![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition: Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE)
|
An ODE is an expression which describes a relationship between a function of one variable and its derivative. The solution to a differential equation is a function which satisfies that relationship.
|
|
|
Definition: Autonomous Differential Equation (Time-Independent)
|
If the expression F(y,t) in the ODE (dy/dt) = F(y,t) does not specifically involve t, then it is an autonomous or time-independent differential equation.
|
|
|
Definition: Non-Autonomous Differential Equation (Time-Dependent)
|
If a differential equation specifically involves t (i.e. it must be written as (dy/dt) = F(y,t), then it is non-autonomous or time-dependent.
|
|
|
Definition: First Order Differential Equation
|
A differential equation which only involves the first derivative of the unknown function.
|
|
|
Definition: ith Order Differential Equation
|
An equation which involves derivatives up to and including the ith.
|
|
|
Definition: Partial Differential Equations
|
Partial differential equations describe a relationship between a function of several variables and its partial derivatives.
|
|
|
Definition: Initial Value Problem
|

|
|
|
MC: The solution to a differential equation is: a) a function; b) a number
|
a) The solution to a differential equation is a function.
|
|
|
What is a differential equation that has a constant function as its solution called?
|
1) a steady-state, 2) a stationary solution, 3) a stationary point, 4) a rest point, or 5) an equilibrium
|
|
|
Definition: General Solution of a Differential Equation
|
A parameterized solution y(t,k) of a differential equation dy/dt = F(y,t) is called a general solution if every solution of the differential equation can be achieved by letting k take on different values.
|
|
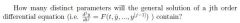
|

|
|
|
How do you solve an ordinary differential equation?
|
Step 1: Guess a solution
Step 2: Differentiate the solution with respect to t Step 3: Check if derivative satisfies original differential equation |
|
|
Definition: Homogeneous Differential Equation
|

|
|
|
Definition: Non-Homogeneous Differential Equation
|

|
|
|
Separable Differential Equation
|
The differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x,y) is called separable, if f(x,y) = h(x)g(y); that is, if dy/dx = h(x)g(x).
|
|

|

|
|
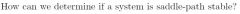
|

|

