![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
148 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CHEMISTRY UNIT |
So much I don't understand... |
|
|
CHAPTER 1 - Atoms, Elements and Compounds |
... |
|
|
What does WHMIS stand for? |
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System |
|
|
Ernest Rutherford made which model of an atom? |
The Rutherford or solar system model. |
|
|
The solar system model featured what? |
A nucleus at the centre with electrons moving around it. |
|
|
Which model of an atom consisted of different energy levels? |
The Bohr model. |
|
|
The Bohr model showed what? |
Different energy levels with a limit of energy allowed on each. |
|
|
An atom consists of what? |
A nucleus, protons, electrons and neutrons. |
|
|
The nucleus of an atom contains what? |
Protons and neutrons. |
|
|
Electron dot diagrams are of what? |
The outer or last energy level. |
|
|
The groups or families on the periodic table run vertically or horizontally? |
Horizontally |
|
|
How many groups of families are there? |
18 |
|
|
How many periods are there on the periodic table? |
6 |
|
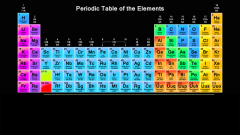
Pink represents which group of elements? |
Alkali metals |
|
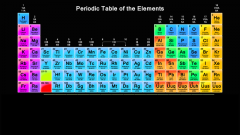
Purple represents which group of elements? |
Alkaline earth metals |
|
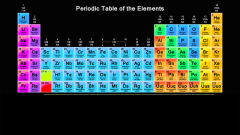
Light blue represents which group of elements? |
Metals |
|
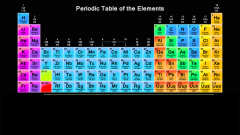
Green represents which group of elements? |
Metalloids |
|
Dark blue represents which group of elements? |
Non-metals |
|
Yellow represents which group of elements? |
Halogens |
|
Orange represents which group of elements? |
Noble gases |
|
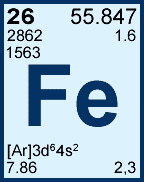
26 is what? |
The atomic number |
|
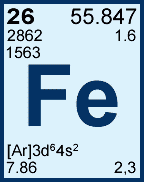
55.847 is what? |
The atomic mass |
|
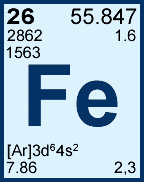
2 and 3 are what? |
The common ion charges (most common comes first) |
|
|
How do you determine the number of protons in an element? |
Number of protons is equal to the atomic number |
|
|
How do you determine the number of electrons? |
Number of electrons is equal to the number of protons |
|
|
How do you determine the number of neutrons? |
The atomic mass - the atomic number = the number of neutrons |
|
|
What is an isotope? |
An isotope is when an element has a varying amount of neutrons. |
|
|
What are valence electrons? |
It is the electrons on the outermost layer. They determine the reactivity and bonds of an element. |
|
|
What is the relation between the group number and the number of valence electrons? |
The group number is equal to the amount of valence electrons that and element has. |
|
|
What is the relation between the periods and electrons? |
Period number is equal to the number of occupied energy levels. |
|
|
What is an ion? |
Atoms or groupes of atoms that carry a charge. Electrons are either lost or gained to become stable. |
|
|
Why do ions form? |
To have a full outer layer/shell done by losing or gaining an electron. |
|
|
What is an anion? |
An ion with a negative charge |
|
|
What is a cation? |
An ion with a positive charge |
|
|
A metal ion has what charge? Does it accept or give up electrons? |
Metal ions have a positive charge and gives electrons |
|
|
A non-metal ion has what charge? Does accept or give up electrons? |
Non-metal ions have a negative charge and accept electrons |
|
|
How is a non-metal ion named? |
"-ide" is added to the end. EX: fluorine atom becomes a fluoride anion |
|
|
What is an ionic compound? |
Made of a metal and a non-metal. Binary ionic compounds are formed from just two elements. One or more atoms from the metal are transferred to the non-metal. They have opposite charges so they will attract each other. Held together by the ionic bonds in a repeating pattern called a crystal lattice. |
|
|
What is a molecular compound? |
Formed by two non-metals, no ions formed. Consist of independent groups of atoms that share electrons. Most molecules are compounds, when different types of atoms share electrons (EG: Co2) but some elements also exist as molecules. Joined by covalent bonds. |
|
|
What are single and double covalent bonds? |
Single covalent bond - One pair of electrons are shared, one from each atom Double covalent bond - When two atoms share two pairs of electrons |
|
|
Steps to drawing election dot diagrams for ionic bonds? |
