![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 5 axes in psychiatric diagnosis?
|
Axis I: the clinical psychiatric disorder (includes substance abuse and childhood disorders)
Axis II: Personality disorder, retardation Axis III: All other medical illnesses Axis IV: Psychosocial and environmental stressors Axis V: Global Assessment of Function (number from 0 – 100 reflecting a person’s general level of function) |
|
|
What are the 3 Ds that define mental illness?
|
3 Ds: dysfunction, distress, disability
“A clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with present distress (e.g. a painful symptom) or disability (i.e. impairment in one or more important areas of functioning) or with a significant increased risk of suffering death, pain, disability, or an important loss of freedom.” |
|
|
What is Schneiderian hallucination?
|
Schneiderian hallucination is an overheard (mumbling) conversation (muffled voices). If you ask the pt what they heard, they would say they couldn’t make it out, although they may be able to describe other attributes of the conversation.
|
|
|
What is the role of dopamine in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia?
|
• Excess dopamine in the mesolimbic dopamine tract may be responsible for the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
• Decreased dopamine in the mesocortical tract may be responsible for the negative and cognitive symptoms. |
|
|
What are the positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
|
• Hallucinations:
o Auditory, visual, tactile o gustatory, or olfactory • Delusions: o Fixed, false beliefs o (bizarre versus non-bizarre) • Disorganization of thoughts o and behavior |
|
|
What are the negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
|
• Affective flattening
o Intonation of voice o Facial expression o gestures • Alogia (poverty of speech) • Anhedonia (inability to enjoy things) • Avolition (inability to act) • Social withdrawal * Apathy * Poor hygiene |
|
|
What forms of cognitive impairment would you expect to see in a patient with schizophrenia?
|
• Attention
• Memory (working) • Visuospatial perception • Executive function (cognitive control) |
|
|
What are the subtypes of schizophrenia?
|
• Paranoid (primarily delusions and/or auditory hallucinations)
• Disorganized (disorganized thoughts and/or behavior) • Residual (negative symptoms or attenuated positive symptoms) • Undifferentiated (variable) • Catatonic (mutism and/or negativism) |
|
|
What is the most important prognostic feature in schizophrenia?
|
Most important prognostic feature is gender. Being male is associated with a poor prognosis.
|
|
|
Blockage of dopamine in which pathway can produce the negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
|
Mesocortical
|
|
|
How does efficacy and potency vary from anti-psychotic to anti-psychotic?
|
• All antipsychotics have same/similar efficacy (different potency) for positive symptoms in schizophrenia, except clozapine (which has a greater efficacy)
• Potency is related to affinity for the dopamine receptor (i.e., greater potency = greater affinity for D2 receptors) |
|
|
How does one treat Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome?
|
Treatment is supportive (can use dopamine agonists like bromocriptine and muscle relaxants like dantroline)
|
|
|
Blocking dopamine in which brain pathway causes extrapyramidal side effects (EPS)?
|
Nigrostriatal dopamine pathway
|
|
|
Blocking dopamine in which brain pathway causes a decrease in hallucinations and delusions?
|
Mesolimbic dopamine pathway
|
|
|
Blocking dopamine in which brain pathway causes a worsening of “secondary” negative symptoms?
|
Mesocortical dopamine pathway
|
|
|
Blocking dopamine in which brain pathway causes increased prolactin secretion?
|
Tuberoinfundibular dopamine pathway
|
|
|
What are key differences between typical and atypical antipsychotics?
|
• Atypical:
o Less movement-related disorders o Blocks both serotonin and dopamine (more serotonin than dopamine) |
|
|
Blockade of which neurotransmitter causes hypotension (including orthostatic hypotension), dizziness, and sedation?
|
Alpha-1 adrenergic blockade
|
|
|
Blockade of which neurotransmitter causes sedation and weight gain?
|
H1 histaminic blockade
|
|
|
Blockade of which neurotransmitter causes memory and cognitive deficits, xerostomia, constipation, tachycardia, blurred vision, urinary retention, and hyperthermia?
|
Anticholinergic (muscarinic) blockade
|
|
|
How would you treat tardive dyskinesia, the long term (often permanent) neurological impairment that is characterized by involuntary dyskinetic movements?
