![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does DNA stand for? |
Deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
DNA consists of four different building blocks called? |
Nucleotides |
|
|
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA? |
adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosis (A,T,G,C) |
|
|
Gene |
A segment of DNA that codes for a single protein. |
|
|
Mutation |
When DNA is copied incorrectly |
|
|
Genetics |
It is the study of how traits are inherited |
|
|
Mitosis |
The process that produces body cells, such as skin cells, that have a full set of chromosomes. |
|
|
Allele |
Each form of a gene for a particular trait |
|
|
Meiosis |
The process that produces sex cells, which have one-half the complete number of chromosomes. |
|
|
Dominant allele |
One whose trait always shows up when the organism has the allele. |
|
|
Recessive allele |
An allele whose trait is expressed in the phenotype only if the organism's alleles are both for the recessive trait. Its always hidden by the dominant allele. |
|
|
The combination of alleles that an organism has for a particular trait. |
Genotype |
|
|
The state in which the two alleles are different (Ff or fF) |
Heterozygous |
|
|
Homozygous |
The state in which both alleles are the same. (FF or ff) |
|
|
The generic characteristics of an organism that can be seen and measured. |
Phenotype |
|
|
Simple inheritance |
Inheritance that involves one set of alleles that produce only two kinds of phenotypes. |
|
|
A trait that requires only one dominant allele. |
Complete dominance |
|
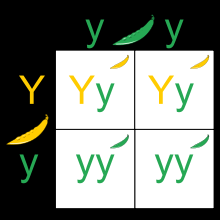
Punnett Square |
A table used to help predict the likelihood of genotypes that can be passed from parents to offspring |
|
|
Complex inheritance |
Patterns of inheritance that differ from simple patterns of inheritance. Traits results from the influence of multiple factors. |
|
|
Incomplete inheritance |
A situation in which neither alleles is dominant and the phenotype shows a blend of characteristics from both expressed alleles. |
|
|
When more than two allele forms exist for a trait |
Multiple alleles |
|
|
Codominance |
A pattern of inheritance where multiple alleles can have more than one dominant trait expressed. |
|
|
A trait that is determined by the alleles on a sex chromosome |
sex-linked trait |
|
|
When a parent organism carries only one allele for a certain trait |
Hemizygous |
|
|
Quality of some traits where several genes are involved, and those genes have multiple alleles. |
Polygenic |
|
|
Selective breeding |
A method of getting offspring with new abilities that are desired by having parents with certain traits reproduce. |
|
|
Genetic engineering |
The ability to select a gene from one kind of organism and insert it into the genetic make-up of another. |
|
|
Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) |
An organism that expresses a trait received from the DNA of another kind of living thing. |