1. Draw electron dot diagrams for the atoms 2. Show how the electron (s) move (s) to anion 3. Show the compound name, electron dots and charge |
|
|
Steps to drawing electron dot diagrams for covalent bonds? |
1. Draw electron dot diagrams for the atoms 2. Show how the electrons are shared, joining with circles 3. Show the structural formula |
|
|
CHAPTER 2 - Names, Formulas and Properties |
... |
|
|
What is a binary molecular compound? |
Two non-metals bonded covalently |
|
|
How do you write the formulas for molecular compounds? |
Write out the symbols in the same order and add subscripts to show the number of atoms. |
|
|
How do you write the the naming of binary molecular compounds? |
The first element remains the same. The ending of the second element changes to "-ide". Prefixes are added to both elements depending on the amount of atoms. If there is only one atom of the first element, no prefix is added. |
|
|
What are the prefixes used for naming binary molecular compounds? |
1. mono 2. di 3. tri 4. tetra 5. penta 6. hexa 7. hepta 8. octa 9. nona 10. deca |
|
|
What is a binary ionic compound? |
A positively charged metal and a negatively charged non-metal |
|
|
How do you write the formulas for binary ionic compounds? |
Write the symbols and charges for the negative and positive ions. Determine the lowest whole number ratio that will provide a net charge of zero. Use subscripts to indicate the number of ions needed to provide a net charge of zero. |
|
|
How do you name a binary ionic compound? |
The first ion remains the same. "-ide" is added to the end of the second ion. No references to the number of ions and no prefixes are added. |
|
|
What are multivalent metals? |
Metals that con form one or more ions - isotopes |
|
|
How do you name a binary ionic compound that has multivalent metals? |
Work backwards to determine the charge of the on the positive ion. Indicate there charge on the positive ion using roman numerals in brackets following the name. |
|
|
How do you write the formulas for binary compounds with multivalent compounds? |
use the stock system to determine which charge the positive ion has. Write the formula as usual. |
|
|
What are polyatomic ions? |
Two or more ions that act as a unit. |
|
|
How do you write the names of acids? |
Name the hydrogen compound as if it were ionic. Change the ionic name to an acid name using the right rule. |
|
|
Exeptions of writing acids? |
1. "sulf" acids - add "ur" after "sulf" 2. "phos" acids - add "or" after "phis" 3. COO acids - hydrogen atom is placed at the end |
|
|
How do you name bases? |
Named as any other ionic compound. Always finish with hydroxide |
|
|
Acids all contain? |
Hydrogen |
|
|
Acids react and release? |
Hydrogen ions |
|
|
Bases dissolve in whiter and release? |
Hydroxide ions |
|
|
Acid rages from --- to --- on the pH scale? |
0 to 7 |
|
|
What are the boiling and freezing points of water? |
100 degrees celcius and 0 degrees celcius. |
|
|
What happens to water's pressure when it freezes? |
It becomes very high and powerful |
|
|
What happens when electrical energy is run through water? |
Water is broken down into it's two elements. |
|
|
What is the angle between the two hydrogen atoms in a water molecule? |
105 degrees |
|
|
Water has a high --- |
Surface tension created by hydrogen bonding |
|
|
CHAPTER 3 - Chemical reactions |
... |
|
|
Evidence of chemical change? |
Heat, light, energy gain or loss. A new substance is formed. |
|
|
What is an endothermic reaction? |
When heat is taken during a reaction. Happens inside. |
|
|
What is an exothermic reaction? |
When heat is released during a reaction. Happens outside. |
|
|
What is a formation/composition/synthesis reactions? |
When two elements are joined to make a compound. |
|
|
What is a decomposition reaction? |
When a compound breaks into two elements. |
|
|
What is a single replacement reaction? |
C + AB = A + CB One element is switched out. |
|
|
What is a double replacement reaction? |
When two compounds switch out two elements. AB + CD = AC + BD |
|
|
What is a combustion reaction? |
Contains a compound made of hydrogen and carbon. Requires oxygen. Products are ALWAYS carbon dioxide and water vapour. |
|
|
How do you test for the presence of hydrogen? |
A burning wooden splint is lowered into a jar that contains an unknown gas. A popping noise will be heard if there is hydrogen. |
|
|
How do you test for the presence of oxygen? |
A glowing wooden splint is lowered into a jar that contains an unknown gas. If the splint glows brighter or reignites if oxygen is there. |
