![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Atom |
The smallest unit of an element, cannot be broken down more |
Ex. One atom of hydrogen The element was broken down to its smallest concentration, the atom. |
|

Atomic Mass |
the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the mass number) or to the average number allowing for the relative abundances of different isotopes. |
Atomic mass of Helium: 4.003 The atomic mass is the number of protons and neutrons. |
|

Atomic Mass Unit |
a unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights |
Ex. 12 amu equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. It is equal to approximately 1.66 x 10-27 kg. |
|

Atomic number |
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table. |
Ex. He's atomic number is 2 The higher the atomic number, the heavier the element. |
|

Atomic Symbol |
Notation for one of the chemical elements, with mass# and atomic # |
Ex. 1.0079 H 1 is hydrogen The atomic symbol for Zinc is 65.39 mass, atomic number 30? Zn. |
|

Chemical Symbol |
Notation for one of the chemical elements |
ex. H is helium The chemical symbol for zinc is Zn. |
|
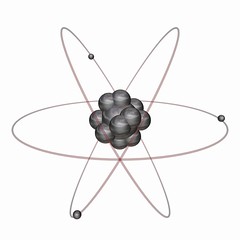
Electron |
Negative elementary electric charge |
If an atom loses an electron it becomes positive. |
|

Group |
Column of elements in the periodic table |
Ex. Zn, Cd, Hg, Uub Zn, Cd, Hg, Uub are all in the same group on the periodic table. |
|

Isotopes |
each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and hence differ in relative atomic mass but not in chemical properties; in particular, a radioactive form of an element. |
Ex. C12 vs C13 One isotope of Carbon is radioactive. |
|

Mass number |
the total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus. |
Ex. C12 The atomic number of C is 12. |
|

Metal |
Definition of Metals. Elements that form cations when compounds of it are in solution and oxides of the elements form hydroxides rather than acids in water. |
Ex. Iron Iron, gold, and silver are metals. |
|

Metalloid |
an element (e.g., germanium or silicon) whose properties are intermediate between those of metals and solid nonmetals. They are electrical semiconductors. |
Ex. Germanium germanium is intermediate between those of metals and solid non metals. |
|

Neutron |
a subatomic particle of about the same mass as a proton but without an electric charge, present in all atomic nuclei except those of ordinary hydrogen. |
Ex. In an atom a neutron has about the same mass as a proton. |
|

nonmetal |
Any of a number of elements, such as oxygen or sulfur, that lack the physical and chemical properties of metals. |
Ex. Oxygen Sulfer is a nonmetal, iron is a metal. |
|

Nucleus |
Positively charged center of an atom containing protons and neutrons |
The nucleus contains almost all the mass of the atom |
|

Period |
Horizontal rows on the periodic table |
Ex: H, He The periodic table has seven periods. |
|

Proton |
Particle found in the nucleus with a positive charge |
Ex. He has 2 protons The number of protons gives the atomoc number. |
|

Subatomic particle |
Protons, neutrons, and electrons, smaller than the atom |
Ex. Proton Sub atomic particles make up the atom. |

