![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
203 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
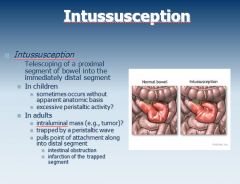
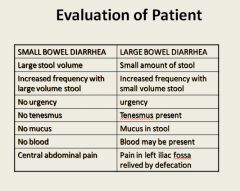
What is the difference between acute and chronic diarrhea?
|
Acute is diarrhea lasting less than 4 weeks.
Chronic is diarrhea lasting more than 4 weeks. |
|
|
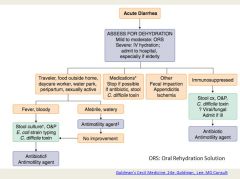
What is the top (and really the only) differential diagnosis for acute diarrhea?
|
Infection!!!
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
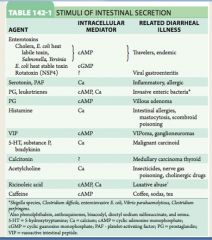
|
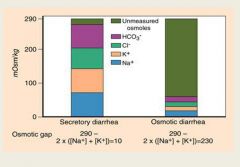
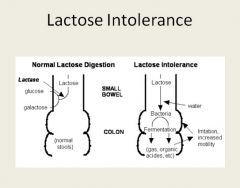
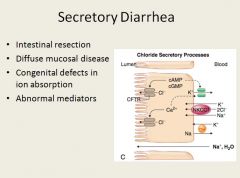
In secretory diarrhea, the osmotic gap is normal.
In osmotic diarrhea, there are unmeasure osmoles, such as lactose present. |
|

|
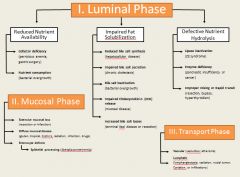
|
|
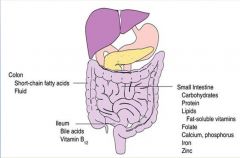
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
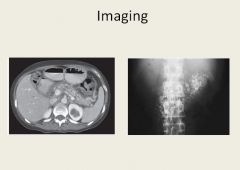
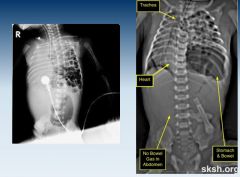
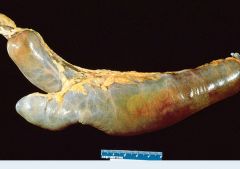
Small calcifications where pancreas is located due to chronic pancreatitis.
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
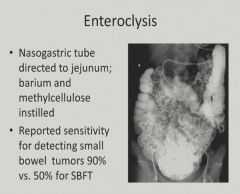
|
|
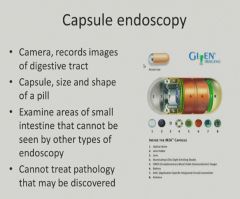
|
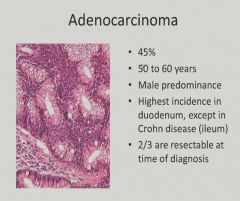
|
|

|
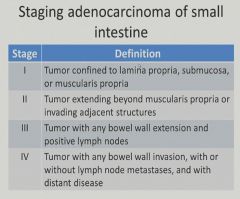
|
|

|

|
|

|
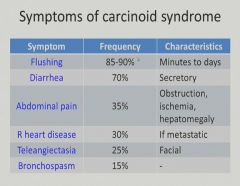
|
|
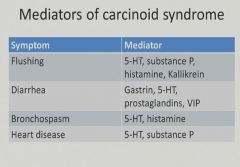
|
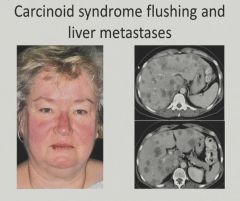
|
|
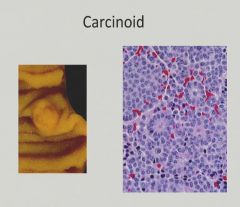
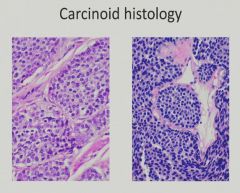
"Salt and Pepper" chromatin pattern with some acinar formation
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
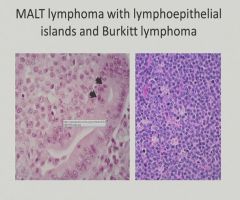
|