|
|
How do you test for the presence of carbon dioxide? |
A glowing wooden splint is lowered into a jar that contains an unknown gas. If there is carbon dioxide, the splint will completely extinguish. |
|
|
How do you test for water? |
Colbalt (II) chloride paper can be used to test for gaseous or liquid water. The paper will change from blue to pink. |
|
|
What is the mole? |
Unit used to me sure chemicals |
|
|
What is Avogadro's number? |
It is 6.02 x 10 to the power of 2. It is the number of atoms in 12g of carbon (with the isotope containing protons and 6 neutrons). It is the basis for the unit of moles. |
|
|
PHYSICS UNIT |
yay..... |
|
|
CHAPTER 4 - Thermal Energy and Work |
... |
|
|
Rules for determining a significant digits? |
1. All non-zero numbers are significant 2. Zeros that are between two significant digits are significant 3. Zeros to the left are NOT significant 4. Zeros to the right are significant IF there is a decimal point before of after them
|
|
|
How do you express a number using scientific notation? |
The decimal is placed after the first digit. If the number is less than one the exponent is negative. |
|
|
To remember when rounding? |
One number is allowed to be guessed. (something like that...) |
|
|
What is the current theory of heat? |
The kinetic molecular theory, developed by Count Rutherford. |
|
|
Current ideas about energy and work? |
Heat = energy Heat transfer from one object to another Julius Robert Mayer confirmed his observations (excellent work but poor presentation) James Prescott Joule presented the same concept and it was more polished (received credit) |
|
|
What is the first law of thermodynamics? |
Energy can not be created or destroyed. It can, however, be transferred or transformed into another form. |
|
|
What is the second law of thermodynamics? |
It is not possible for any process to remove thermal energy from a source and converted entirely into work. |
|
|
What is the basic principle of the steam engine? |
They transform thermal energy into mechanical energy. |
|
|
What was the first stem engine? Who invented it? |
Hero's stem engine. Invented by Hero. It was first used as a toy. |
|
|
Who invented the Savery Steam Engine? What was it's main purpose? |
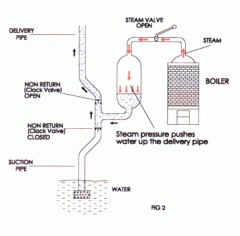
Savery's (the inventor) was the first practical steam engine used to pump water from the mines in 1698. |
|
|
What is the basic idea of Newcomen' Steam engine? |
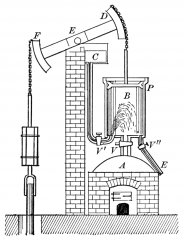
Relies on atmospheric pressure to push a piston down and to push water up and out of the mine. |
|
|
What is the basic idea of Watt's steam engine? |
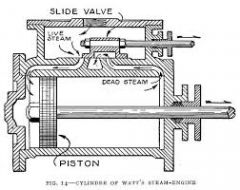
Watt is renowned for his improvements to the steam engine. He designed a separate condensing chamber for the steam which prevents enormous loss of steam . Watt adapted his engine to perform more than just pumping water. |
|
|
How does the internal combustion engine generally work? |
Study page!!!! |
|
|
What is the most used energy source in Canada? |
Conventional oil (includes shale and oil sands) |
|
|
What are the two kinds of energy sources? |
Renewable and non-renewable |
|
|
What are the four main energy sources in Canada? |
1. Fossil fuel burning plants 2. Nuclear power plants 3. Hydro-electric generating stations 4. Wind energy |
|
|
CHAPTER 5 - Energy and Motion |
... |
|
|
What is a scalar quantity? |
Describes magnitude - size or amount
EX: distance, speed, time, temperature, mass |
|
|
What is a vector quantity? |
Describes magnitude AND direction.
EX: velocity, displacement, position |
|
|
What is position? |
A vector quantity that describes a specific point relative to a reference point |
|
|
What is the distance between distance and displacement? |
Distance: A scalar quantity that describes the length between two points.
Displacement: A vector quantity that describes a straight line distance. |
|
|
What is the distance between speed and velocity? |
Speed: A distance traveled by an object divided by the time interval
Velocity: The displacement of an object divided by the time interval |
|
|
What is uniform motion? |
It describes a constant velocity. Represented by a straight line on a posistion-time graph. |
|
|
How is accreted motion represented on a distance-time graph? |
By a curved line |
|
|
How are the motions represented on the two different graphs? |
Position-time graph: Uniform is straight and acceleration is curved.
