![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
REACH:
|
percentage target audience, home, or individuals that are exposed to the advertiser’s message (usually in a four week period).
|
|
|
COVERAGE:
|
refers to the POTENTIAL AUDIENCE that might receive the message through a media vehicle.
-Normally expressed as a percentage of a population of a population group. |
|
|
MEDIA PENETRATION:
|
how many markets the media penetrates
|
|
|
FREQUENCY:
|
the number of times the viewer is exposed to the media vehicle within a specific period of time.
|
|
|
SCHEDULING:
|
involves setting the time for advertisements or commercials to run.
This should be done to coincide with when the target audience can be reached. |
|
|
CONTINUITY:
|
= STEADY PLACEMENT of advertisements over designated period of time.
*It is the regularity in the pattern so that no gaps or lapse occur. (Skin care products, shampoo, towels, etc...) |
|
|
FLIGHTING:
|
HEAVILY advertise during a certain period of time, and then GRADUALLY DECREASE the frequency and intensity. Commonly used for advertising seasonal items (ski apparel, taxes, swimwear).
|
|
|
PULSING:
|
using continuity and flighting together, but MAINTAINING CONTINUITY of advertising @ CERTAIN TIMES of the year, flighting at specific times. (like special new reports right before they broadcast, and then after, they go bak to their normal ads. OR cosmetics with new products).
|
|
|
RATINGS, GROSS RATING POINTS, AND SHARE:
|
-the measurement of how many viewers are exposed to the ads.
-Established by independent research services (like Nielsen Media Research) -Calculated by dividing the number of households (HH) tuned to a particular show by the total number of households. |
|
|
GRP’s:
|
=gross rating points:
-another method of measuring media. Measurement combines the program’s rating with the average number of times the home is reached during the defined time -period=the frequency of exposure. |
|
|
SHARE:
|
refers to the size of an audience for any given time period. (Number of TV households tuned into a program / number.
|
|
|
MEDIA PLANNING:
|
persons job determining what media, and how much, and where
|
|
|
MEDIA OBJECTIVES:
|
-Get an 80% coverage (audience reach) within a 6-month period.
-Reach 60% of the target audience at least 3x in a 6-month period -Concentrate heaviest advertising in fall/winter, and lighter in spring/summer |
|
|
DIFFICULTIES IN MEDIA PLANNING:
|
-Inconsistent terminology
-Inconsistent measuring tools -measurements differ from one medium to another -Lack of information-testing -Expansion into new markets are hard to measure. -Time urgency-misjudged -Decisions can be made when you are working against time. -Difficulty measuring effectiveness |
|
|
PRINT MEDIA COST:
|
Magazines measure in CPM: cost per thousand (M=roman numeral)
-If magazine A has 2 million readers, and the cost for a full page (4-color ad) is $25,000 then: CPM = $25,000 / 2000 x(1000) = $12.50 (costs $12.50 to reach 1,000 readers of this magazine) |
|
|
BROADCAST COSTS:
|
-Television and radio use cost per ratings point (CPRP)
-CPRP = Cost of Commercial Time / Program Rating |
|
|
DIRECT MARKETING:
|
A form of advertising.
-Sponsored message delivered via: print, broadcast, or interactive media that requires the consumer to respond in some way. (Can be a form of personal selling) |
|
|
MEDIUMS OF DIRECT RESPONSE MARKETING:
|
Direct-mail, telemarketing, interactive media, interactive print and broadcast media, the internet.
EX: “Chance to win a prize, everyday for a month. OR: Text “.......” daily to win!” Top Ten = Email and Internet-Ads |
|
|
ADVANTAGES OF DIRECT MARKETING:
|
-Convenience: consumers can shop at home
-Instant payment: most of the time, consumers pay by credit cards -Selective reach and segmentation: company can strategize to target specific niches, locations, psychographics, zip code areas, etc... -Frequency: # of times to advertise, promote the message -Effectiveness: quick and reliable way to measure or evaluate success or failure, and allows companies to create a customer data base to track sales |
|
|
DISADVANTAGES OF DIRECT MARKETING:
|
-Image: consumers consider direct mailers as uninvited solicitations = “junk mail”
-Accuracy: can be a problem if the company’s database is not up-to-date |
|
|
ONE-STEP APPROACH:
|
an appeal that directly obtains an order or purchase. Catalogs use this.
|
|
|
TWO-STEP APPROACH:
|
company or promoter makes an offer to customers.
Once the customer calls or inquires, he/she must give information about himself/herself in order to purchase items |
|
|
DIRECT MAIL:
|

The most used traditional direct-form of marketing media.
Includes: catalogues, cards, card decks, letters, brochures, pamphlets, flyers, CDs, etc.... -Inserts: inside, outside or attached to something as part of the package or bill -Co-op mailings: combines ads of noncompetitive advertisers in the same envelope |
|
|
CATALOGUES:
|
Offer a wide range of products
*There are 8000 titles devoted to every product line for women, men and children -Offer to sell products to consumers who are not near a brick-and-mortar -Saves time, is stress free, and convenient -Can increase image through creative publications and illustrations -Consumers are not able to touch, feel, and try on products before purchase |
|
|
TELEMARKETING:
|
=Second largest traditional direct media strategy
Advantages: personal approach by the caller -Instant feedback -Opportunity for multiple sales -Reach wider audiences Disadvantages: -Costly -Difficulty in reaching consumers |
|
|
DIRECT MARKETING MEDIA:
|
=Broadcast media: radio and television
*There are 3-types of D.R. television media= Informercials (detailed and informative) *asked to call 1-800 #, Home-shopping, TV Spots Short form programs are less than 30-seconds Also: Movie trailers, Product promotions, and Mini-episodes |
|
|
SUPPORT-MEDIA:
|