|
|

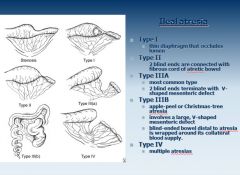
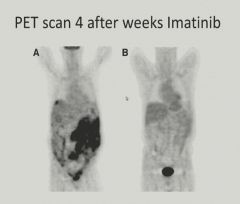
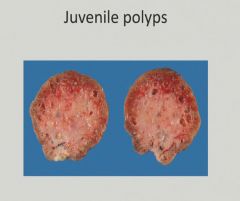
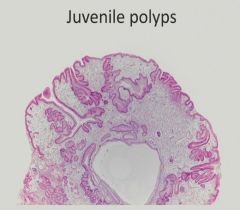
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
|
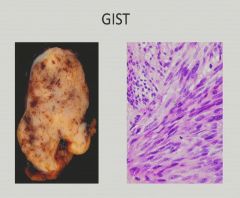
|
|

|

|
|
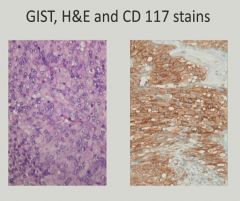
|
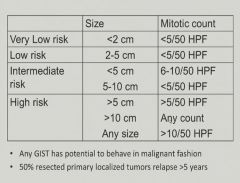
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
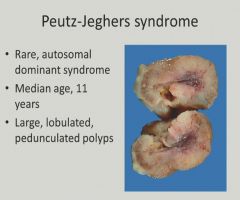
|
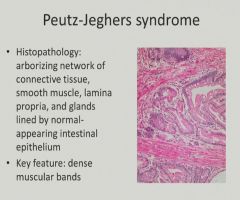
|
|
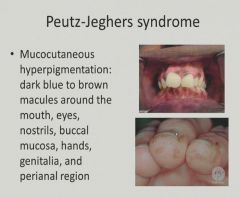
|

|
|
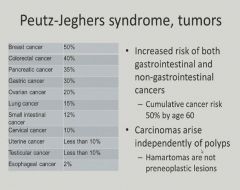
|
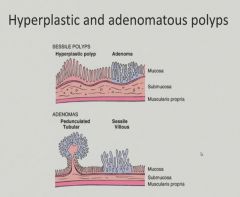
|
|

|
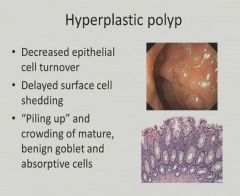
|
|
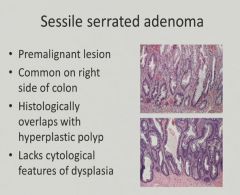
|
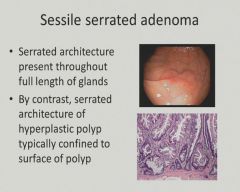
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
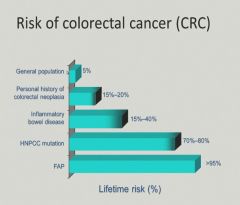
|
|

|
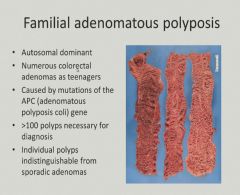
|
|

|
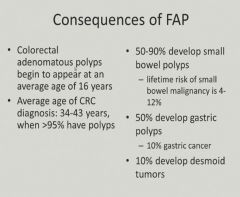
|
|
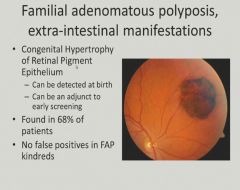
|

