![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
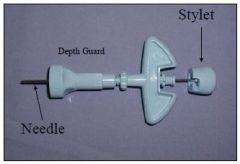
What is this called and what is it used for?
|
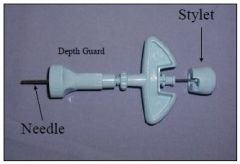
Illinois Sternal Needle - bone marrow collection
|
|
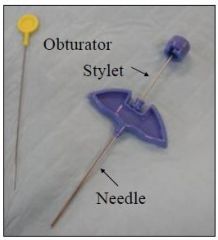
What is this called and what is it used for?
|
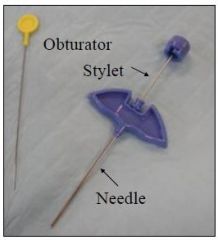
Jamshidi needle, used for bone marrow collection
|
|
|
what are 8 indications for bone marrow aspiration?
|
1. non-regenerative anemia
2. cytopenias 3. abnormal peripheral circulating cells 4. staging of neoplasia 5. infectious disease Dx 6. evaluation of FUO 7. evaluation of hypercalcemia 8. evaluation of paraproteinemia |
|
|
what are 4 advantages of bone marrow aspiration
|
1. technically easy
2. well tolerated 3. accessible tissue in patients with bleeding disorder 4. anesthesia not required |
|
|
what are 5 potential complications of bone marrow aspiration
|
1. bleeding/hematoma
2. iatrogenic trauma 3. iatrogenic infection 4. post-operative pain 5. failure to obtain sample |
|
|
what are the two types of bone aspiration needles?
|
1. Illinois Sternal Needle
2. Jamshidi needle |
|
|
what are the four preferred sites for bone marrow collection in the dog?
|
1. humeral head
2. iliac crest 3. trochanteric fossa of femur 4. sternebrae (rare) |
|
|
what type of needle is used most commonly to collect bone marrow biopsy samples?
|
Jamshidi needle
|
|
|
what are three indications for bone marrow biopsy?
|
aids characterization of lesions causing:
1. marrow replacement 2. marrow infiltration 3. aplastic or hypocellular processes |
|
|
what are four indications for lymph node aspiration?
|
1. lymphadenopathy (inflammation, hyperplasia, neoplasia)
2. staging neoplasia 3. hypercalcemia 4. FUO |
|
|
what are five advantages of lymph node aspiration?
|
1. no sedation required
2. inexpensive 3. rapidly and easily performed 4. tissue accessible 5. minimal complications |
|
|
what four lymph nodes are commonly aspirated on the dog?
|
1. submandibular
2. superficial cervical (prescapular) 3. popliteal 4. inguinal |
|
|
what are two different methods for lymph node aspiration?
|
1. Syringe method (e.g. with an Aspergun™)
2. Woodpecker method |
|
|
what are four ways in which joint fluid is analyzed?
|
1. gross
2. cytologic 3. biochemical 4. microbiologic |
|
|
what are five GENREAL indications for arthrocentesis?
|
1. joint pain
2. joint effusion 3. radiologic evidence of arthropathy 4. FUO 5. vague lameness |
|
|
what are four SPECIFIC indications for arthrocentesis?
|
1. monoarthropathy (trauma, sepsis, neoplasia)
2. polyarthropathy (infectious, immune mediated) 3. contrast arthrography (infrequently used) 4. intra-articular drug delivery |
|
|
what are three basic etiologies for monoarthropathy?
|
1. trauma
2. sepsis 3. neoplasia |
|
|
what are two basic etiologies for polyarthropathy?
|
1. infectious
2. immune-mediated |
|
|
how much fluid does the normal canine joint have?
|
< 0.5 mL
|
|
|
what is the basic procedure for bone marrow aspiration?
|
1. lateral recumbency w/ restraint
2. palpate anatomic landmarks 3. surgical sterile prep 4. prior to final scrub, lidocaine in skin 5. sterile gloves (and drape optional) 6. aseptically draw 2 mL EDTA into a 12 mL syringe 7. remove stylet from aspiration needle, attach syringe, and flush EDTA through needle onto a Petri dish. Remove syringe and replace stylet 8. 3-mm stab incision into bone marrow site 9. with stylet in place, advance needle and bore through bone 10. when cortex is penetrated, remove stylet and attach syringe 11. aspirate 12. detach syringe (leaving needle in place) and eject contents onto Petri dish containing EDTA 13. remove needle |
|
|
what is the most painful part of the bone marrow aspiration procedure?