Outdoor media (outside your home)
*May be the oldest form of advertising -Accounts for over $3.5 million in total ad spending -Accounts for 1.3% of total ad expenditures -Transit-media: bus stops, trains, metro signage -Out of home media: Kiosks, street furniture, newsstands, benches, walls |
|
|
INTERACTIVE MEDIA:
|
-Internet: global communication system that started in 1969
-E-commerce (biz. over the internet) = PPC, Banner Ads, Regular Sponsorship (occurs when a company pays to sponsor a section of a site), Pop-Up, and Pop-Unders |
|
|
Advantages [of interactive media]:
|
-Target marketing: possible to specifically select target niche
-Message tailoring: precise message to precise customers -Interactive capabilities: any interaction of consumer and company -Information access: consumers can have access to all kinds of information -Creativity is limitless -Exposure is best for price paid -Speed |
|

What form of advertising is this?
|

Co-Op Advertising= (typically more than 2 pages= ex: Neiman’s and Saks ads.
Always shows the retailer, but also says what brand the clothes in the ad are) -Benefits: Gives both parties more exposure, Mutually beneficial -Disadvantages: manufacturer identity is not equal, -accounting records ($ due) are hard to follow-up with (which designer paid and who didn’t), -Manufacturer has no control over placement of in-store merchandise -Retailer can see advertising allowance as a form of discount |
|
|
Diminishing returns curve:
|
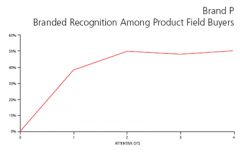
money dedicated to Adv. department right away in introduction phase (but money is only increased for ads if they see the returns)
|
|
|
Diminishing returns curve:
|
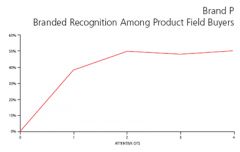
money dedicated to Adv. department right away in introduction phase (but money is only increased for ads if they see the returns)
|
|
|
S-Shaped Curved:
|
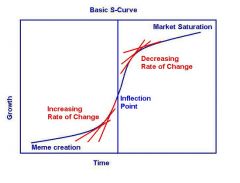
don’t initially invest in ads and then if the product takes off they really launch
|
|
|
Budget Allocation (in advertising):
|
-Top-Down Approach:
-All-one-can-afford -Arbitrary allocation -Competitive parity -Percentage of sales -Return on investment |
|
|
The Roles of PR:
|
-Establishing and promoting favorable PUBLIC IMAGE about client’s event, products, brands.
-Generate GOOD RELATIONS between a company and its customers -The PR of a company is responsible for the planned and continual effort to MAINTAIN the institution’s understanding of its public and the public’s UNDERSTANDING of the company -Analyzes PUBLIC OPINION -Not a promotion, but uses promotion to GET the company’s INFORMATION ACROSS -EXPLAINS THE IMAGE of a company through STRATEGIES designed to create public acceptance. -Maintain a steady-flow of positive information about a company during bad times. |
|
|
Negative Images of PR:
|
-Lack of respect for the profession
-'at all cost': many citizens view PR as having unethical and unnecessary practices -One-way viewpoint, or selfish viewpoint leads to mistrust from public. -'Spinning': twisting facts to favor your opinions or message |
|
|
Development [through PR]:
|
=Tool used to provide support for charitable / non-profit organizations through fund raising and memberships
-Helps finance operations such as museums, costume societies, and universities, etc.... -Fundraising enhances PR acceptance |
|
|
Internal Relations:
|
=Relates to the management of a company’s employees by CREATING CORPORATE CULTURE to retain good employees.
-Keeps employees informed, motivated, and able to support the company’s culture. -Newsletters, job positions. -Internal relations department deals with employee training, safety, etc... |
|
|
Issues Management:
|
Proactive process to: Anticipate, Identify, Evaluate, and Respond
-Process public policy issues that affect the organization’s relationship with the public. -Strategic responses (crisis management) |
|
|
Lobbying:
|
Involves a PR specialist building and maintaining relationships with government, primarily to influence legislation and government regulations.
*Lobbying can be viewed as a way to manipulate government for self-interest. |
|
|
Press Agentry:
|
creating newsworthy stories and events to attract attention from the mass-media in order to gain public notice.
-Press agents are more interested in attracting public notice than building public trust. -Press agents play a significant role in the entertainment, sports, tourist attraction, and celebrity business industries. |
|
|
Public Affairs:
|
Role of public relations people is to build and maintain governmental and local community relations in order to have some bearing on public policy.
*Some public relations specialists work with federal, state and local government to ensure public safety. |
|
|
Publicity:
|
Publicity is communication by the initiating party seeking to tell others about a product, service, idea, or event and delivered to the public at the discretion of the media.
*News or information is disseminated through media - but without the benefit of paid placement in the media, print or broadcast. |