|
|

|
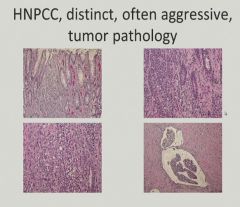
|
|
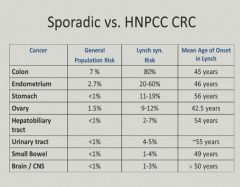
|
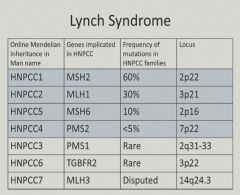
|
|

|

|
|
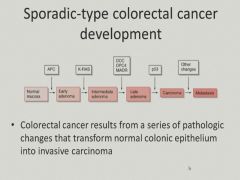
|

|
|

|

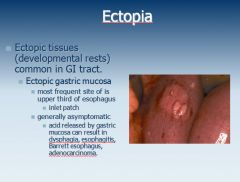
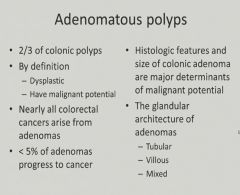
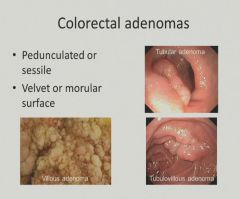
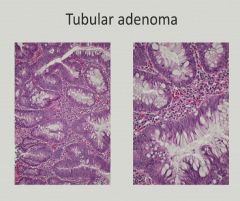
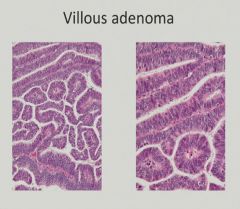
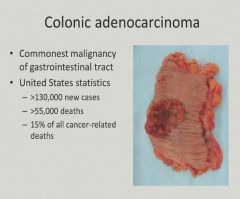
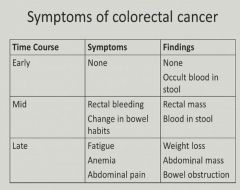
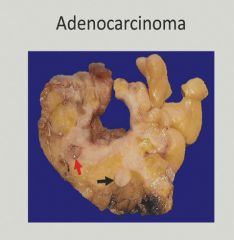
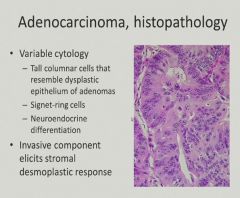
Blood loss and fatigue - anemia = CRC unless proven otherwise
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
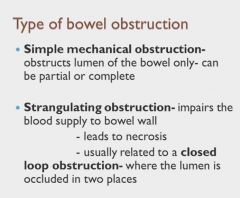
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
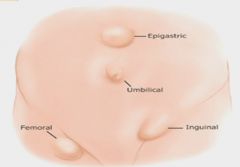
|
|
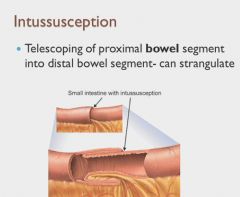
|

|
|

|
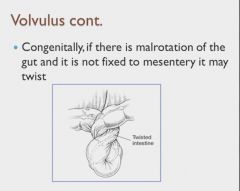
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
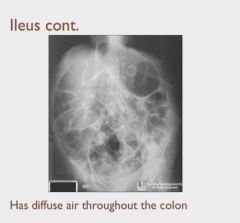
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
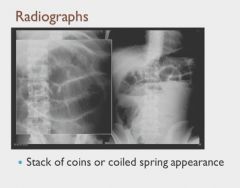
|
|
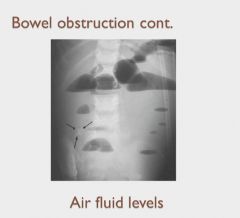
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
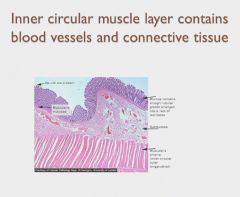
|
|

