![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are weld sizes indicated? |
Throat Thickness - represented by the letter 'a' |
|
|
What is the numerical representation for MIG welding? |
131 |
|
|
What is the numerical representation for MIG welding? |
MAG welding
|
|

Describe 'Ohm's Law'
|
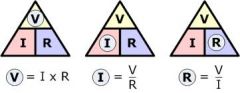
V = I x R (voltage = current x resistance)
or I = V/ R (current = voltage / resistance) or R= V/I (resistance = voltage / current) Resistance is measured in Ohms |
|
|
Describe the formula for calculating electrical power
|
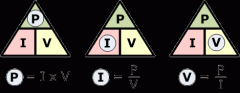
P = V x I (power = voltage x current)
or V + P / I (voltage + power / current) or I = P / V (current = power / voltage) |
|
|
What is Coefficient of linear expansion
|
The term for when a length of material expands due to it's temperature being raise by 1º
|
|
|
How can heat distortion be controlled? |
Reduce the amount of welded joints |
|
|
Identify the welding position PA
|
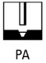
Flat position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PB
|

Horizontal Vertical position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PC |
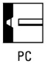
Horizontal position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PD |

Horizontal Overhead position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PE |
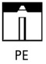
Overhead position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PF |
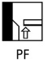
Vertical Upwards position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PG
|
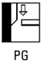
Vertical Downwards position
|
|
|
How can heat distortion be corrected mechanically? |
Large sections with a press |
|
|
How can heat distortion be corrected using heat? |
Heat uniformly to 650ºc then cooling normally |
|
|
Which standards cover welding symbols? |
BS EN 22553 welded, brazed and soldered joints - symbolic representation on drawings
|
|
|
Name the different types of heat distortion from welding
|
Angular |
|
|
Shielding gas is usually made up from what gases? |
Argon |
|
|
What is a rectifier? |
An electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC)
|
|
|
What is a solenoid?
|
An electromagnet
Made from a soft iron shaft with insulated wire coiled around it When a current is passed through the wire the solenoid becomes magnetic The more wire coiled, the greater the magnetism created Clockwise wire direction is north polarity - negative Anti-clockwise wire direction is south polarity - positive |
|
|
Describe an AC/DC inverter |
Silicon controlled rectifiers convert and reduce current |
|
|
Describe a DC welder generator
|
Powered by petrol or diesel |
|
|
What are the three most common colour coded plugs and sockets? |
Yellow 100V - 130V
Blue 200V - 250V Red 380V - 480V |
|
|
Describe an AC/DC transformer rectifier
|
Steps down the voltage
Increases the current Converts AC current to DC current Can be used for a variety of processes including MMA, MIG/MAG and TIG |
|
|
How much carbon does steel need to contain for it to be heat treatable? |
0.3% or more
|
|
|
How does heat treatment change the crystalline structure of metal? |
Structure changes from body centre cubic (ferrite) to face centre cubic (austenite)
|
|
|
What power control characteristics are used for MIG/MAG welding? |
Constant voltage (flat characteristic, constant potential) - |
|
|
Describe Dip Transfer |
The electrode intermittently short-circuits, causing it to dip into the weld pool and transfer metal
Occurs when volts and current are at low settings
It is used when welding thin material |
|
|
Describe Spray Transfer |
Metal from the electrode is sprayed by electromagnetic force, in a continuous stream onto the material
A high voltage method of transfer
Causes a large weld pool and a lot of metal to be deposited
Suitable for thicker materials over 6mm |
|
|
Describe Pulse Transfer |
A variation of spray transfer
The spray is controlled so the method can be used at lower settings and so can weld lighter material
Good for welding in all positions
Better penetration than dip transfer, but less metal is deposited than spray transfer |
|
|
What current and voltage range should be used when using 0.6mm diameter wire in dip transfer? |
30 - 80 A 15 - 18 V |
|
|
What current and voltage range should be used when using 0.8mm diameter wire in dip transfer? |
45 - 180 A 16 - 21 V |
|
|
What current and voltage range should be used when using 1.0mm diameter wire in dip transfer? |
70 - 180 A 17 - 22 V |
|
|
What current and voltage range should be used when using 0.8mm diameter wire in spray transfer? |
150 -250 A 25 - 33 V |
|
|
What current and voltage range should be used when using 1.0mm diameter wire in spray transfer? |
230 - 300 A 26 - 35 V |
|
|
Which process out of MIG or MAG creates the brightest arc? |
MIG |
|
|
Why are active gases mixed with Inert shielding gas? |
To increase arc temperature and improve fluidity of the weld pool |

