![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
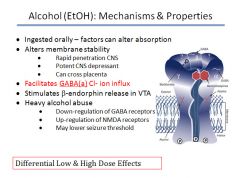
|
|
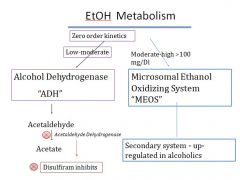
Normally ADH has a higher affinity for alcohol than MEOS so it metabolizes low doses of alcohol. ADH requires nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a co-factor. NAD+ gets reduced to NADH during metabolism. When large amounts of alcohol get consumed, NAD+ gets depleted & the 2nd MEOS system then metabolizes the remaining alcohol.
|
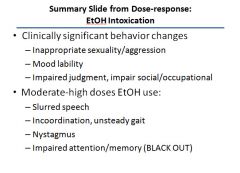
|
|

|

|
|
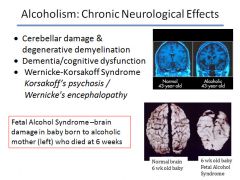
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|

|
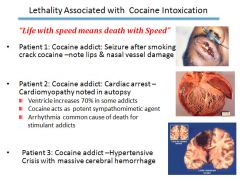
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
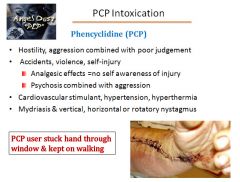
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

Review of normal process: When serotonin activates post synaptic 5HT2A, which is coupled to Gαq, it stimulates phospholipase C (PLC) phosphoinositol system. Atypical antipsychotics stop serotonin from activating the 5HT2A receptor.
|

|
|

Notes: 1st generation typical antipsychotics (including chlorpromazine & thioridazine) have high risk of EPS as well as tardive dyskinesia (next slide) due to potent block of D2 receptor. Haloperidol has very high affinity for the D2 receptor & is more potent than some of the other typical antipsychotics.
|

|
|
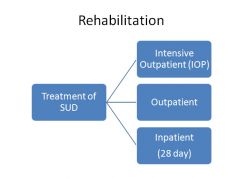
|

|
|

|
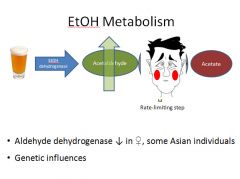
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