Velocity-time graph: Both are straight |
|
|
What are the four types of potential energy? |
1. Elastic Potential energy - elastics, springs 2. Chemical Potential energy - photosynthesis 3. Nuclear Potential energy - fusion, fission 4. Gravitational Potential energy
|
|
|
CHAPTER 6 - Energy Conversions and Efficiency |
There's only one question.... |
|
|
What is efficiency? |
The percentage of energy that is converted into work. |
|
|
UNIT 3 - Cycling of Matter in Living Systems |
Great.... |
|
|
CHAPTER 7 - The Basis of Life |
... |
|
|
What is biogenesis and abiogenesis? |
Biogenesis - Living
Abiogenesis - Not living |
|
|
What are the 3 cell theory statements? |
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest functional unit of life. It is the basis of life 3. All cells are produced from other cells |
|
|
How do you calculate the size of something viewed under the microscope? |
Know the diameter of the field go view. Estimate the fit number that could fit across the diameter. Divide the field of view by the fit number. |
|
|
What organelles are different between plant and animal cells? |
Vacuole - Present in both but differ in amount and size Chloroplasts - Present only in plant cells Cell wall - Present only in plant cells Centrioles - Mainly present in animals and some plants |
|
|
CHAPTER 8 - Dynamic Cells |
... |
|
|
What is concentration and concentration gradient? |
Concentration - The amount of solute in a solution
Concentration gradient - The difference of concentration between two areas or two solutions. |
|
|
What is passive transport? |
Transportation across a membrane using only kinetic energy. Only happens down a concentration gradient. |
|
|
What is diffusion? |
Small particles moving through the membrane pores. Moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration. |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
Water moving through the cell membrane. |
|
|
What is facilitated diffusion? |
Small particles moving through the membrane with the help of currier proteins. |
|
|
What is active transport? |
Requires ATP and kinetic energy. Materials moving across the membrane with the help of carrier molecules. |
|
|
What is endocytosis? |
When the membrane engulfs the material. |
|
|
What is exocytosis? |
When the membrane expels materials. |
|
|
What is phagocytosis and pinocytosis? |
Pinocytosis - water and small ions moving into the cell (drinking)
Phagocytosis - larger chunks moving into the cell (eating) |
|
|
What is hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic? |
Hypotonic - Having a concentration of solutes low enough to lose water across a membrane to another solution.
Hypertonic - Having a concentration of solutes high enough to gain water across a selectively permeable membrane from another solution.
Isotonic - Having the same solute and water concentration of that of the other solution on the other side of the membrane.
|
|
|
CHAPTER 9 - Plants |
kill me.... |
|
|
What is cell resperation? |
Opposite of photosynthesis |
|
|
What is the xylem? |
Dead when mature. Made of two conducting cells, the tracheids and vessel elements. |
|
|
What does the xylem do? |
It carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves. |
|
|
How is material transported using adhesion and cohesion? |
Adhesion and cohesions happens inside the xylem. Water is pulled up due to transpiration. |
|
|
What is the phloem? |
Contains a sieve tube and companion cells. Carries phloem sap (sugar, nutrients and water) down the stem and roots. |
|
|
What does the phloem do? |
Carries phloem sap (sugar, nutrients and water) down the stem and roots. |
|
|
How is material transported in the phloem? |
Pressure is created in the tube which forces the fluid downwards. Source to sink |
|
|
What is a tropism? |
A growth response |
|
|
What is phototropism? |
The growth of a plant towards the light |
|
|
What is geotropism/gravitropism? |
The plant growth in response to gravity |
|
|
What are auxins? |
A plant growth hormone produced in plant tips that trigger tropisms. |
|
|
UNIT 4 - Energy Flow in Global Systems |
I actually kinda know this crap |
|
|
CHAPTER 10 - Solar Energy and Climates |
... |
|
|
What is an open, closed and isolated system? |
Open - Allow energy and matter to cross
Closed - Allows only energy to cross
Isolated - Energy and matter can not cross |
|
|
What is inside of a biosphere? |
A thin layer of air (atmosphere), land (limo sphere), and water (hydrosphere) |
|
|
What is the difference between climate and weather? |
Climate - long-term patterns in temperature, pressure, humidity and precipitation
Weather - the conditions of temperature, pressure, humidity and precipitation |
|
|
CHAPTER 11 - Climate and Biomes |
.... |
|
|
What are the natural causes of climate change? |
1. Earth's tilt and orbit 2. Continental drift 3. Weathering 4. Catastrophic events 5. Feedback |
|
|
How do you remember the elements that only exits in molecular form? |
I'll bring clay for our new house 4 pouring 8 sidewalk block. |

