![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dot Product of Vectors
|
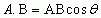
|
|
|
Cross Product of Vectors
|
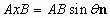
|
|
|
Vector Magnitude
|
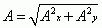
|
|
|
Vector Direction
|
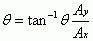
|
|
|
Average Speed
|
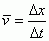
|
|
|
Average Velocity
|
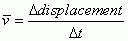
|
|
|
Average Acceleration
|
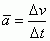
|
|
|
Kinematic Equation with Acceleration Missing
|
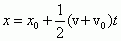
|
|
|
Kinematic Equation with Time Missing
|
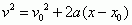
|
|
|
Kinematic Equation with Distance Missing
|
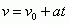
|
|
|
Kinematic Equation with Vf Missing
|
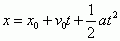
|
|
|
Kinematic Equation with Vi Missing
|
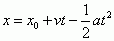
|
|
|
Newton's Second Law
|
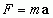
|
|
|
Force of Kinetic Friction
|
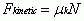
|
|
|
Force of Static Friction
|
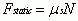
|
|
|
Work
|
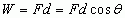
|
|
|
Work done by Gravity
|
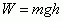
|
|
|
Kinetic Energy
|
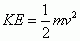
|
|
|
Work-Energy Theorm
|
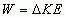
Think of the Force as increasing the Energy over time. It's Work!
|
|
|
Potential Energy
|
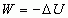
|
|
|
Gravitational Potential Energy
|
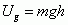
|
|
|
Mechanical Energy
|
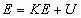
|
|
|
Average Power
|
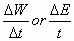
|
|
|
Instantaneous Power
|
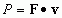
|
|
|
Hooke's Law
|
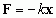
|
|
|
Frequency
|
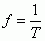
|
|
|
How do you extend the period of a spring?
|
Heavy mass, easily stretched spring
|
|
|
How do you extend the period of a pendulum?
|
Lengthen the String
|
|
|
Potential Energy of a Spring
|
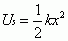
|
|
|
Momentum
|
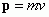
|
|
|
Impulse
|
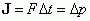
|
|
|
Center of Mass
|
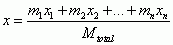
|
|
|
Angular Frequency
|
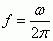
|
|
|
Angular Period
|
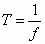
|
|
|
Angular acceleration
|
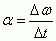
|
|
|
Angular Velocity
|
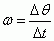
|
|
|
Relationship between Linear and Angular Variables
|
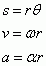
|
|
|
Torque
|
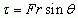
If perpindicular, sin can be ignored
|
|
|
Newton's Second Law in terms of Rotational Motion
|
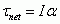
|
|
|
Kinetic Energy of Rotation
|
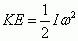
|
|
|
Angular Momentum
|
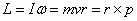
|
|
|
Kelvin Conversion
|
K = C + 273
|
|
|
Relationship between Heat and Temperature
|
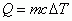
|
|
|
Coefficient of Linear Expansion
|
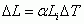
|
|
|
Coefficient of Volume Expansion
|
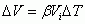
|
|
|
Ideal Gas Law
|
PV=nRT
|
|
|
Boyle's Law
(Relationship between Pressure and Volume) |
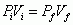
|
|
|
Charles's Law
(Relationship between Volume and Temperature) |
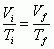
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
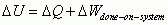
|
|
|
Efficiency of an Engine
|
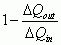
|
|
|
Coulomb's Law
|
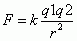
|
|
|
Formula's Defining Electric Field
|
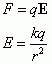
|
|
|
Electric Potential Energy
|
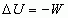
|
|
|
Work done by an Electric Field
|
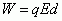
|
|
|
Electric Potential
|
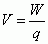
|
|
|
Stored Energy of a Capacitor
|
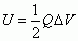
|
|
|
Magnetic Force on a moving charge.
|
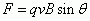
|
|
|
Radius of a Circle by a Charged Particle on a Magnetic Field
|
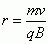
|
|
|
Magnetic Force on a Current
|
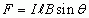
|
|
|
How do you increase the magnetic field produced by a current?
|
Increase Current, reduce radius.
|
|
|
Motional Emf
|
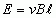
|
|
|
Magnetic Flux
|
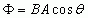
|
|
|
Lenz's Law
|
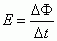
|
|
|
Wave Formula
|
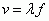
|
|
|
Index of Refraction
|
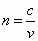
|
|
|
Snell's Law of Refraction
|
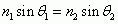
|
|
|
Equation for the Focal Length of a Lens
|
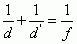
|
|
|
Lens Magnification
|
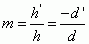
|
|
|
Photon Energy
|
E=hf
h is a constant f is frequency |
|
|
Particle Wavelength
|
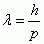
h is a constant
p is momentum |
|
|
Relativistic Factor
|
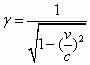
Gamma is the factor of how clocks slow down
|

