the amplitude? |
Maximum height of the wave measured from the middle |
|
|
What is the wavelength? |
Shortest distance between a point on a wave and the same point on the next wave. For example, the distance from one peak to the next peak |
|
|
What is the frequency? |
The number of waves passing a point per second. A frequency of 6 Hz would mean six waves pass a point every second |
|
|
What happens to a speed of light ray as it passes from glass to air? |
Speeds back up |
|
|
What is total internal reflection? |
Total internal reflection is when light reflects of the inside surface of the glass. |
|
|
What is the critical angle? |
The critical angle is the angle that achieves total internal reflection |
|
|
How does an endoscope work? |
It reflects (bounces) back to the doctors eye, giving the doctor a view of the patients stomach |
|
|
How do you remember the reactivity series? |
Please - Pottasium Stop - Sodium Calling - Calcium Me - Magnesium A - Aluminium Cute - Carbon Zebra - Zinc |
|
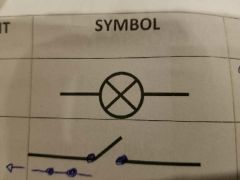
What symbol is this? |
Lamp |
|

What symbols are these? |
Open switch and closed switch |
|
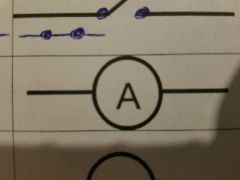
What symbol is this? |
An ammeter |
|
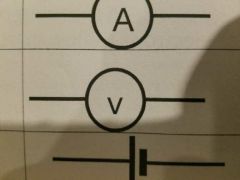
What symbol is this? |
Voltmeter |
|
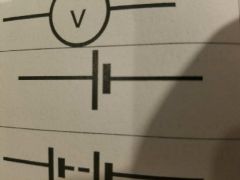
What symbol is this? |
Cell |
|
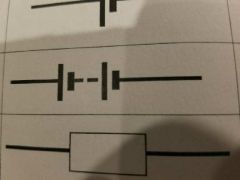
What symbol is this? |
Battery |
|
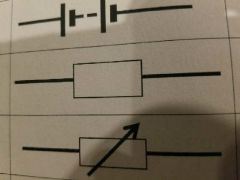
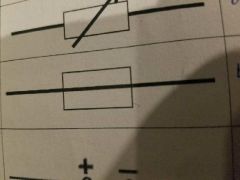
What symbol is this? |
Resistor |
|
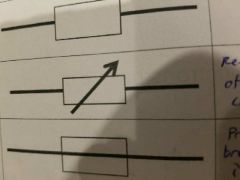
What symbol is this? |
Variable resistor |
|
What symbol is this? |
Fuse |
|

What symbol is this? |
Power pack |
|
|
What does a lamp do? |
Converts electricity energy into heat and light |
|
|
What does an open and closed switch do? |
Turns current on and off |
|
|
What is an ammeter? |
Measures current (in amperes/amps) |
|
|
What is a voltmeter? |
Measures voltage (volts) |
|
|
What does a cell do? |
Source of energy for the circuit |
|
|
What is a bettery? |
Source of energy for the circuit |
|
|
What is a resistor? |
Opposes current |
|
|
What is a variable resistor? |
Resistor whose valve of resistance can change |
|
|
What is a fuse? |
Protects circuit by breaking when current is too high |
|
|
What is a power pack? |
Source of energy for the circuit |
|
|
What is current measured in? |
Amperes |
|
|
Why do we need to eat food? |
To keep our cells alive |
|
|
What is an ion? |
An ion is a charged atom or molecule |
|
|
Why are ions charged? |
Because the number of electrons do not equal the number of protons in the atom or molecule |
|
|
Does an electron have a positive or negative charge? |
Negative charge |
|
|
Does a proton have a positive or negative charge? |
Positive charge |
|

Connect the letters with these answers |
A - hot air blast B - limestone, carbon and iron oxide C - waste gases D - slag E - molten iron |
|
|
What are horizontal rows called in the periodic table? |
Periods |
|
|
What are the vertical rows in a periodic table called? |
Groups |
|
|
An atom is ? by default |
Neutral. If not, it's an ion |
|
|
What can infrared be used for? |
TV remotes |
|
|
What can microwaves be used for? |
Heating food |
|
|
What is the use of ultraviolet? |
Can be used to kill microbes |
|
|
What are gamma rays used for? |
Gamma rays can kill cancer |
|
|
How can x-rays and ultraviolet rays. Be dangerous? |
X-rays can cause radiation sickness and ultraviolet speeds aging of the skin |
|
|
What colours is white light split into when entering a triangular prism? |
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet |
|
|
What wave cannot travel through a vacuum? |
Sound |
|
|
How do you calculate the nucleon number in an atom? |
The number of protons and neutrons in an atom |
|
|
How do you calculate the atomic number? |
The number of protons in an atom |
|
|
What is the difference between solid, liquid and gas particles? |
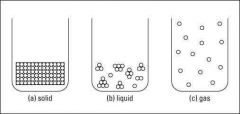
|