|
aspiration of the bone marrow
|
|
|
what is the appearance of aspirated bone marrow?
|
dark red, fat particles, more viscous than blood
|
|
|
how do you avoid dilution of bone marrow with peripheral blood?
|
aspirate < 1 mL of marrow
|
|
|
what are the 3 ways that bone marrow aspirate can be processed after the sample has been placed on the Petri dish with EDTA?
|
1. 20-30+ slides
2. inoculation into a culturette 3. remaining fluid into an EDTA (lavender) tube |
|
|
to obtain a bone marrow biopsy, and the needle is through the cortex, what is the procedure?
|
1. loosen sample by alternate rotation and wobbling of needle
2. partially withdraw, redirect, and advance 3. repeat step 1 |
|
|
after a bone biopsy needle is removed from the patient, how is the sample obtained from the needle and processed?
|
- in retrograde fashion (needle to hub), advance obturator
- place biopsy into fixative |
|
|
what is the basic procedure for the syringe method lymph node aspiration?
|
1. restrain patient and isolate lymph node
2. needle (with or without aspiration gun) into lymph node 3. negative pressure and redirect; repeat negative pressure 4. release negative pressure 5. withdraw needle 6. detach needle from syringe, fill syringe with air, expel contents onto microscope slide |
|
|
what is the basic procedure for the Woodpecker method lymph node aspiration?
|
1. restrain patient and isolate lymph node
2. introduce needle without attached syringe 3. withdraw and redirect several times 4. remove needle from lymph node 5. expel onto slide with air-filled syringe |
|
|
what are three complications of arthrocentesis?
|
1. cartilage damage
2. iatrogenic infectious arthritis 3. iatrogenic hemarthrosis |
|
|
why is sedation or anesthesia used for arthrocentesis?
|
1. reduce risk of cartilage damage (patient movement)
2. reduces risk of patient hemarthrosis 3. normal joint capsule is extensively innervated with nociceptors 4. if there is effusion, it is always painful |
|
|
what part of the carpus is easiest for arthrocentesis?
|
radiocarpal joint (craniomedial aspect of carpus)
|
|
|
how is the limb held and landmark found for radiocarpal arthrocentesis?
|
flex carpal joint and palpate for depression over the craniomedial aspect of radius
|
|
|
what vascular structure should be avoided when doing a radiocarpal arthrocentesis?
|
superficial branch of cephalic vein
|
|
|
if there is effusion in the elbow joint, which pouches are most commonly swollen?
|
caudolateral and craniomedial pouches
|
|
|
what is the typical site of arthrocentesis of the elbow?
|
caudolateral pouch
|
|
|
how is an arthrocentesis of the caudolateral pouch of the elbow performed?
|
- caudolateral pouch is between the lateral humeral epicondyle and the olecranon
- place needle just lateral to triceps tendon - direct needle caudolateral → craniomedial to avoid contact with the anconeal process |
|
|
how is the patient positioned for shoulder joint arthrocentesis?
|
lateral recumbency, affected limb up, joint mildly flexed
|
|
|
how is an arthrocentesis of the shoulder joint performed?
|
- lateral recumbency, affected limb up, joint mildly flexed
- palpate point of greater tubercle and acromion - needle should be placed so it passes just lateral and proximal to the greater tubercle in the craniolateral to caudomedial direction |
|
|
in which joint pouches is stifle joint effusion usually located?
|
medial and/or lateral parapatellar areas
|
|
|
how is the patient positioned for stifle joint arthrocentesis?
|
lateral recumbency, affected limb up, joint mildly flexed
|
|
|
how is an arthrocentesis of the stifle joint performed?
|
- lateral recumbency, affected limb up, joint mildly flexed
- palpate patella, patellar ligament and tibial tuberosity - needle can be placed medial or lateral to the patellar ligament - divide the distance from the patella → tibial tuberosity into thirds; place needle in DISTAL two-thirds - direct needle slightly proximally, toward the center of the joint |
|
|
why can successful aspiration of stifle joint fluid be difficult?
|
soft tissue structures in the joint (fat pad, ligaments)
|
|
|
what are two sites of approach for tarsal arthrocentesis?
|
1. craniolateral
2. caudolateral |
|
|
how is the needle directed in the craniolateral approach to tarsal arthrocentesis?
|
direct needle between the lateral malleolus of the fibula and the talus
|
|
|
how is the needle directed in the caudolateral approach to tarsal arthrocentesis?
|
needle directed distally, attempting to penetrate opening between tibia, fibula, and tarsus
|