|
Treat Tardive Dyskinesia with anticholinergics (benztropine, diphenhydramine)
|
|
|
What are the adverse drug reactions related to dopamine blockade?
|
• Tardive dyskinesia
• Dystonic reactions • Drug-induced parkinsonism • Akathesia • Hyperprolactinemia |
|
|
What are all the first generation antipsychotics that Cronenwett mentioned in his syllabus?
|
1. Haloperidol
2. Fluphenazine 3. Perphenazine 4. Thiothixine 5. Chlorpromazine 6. Thioridazine |
|
|
Which second-generation antipsychotic has the greatest efficacy, and what is an serious adverse effect that it can cause?
|
Clozapine can cause agranulocytosis (1-2% incidence)—can be fatal. Clozapine should be discontinued if WBC drops below 3,000/mcL or 50% of the patient’s normal level.
Not associated with Tardive Dyskinesia, and in some cases can actually improve TD |
|
|
Which second generation antipsychotics have reported new onset DM2?
|
• Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
• Quetiapine (Seroquel) |
|
|
Which second generation antipsychotic has a black box warning that it can increase the QT interval (thus, some recommend having baseline EKG before administration)?
|
Ziprasidone
|
|
|
Which antipsychotics cause the least disturbances in metabolic profiles?
|
• Aripiprazole
• Ziprasidone |
|
|
What is the difference between efficacy and potency?
|
• Efficacy is the ability to achieve a desired clinical effect.
• Potency is a measure of how much medication is needed to achieve the desired efficacy, and it is related to the affinity of a drug for its targeted receptor. |
|
|
What is an example of negative reinforcement?
|
If a person experiences anxiety in a situation and leaving the situation decreases anxiety, the avoidance behavior will be increased.
|
|
|
What is an example of positive reinforcement?
|
• An example of positive reinforcement could be the increased attention one might receive from a spouse or a friend when exhibiting fearful behavior.
• Positive reinforcement increases the frequency of a behavior by pairing it with a positive stimulus. |
|
|
What symptoms are associated with a panic attack?
|
• Discrete period of discomfort in which symptoms peak within 10 minutes.
• Must have four of the following: – heart palpitations (69%*) – Sweating or trembling (89%) – Numbness (65%) – sensation of shortness of breath (80%) – chest pain (69%) – sensation of choking (54%) – Dizziness (82%) – abdominal distress (NA) – derealization or depersonalization (80) – fear of dying or losing control (81%) |
|
|
What drug(s) has/have proven effectiveness in preventing suicide?
|
• Lithium
o Lithium has anti-aggressive and anti-impulsive effects • Clozapine |
|
|
What symptoms are associated with alcohol withdrawal?
|
• Two or more of the following, developing in hours to days:
– Autonomic hyperactivity (sweating,HR, BP) – Increased hand tremor – Insomnia – Nausea or vomiting – Transient tactile, visual, auditory hallucinations or illusions – Agitation, anxiety – Grand mal seizures |
|
|
What IQ qualifies for intellectual disability?
|
<70 (at least 2 standard deviations below the mean)
|
|
|
What severity of intellectual disability (ID) makes up the bulk of that population?
|
“Mild” ID makes up 75% of ID population
|
|
|
What disease causes the most common inherited form of severe intellectual disability (ID)?
|
Fragile X Syndrome
|
|
|
What neurotransmitters are involved in currently available antidepressants?
|
All currently approved antidepressants increase either:
• Serotonergic • Noradrenergic • Dopaminergic Drive |
|
|
What is cyclothymia?
|
• Recurrent milder depressive symptoms and hypomanias
• Analogous to dysthymia but with periods of hypomania • Does not have fully syndromal major depressive episode during first 2 years |
|
|
T/F: response to medication is diagnostic of ADHD.
|
F: response to medicine is NOT diagnostic of ADHD
|
|
|
What are the subtypes of ADHD?
|
• Inattentive Type
• Hyperactive/Impulsive Type • Combined Type • ADHD Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat ADHD?
|
• Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
• Amphetamines |
|
|
When does regression occur in autistic children?
|
One-third of autistic patients present with regression at 15-18 months after relatively normal development.
