![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a Gene? |
These control the traits an offspring will have and can also be hereditary. Genes are made up of genomes and are located on chromosomes. |
|
|
What is a Chromosome? |
Chromosomes: These are located in the nucleus of a cell, chromosomes are made of protein and are the makeup of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
|
|
Explain Dominant and Recessive Alleles |
Dominant alleles are often represented by a capital letter and usually are more inheritable than recessive alleles. Recessive alleles are represented by a lowercase letter. you can still inherit recessive traits. |
|
|
Explain the term Homozygous. |
Someone who is homozygous for a trait either has two dominant or two recessive alleles for a trait. |
|
|
Explain the term Heterozygous. |
Someone who is heterozygous for a trait has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait. |
|
|
What is a Genotype? |
Using punnet square symbols as an example the genotype would be the order of letters symbolising if a person is heterozygous or homozygous. |
|
|
What is a Phenotype? |
A phenotype is the individual trait itself, wether the person has it or not. |
|
|
What are the behaviour of chromosomes during mitosis? |
Prohpase: chromosomes condense Metaphase: Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell plate Anaphase: Chromosomes (now sister chromatids) split in half and go to opposite sides of the cell Telophase: Chromatids begin to decondense at opposite ends of the cell. Cytokinesis: the cell splits |
|
|
What is the difference between Meiosis and Mitosis? |
Meiosis has two rounds of genetic separation and cellular division while mitosis only has one of each. Mitosis produces 2 diploid cells 2n=23 in humans. While Miosis produces 4 daughter cells haploid in nature n=46. Meiosis is also responsible for our gamete or sex cell production. |
|
|
What happens during fertilization? |
Meiosis occurs, fertilization occurs by haploid and haploid coming together to create diploid, a zygote is formed and mitosis occurs. |
|
|
How do Chromosomes behave during fertilization? |
Meiosis has two phases. First, the homologous chromosomes pair up forming a tetrad (paired diads). This is when the maternal diploid pairs with the paternal diploid to form a tetrad. The non-sisters align together into a synaptonemal complex. This aligns the two at gene loci despite their having different alleles for the genes. Cross over proceeds. Phase 2 then persists as Mitosis again. |
|
|
What is the makeup of DNA? (including shape) |
DNA has a backbone made up of Deoxyribose sugars, Phosphates and a backbone to hold them together. There is two backbones and inbetween them are nitrogen bases attached to the sugars. Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. Adenine will pair with Thymine and Guanine Cytosine and vice versa. If one of these nitrogen bases do not pair correctly this results in mutation. The two backbones twist and condense drastically to make a double helix shape. |
|
|
What is the process of DNA replication? |
1. DNA is unzipped |
|
|
How are amino acids determined? |
Amino acids are determined by triplet codes of DNA nucleotides. each three nucleotides makes up an amino acid codon. A start codon is required for the reading of these codons to take place usually ATG also Methionine. then in order for them to stop being read a stop codon is put in place at the end. |
|
|
What is a few roles of proteins in the human body? |
1. Defense (antibodies) 2.Strength (muscle development) 3.Hormones (messages) 4.aiding in Digestion 5. Color (hair, eyes)
|
|
|
How do punnet squares determine probability of a trait? |
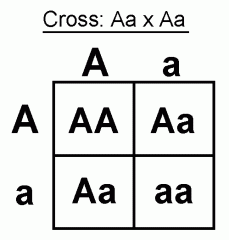
Punnet squares can determine probability of an offspring inheriting a trait via ratios accurate up to a quarter (25%-100%) We analyze and cross the parents genotype and look at the resulting phenotype. |
|
|
Genetic crosses for sex linked traits? |
We can make a regular punnet square as shown in the previous flashcard although our genotypes will now be X and Y chromosomes! and yes literally draw big X's and Y's. The father should receive an X and Y chromosome and the mother two X's then we put our other genotype (being the sex linked trait itself) in the top right corner of our chromosomes. The Y chromosome receives no gene as it cannot carry any. After this we do the punnet square as normal. |
|
|
What is Haemophilia? |
Haemophilia is a sex linked recessive disease causing low or no platelet levels in our blood. This causes our blood to be unable to clot and severe bleeding to occur. often the slightest cut can require medical attention. Our punnet symbol for Haemophilia would be Xh. |
|
|
What is Cystic Fibrosis? |
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder located on chromosome 7. Causing the lungs and intestines to fill up with mucus Cystic Fibrosis requires individuals to get their lungs pumped often. symptoms include weezing, shortness of breath, and bouts of panic. |
|
|
What is Sickle Cell Anemia? |
Sickle cell Anemia is another autosomal recessive disorder located on Chromosome 11. This disorder causes a low Hemoglobin level causing the red blood cells to take a sickle shape making it much more difficult for them to transport oxygen. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fainting. |
|
|
What is Huntington disease? |
Huntington disease is an autosomal dominant disorder located on the 4th chromosome. This disease causes brain degeneration and inevitably death. There is no cure for this disorder. |
|
|
Trisomy 21 |
Trisomy 21 or Downs syndrome is a disorder located on the 21st chromosome caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. There is a vast spectrum of intelligence involved in downs syndrome and inheritants of this disorder are not always on the lower end. Many savants or people who are extremely intelligent or gifted in a certain intellectual aspect had Trisomy 21. symptoms include stunted growth, Characteristic facial features and in most cases low IQ. |
|
|
What is Gene Splicing? |
1. A bacterial DNA plasmid is cut open 2. The desired gene is placed into the plasmid (ie insulin) 3. The recombinant DNA plasmid is placed into bacteria 4. Bacteria start producing the desired protein (insulin) |
|
|
What is Gene therapy? |
1.The cut gene is placed into a harmless virus 2. The desired gene that does not produce mucus is cut 3. The virus places the desired gene into each of the lung and digestive cells which stop producing mucus, The harmless virus is placed into the person with the disease. |
|
|
What are Genetically modified ordanisms? GMO. (tomato example) |
1. a desired gene is removed from an organism. (frost resistant fish) 2. The recombinant DNA is placed into a tomato seed and planted. 3. The DNA of a tomato plant is cut and the frost resistant gene is added to the DNA of a tomato. 4. Tomato plants resistant to frost are grown in colder climates. |
|
|
What is DNA fingerprinting? |
1.DNA is extracted. 2. DNA is cut into pieces by an enzyme. 3. DNA is placed onto electrophoresis gel and electric currents separate the DNA. 4. The patterns are analyzed and a match is determined. |
|
|
What is cloning? |
1.DNA is removed from a healthy adult organism 2. The DNA of a fertilized egg is removed and replaced with that organisms DNA 3. The fertilized egg is placed into the uterus of a female sheep. 4. A baby organism is born that is genetically identical to the healthy adult organism. |

