![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
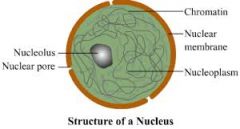
Nucleus (3 parts) -Chromatin -Nucleolus -Nuclear Membrane |
Functions: Contains the DNA of the cell. Nucleolus-Condense to form the Chromosomes. Nuclear Membrane-Center producers ribosomes (rRNA) and transfer RNA( RNA) |
|
|
|
Ribosome |
site of protein. "Amino acids are assembled into protein based on instructor given by mRNA" |
|
|
|
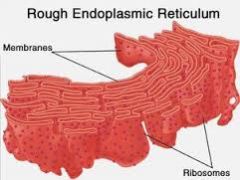
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Studded with ribosomes (rough apparence/texture) -Helps to assemble proteins (presence of ribosome) -Takes in proteins and helps prepare for transport throughout cell. |
|
|
|
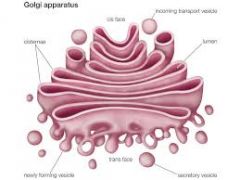
Golgi Apparatus |
Receives, sorts, modifies and packages macromolecules to different parts of cell. |
|
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Several functions based on specific cell.... Synthesize lipids (phospholipids and steroids) Detoxifies liver cells. Store calcium in muscle cells. |
|
|
|
Central Vacuole |
Store water, nutrients and waste products. Play a role in intractcelluar digestion, regulate tugor/water pressure (ability for plants to stand up)
|
|
|
|
Food Vacuole
|
Small, store water and nutrients temporarily |
|
|
|
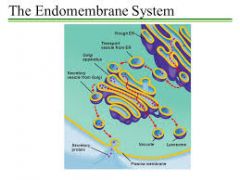
Secretory/ Transport Vesicle
|
Package for transportation materials around other cell, Transport macromolecules and from Golgi Apparatus. |
|
|
|
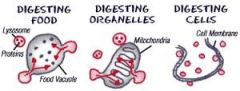
Lysosome
|
Contain hydrolytic enzymes that are involved in breaking down waste, organelle viruses, and bacteria
|
|
|
|
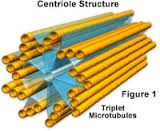
Centriole
|
Fused microtubules. Helps to organize cell division (creates spindles fibers used in a cell division
|
|
|
|
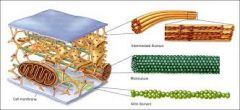
Cytoskeleton
|
Helps maintain cell shape. Help in cell motility ( internal movement of cell organelles
|
|
|
|
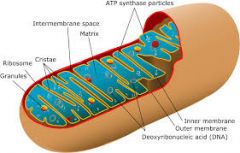
Mitochondria
|
site of cellular respiration. Convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convent ford the cell use (ATP) |
|
|
|
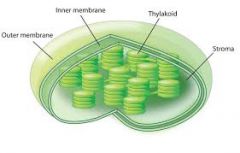
Chloroplast
|
site of photosynthesis. capture energy from the sunlight and convert it into food that contains chemical energy
|
|
|
|
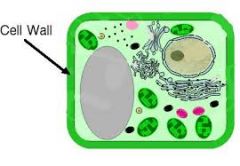
Cell Wall
|
Composed of cellulose. Rigid protective barrier that provides helps to maintain cell shape.
|
|
|
|
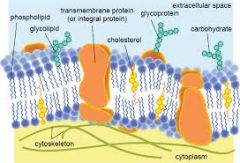
Cellular (Plasma) Membrane
|
Phospholipid bilayer. Flexible protective barrier that regulates what enters and leaves the cell.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