|
|
|
Which antidepressant has a 2-3 fold increased risk of teratogenicity compared to other antidepressants?
|
Paroxetine has a 2-3 fold increased risk of teratogenicity, specifically a ventral septal defect.
|
|
|
What is the serotonin syndrome?
|
The serotonin syndrome is a serious and potentially fatal syndrome of serotonin overstimulation characterized by:
1) Diarrhea 2) Restlessness 3) Extreme agitation, hyperreflexia, autonomic instability 4) Myoclonus, seizures, hyperthermia, shivering and rigidity 5) Delirium, coma, confusion, cardiovascular collapse It can occur if SSRIs are co-administered with monoamine oxidase inhibitors |
|
|
In what antidepressant medication is it important to follow patients’ blood pressures?
|
• SNRIs (Venlafaxine, Desvenlafaxine, Duuloxetine)
• A potential side effect is increased diastolic blood pressure |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of bupropion?
|
• Bupropion offers weak norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibition, but its hydroxylated active metabolite is responsible for most of the therapeutic effect.
• Ultimately, the medication increases dopamine and NE turnover in the CNS. • It is considered an activating antidepressant that also has use for ADHD |
|
|
Which antidepressants have no sexual side effects?
|
• Bupropion
• Mirtazapine (antagonist at presynaptic inhibitory alpha2 autoreceptors |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of trazodone?
|
• Trazodone inhibits serotonin reuptake and blocks 5HT2 serotonin and alpha1 adrenergic receptors
• It’s not particularly effective as an antidepressant but is used as a sleep aid due to its sedating properties |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of aripiprazole in anti-depressant action?
|
• Although aripiprazole (abilify) is an antipsychotic, it’s used as an add-on to SSRIs in treatment-resistant patienst with mood or anxiety disorders.
• It partially agonizes (modulates) dopamine D2 receptors and serotonin 5HT1A receptors • Antagonizes 5-HT2A receptors |
|
|
Which class of antidepressants are notorious for their narrow therapeutic window and ease of overdose?
|
Tricyclic antidepressants:
• Tertiary o Amitriptyline o Clomipramine o Imipramine • Secondary o Desipramine o Nortriptyline MOA: block reuptake of serotonin and NE and to a lesser extent, dopamine. They also block muscarinic cholinergic receptors, H1 histamine receptors, and alpha 1 adrenergic receptors, accounting for their side effects. Note: these drugs can slow cardiac conduction and stop your heart in an overdose |
|
|
What drugs are the monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and what food compound should be avoided when taking these drugs?
|
• The monoamine oxidase inhibitors are phenelzine and tranylcypromine.
• MOA = inhibits monoamine oxidase, which catabolizes intracellular monoamines (e.g., dopamine, NE, serotonin, tyramine) • One should avoid foods with tyramine, as this can lead to excessive accumulation of NE. |
|
|
What antidepressant should be avoided for people with anxiety?
|
• Bupropion has activating effects and shouldn’t be used in people with anxiety.
• It can also cause grand mal seizures. |
|
|
What mood stabilizer can cause hypothyroidism?
|
Lithium causes hypothyroidism in 5-10% of patients, which can be treated with supplemental thyroid hormone.
|
|
|
How long does it take for lithium to work as a mood stabilizer, and in what percentage of patients is it effective?
|
• Lithium can take 1-3 weeks, and thus it’s not used for treating acute mania
• It’s effective in about 50% of patients. |
|
|
What side effects can valproic acid cause, and what tests should be ordered for patients put on valproic acid?
|
Side effects:
• Weight gain • Hepatotoxicity (not very common) • Pancreatitis (rare) • GI (abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting) • Sedation, tremor, ataxia, alopecia • Thrombocytopenia (rarely) Due to these side effects, LFTs and CBCs are checked regularly |
|
|
Which mood stabilizing drug can lead to the development of a rash that can progress to Steven-Johnson syndrome (a life-threatening condition in which cell death causes the epidermis to separate from the dermis)?
|
Lamotrigine causes rash in about 10% of patients. 1-10% of those who develop rash can then get Steven Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Occurs more commonly in children.
|
|
|
What possible danger could occur from the combined use of valproic acid and lamotrigine?
|
Valproic acid inhibits lamotrigine metabolism, so when they’re used together, lamotrigine is given at a lower dose and titrated up more slowly.
|
|
|
What drug interactions should you be careful about with the use of carbamazepine?
|
Carbamazepine induces heaptic P450 enzymes, so it can decrease other medications, for example:
• Oral contraceptives • Warfarin • Other anticonvulsants |
|
|
Which mood stabilizers should be avoided in pregnancy?
|
Carbamazepine and valproic acid both increase the risk of neural tube defects and other birth defects and thus should be avoided in pregnancy.
