![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
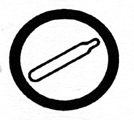
compressed _____
|
gas
|
|

________________ infectious material
|
bio-hazardous
|
|
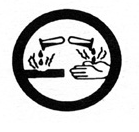
________________ material
|
corrosive
|
|

dangerously ____________ material
|
reactive
|
|

flammable and ___________ material
|
conbustible
|
|

____________ material
|
oxidizing
|
|

poisonous and _____________ material causing immediate and _______________ effects
|
infectious
serious |
|

______________ material causing other toxic effects
|
poisonous
|
|

|
bio-hazardous infectious material
|
|
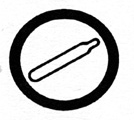
|
compressed gas
|
|
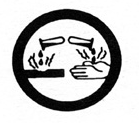
|
corrosive material
|
|

|
dangerously reactive material
|
|

|
flammable and combustible material
|
|

|
oxidizing material
|
|

|
poisonous and infectious material causing immediate and serious toxic effects
|
|

|
poisonous material causing other toxic effects
|
|
|
Describe the particles in a solid:
|
Particles are very close to one another, fixed in position, and they vibrate.
|
|
|
Describe the particles in a liquid:
|
All particles are still close, but now have enough space to slide past one another.
|
|
|
Describe the particles in a gas:
|
All particles are highly energetic and move freely to spread out in their container. Further heating gives particles even more kinetic energy.
|
|
|
_______________ is anything that has mass and volume. According to the kinetic molecular theory, all matter is made of very small ______________ that are constantly moving.
|
matter
particles |
|
|
___________ is the amount of matter in an object. The amount of space an object occupies is its ___________. The ratio of a material's mass to its volume is its _____________.
|
mass
volume density |
|
|
There are three _________ of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Each of these can change when _______________ is added or removed.
|
states
heat |
|
|
The temperature at which ice turns to water is the ________________. The temperature at which water turns to water vapour is the _____________.
|
melting point
boiling point |
|
|
_________________ describes how easily electricity or heat can move through a material.
|
conductivity
|
|
|
________ energy is the energy of movement.
|
kinetic
|
|
|
Particles of a ____________ are packed so tightly together that they can only vibrate in place. Particles of a ____________ are farther apart and can slide past each other. Particles of a ____________ are very far apart and move around freely and quickly.
|
solid
liquid gas |
|
|
The kinetic molecular theory describes what happens to the particles of matter during a _________________.
|
change of state
|
|
|
Oxygen and gold are examples of _____________________, which cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances.
|
elements
|
|
|
What is matter?
|
Any substance or object that has mass or volume.
|
|
|
What is mass?
|
The amount of matter in a substance or object.
|
|
|
What is volume?
|
The amount of space that an object takes up.
|
|
|
What is density?
|
The ratio of a material's mass to its volume.
|
|
|
What is conductivity?
|
How easily something lets electricity or heat move through it.
|
|
|
What is an element?
|
A pure substance whose particles cannot be broken down further and still keep their original properties.
|
|
|
Matter can undergo 2 types of changes: _________ change and _________ change.
|
physical
chemical |
|
|
99.99% of an atom's ______ is in the nucleus
|
mass
|
|
|
Electrons occupy _________ of the volume.
|
most
|
|
|
All of the ____________ charge in an atom is in the nucleus
|
positive
|
|
|
A _____________ change is when new ________ are formed while others are chemical bonds are _________. Is it reversible: _______.
|
chemical
chemicals/substances broken NO |
|
|
A _____________ change has _______ new substances formed. The _________ is changed but not chemical ________.
|
physical
no form composition |
|
|
___________ energy is when energy is ______________ (heat/light)
|
exothermic
released |
|
|
_______________ energy is energy that is _______
|
endothermic
absorbed |
|
|
What are the main points of the KMT?
(Kinetic Molecular Theory) |
1. Matter is made of small particles.
2. There is empty space between particles. 3. Particles are constantly moving. 4. Energy makes particles move. |
|
|
What is a physical change?
|
When a substance changes in form but not its chemical composition.
|
|
|
What is a chemical change?
|
It causes new substances to be formed.
|
|
|
Where is most of the mass in an atom?
|
The nucleus
|
|
|
Where is most of the volume in an atom?
|
The electrons
|
|
|
What is exothermic energy?
|
The process when energy is released.
|
|
|
What is endothermic energy?
|
Energy that is absorbed.
|
|
|
_____________ suggested that matter is made up of atoms.
|
Dalton
|
|
|
_____________ proposed that atoms contain negatively charged particles later called ________________.
|
Thomson
electrons |
|
|
______________ discovered the nucleus and its subatomic particles.
|
Rutherford
|
|
|
_______________ proposed that electrons are located in _________ around the nucleus.
|
Bohr
shells |
|
|
Electrons have different amounts of ________ and can jump back and forth between the energy levels.
|
energy
|
|
|
What is an atom?
|
The smallest particle of an element that has the same properties.
|
|
|
What are some subatomic particles?
|
electrons, protons, and neutrons
|
|
|
What did Dalton suggest?
|
That matter is made up of atoms.
|
|
|
What did Thomson propose?
|
That atoms contain electrons
|
|
|
What did Rutherford discover?
|
The nucleus
|
|
|
What did Bohr propose?
|
Electrons are located in shells around the nucleus.
|