Furthermore, lithium increases the risk for Ebstein’s anomaly (characterized by a dysplastic tricuspid valve) as a birth defect. |
|
|
What are adverse effects that lithium can have on the following: kidney, nervous system, heart?
|
• Kidney: polyuria and polydipsia, which can progress to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Chornic lithium use can also lead to interstitial nephritis and impaired glomerular function.
• Nervous system: sedation and impaired cognition, tremor (can be treated with beta-blockers), ataxia and dysarthria • Heart: cardiac conduction problems (e.g., sinus bradycardia, SA node blockade), AV blockade and ventricular irritability |
|
|
What are important side effects of carbamazepine?
|
• Weight gain
• Sedation • Ataxia • Rash • Agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia (rare but very serious) • Hepatitis • Hyponatremia/SIADH • Hypersensitivity rash LFTs, CBCs and basic chemistries are checked regularly |
|
|
What is an ideal therapeutic range for Li use?
|
0.6-1.2 mEq/L (1.0 is ideal)
|
|
|
How would you characterize someone with schizotypal personality disorder?
|
• M [2] Magical thinking or odd beliefs
• E [31 Experiences unusual perceptions • P [5] Paranoid ideation • E [71 Eccentric behavior or appearance • C [6] Constricted (or inappropriate) affect • U [4] Unusual (odd) thinking and speech • L [8] Lacks close friends • I [1] Ideas of reference • A [9] Anxiety in social situations • R Rule out psychotic disorders and pervasive develop-mental disorder |
|
|
What would you call antisocial personality disorder if it is in someone who’s 14 years old?
|
Conduct disorder (before the age of 15)
|
|
|
How would you characterize borderline disorder?
|
• A [1]Abandonment
• M [6] Mood instability (marked reactivity of mood) • S [5] Suicidal (or self-mutilating) behavior • U [2] Unstable and intense relationships • I [4] Impulsivity (in two potentially self-damaging areas) • C [81 Control of anger • I [3] Identity disturbance • D [9] Dissociative (or paranoid) symptoms that are transient and stress related • E [7] Emptiness (chronic feelings of) |
|
|
How would you characterize avoidant personality disorder?
|
• C [2] Certainty (of being liked required before willing to get involved with others)
• R [4] Rejection (or criticism) preoccupies ones' thoughts in social situations • I [3] Intimate relationships (restraint in intimate relation-ships due to fear of being shamed) • N [5] New interpersonal relationships (is inhibited in) • G [1] Gets around occupational activity (involving significant interpersonal contact) • E [7] Embarrassment (potential) prevents new activity or taking personal risks • S [6] Self viewed (as unappealing, inept, or inferior) |
|
|
What is the difference between a factitious illness and malingering?
|
• Patients with factitious disorders create the presence of a medical condition, either by some active means like ingesting a toxic agent or falsifying lab studies or by deliberately withholding care from an existing illness to worsen it (e.g., not taking insulin for Type I DM). The motivation is unconscious or unknown.
• Malingering is similar to factitious illness in that the patient is aware that they’re making it up, but malingering patients do it for an instrumental end of which they are aware (e.g., avoiding incarceration). |
|
|
Deficits in what side of the brain can produce attention-deficits?
|
Right sided lesions tend to affect attention most profoundly (it’s the dominant center for attention)
|
|
|
What are the components of the CAM test for delirium?
|
1. Acute onset and fluctuating course
o Is there evidence of an acute change in mental status from the patients baseline? Did the (abnormal) behavior fluctuate during the day, that is, tend to come and go, or increase and decrease in severity? Test: observation 2. Inattention o Did the patient have difficulty focusing attention, for example, being easily distractible, or having difficulty keeping track of what was said Test: continuous performance test 3. Disorganized thinking o Was the patient’s thinking disorganized or incoherent, such as rambling or irrelevant conversation, unclear or illogical flow of ideas, or unpredictable switching from subject to subject? Test: Yes/No questions 4. Rating of consciousness • Alert (normal) • Vigilant (hyperalert) • Lethargic (drowsy, easily arousable) • Stuporous (difficult to arouse) • Coma (unarousable) |
|
|
What motives for drinking are most associated with increased risk for alcohol dependence/abuse?
|
Coping motives (forget problems, cheer up)
Enhancement motives (get high, fun) |
|
|
How does the metabolism of the long-acting benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, flurazepam) differ from that of the short-acting agents (e.g., lorazepam, oxazepam, temazepam -- LOT)?
|
The short acting, LOT, agents do not have active metabolites, whereas the long-acting agents do.
Ultimately, all of the drugs are subjected to glucuronide conjugation (a Phase II reaction) and then excreted in the urine. |
|
|
In what kinds of patients can benzodiazepines be patient (i.e., what underlying medical morbidities)?
|
COPD
Obstructive Sleep Apnea |
|
|
What clinical efficacy do the ZAZOLES have? Remeber that the ZAZOLES are: Zaleplon (Sonata), Zolpidem (Ambien), Eszopiclone (Lunesta)?
|
The ZAZOLES reduce th number of awakenings and can restore sleep architecture to normal. They bind to the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABA-A receptor but are not benzodiazepines structurally.
|
|
|
What is the first line drug for treating ethanol withdrawal?
|
Benzodiazepines
|
|
|
What areas of the brain are typically affected in delirium, and what neurotransmitter is often decreased?
|
Right-sided and bilateral lesions are typical for delirium, and the neurotransmitter that's decreased is Acetylcholine.
|
|
|
What is the most common change in the EEG in a confusional state?
|
Slowing
|
|
|
What are the 4 basic questions to keep in mind when diagnosing a delirium?
|
1. Acute onset and fluctuating course.
2. Inattention 3. Disorganized thinking 4. Altered level of consciousness (either lethargic or hypervigilant) |
|
|
What are the 2 pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease?
|
1. Beta-amyloid plaques (consisting of beta-amyloid protein, degenerated synapses, axons, and dendrites)
2. Neurofibrillary tangles (consisting predominantly of a hyperphosphorylated form of the tau protein, which is a microtubule associated protein) |
|
|
What are the core features of Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)?
|
1. Fluctuaqtions in attention and alertness
2. Motor changes of Parkinsonism 3. Recurrent visual hallucinations |
|
|
What are some diagnostic criteria for ADHD?
|
1. Symptoms causing impairment present before age 7 (DSM 5 - before age 12)
2. Impairment present in 2 or more settings 3. Clinically significant impairment in at least one domain of functioning: a. Social b. Academic c. Occupational |
|
|
What areas are impaired in autism disorder?
|
Social relatedness/interaction
Communication Restricted/Repetitive behavior, interests, activities |
|
|
What changes in the eye allow distance vision versus near vision?
|
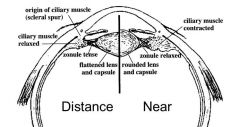
The ciliary muscle relaxes for distance vision so that the lens remains flat, whereas the ciliary muscle contracts to round up the lens for near vision.
|
|
|
What's the weakest point of the eye?
|
Lamina cribrosa
|
|
|
What is uveitis?
|
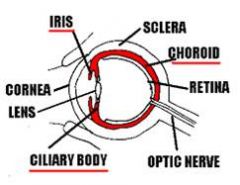
Uveitis is inflammation of the iris, ciliary body, or choroid.
|
|
|
What's the difference between dry and wet age-related macular degeneration?
|
Dry AMD is non-exudative macular degeneration
Wet AMD is exudative macular degeneration |
|
|
How do you define temperament, character, and psyche?
|
Temperament: innate biases in the modulation of behavioral responses to external stimuli; seen early in life
50% of variance is genetic Character: self-concept and interpersonal relatedness Psyche: consciousness, self-awareness, and spirit |