|
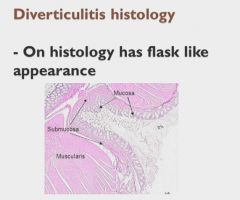
|
|
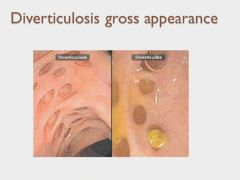
|
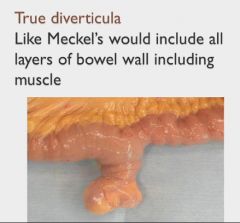
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
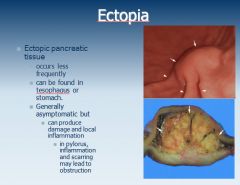
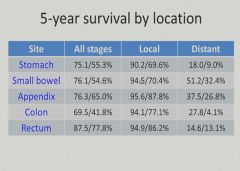
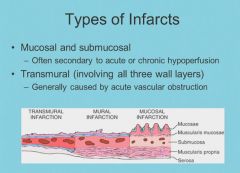
Surgical treatment of diverticulutis:
|

|
|
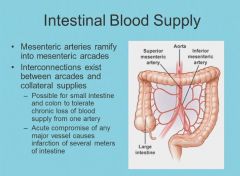
|
|
|

|

|
|

|
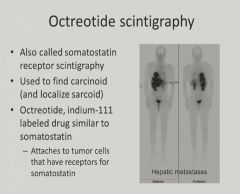
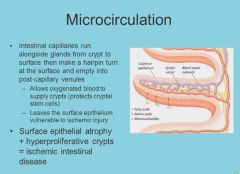
Atherosclerosis
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
A
|
|

|

|
|
|
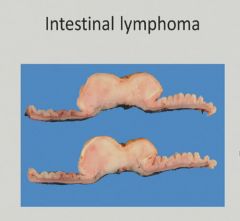
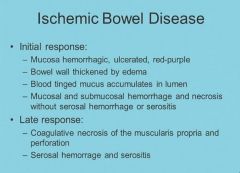
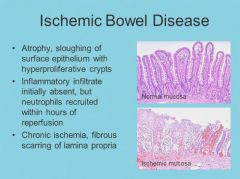
Ischemic bowel disease pearls:
|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
After the first oral feeding.
|
|
|
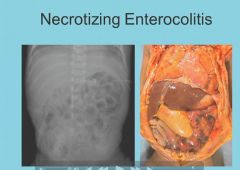
Necrotizing enterocolitis pearls:
|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
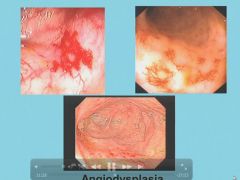
Pathogenesis of angiodysplasia:
|

|
|

|
Cecum
|
|
|
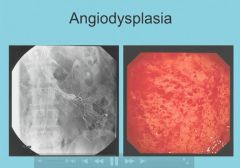
Angiodysplasia Pearls:
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
82 year old male
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
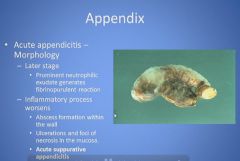
|
|

|

collapse of the submucosal vessels.
|
|

|

|
|
|
Characteristics of S. aureus enterotoxin:
|

Heat stabile toxin. Quick onset of symptoms. No fever. Short duration of vomiting and diarrhea with no blood in stool.
|
|
|
Characteristics of S.aureus food poisoning that point to intoxication rather than infection:
|

|
|

|
Salmonella food poisoning most likely from undercooked chicken. Starts with flu like symptoms followed by cramps and water diarrhea. Loose bowel movements, dehydration and fever develop over a period of days. WBC's seen in stool.
|
|

|

Only for high-risk groups; usually self limiting in all populations.
|
|
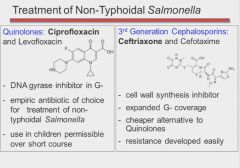
|

Giardia lamblia:
Characterized by prolonged onset; followed by foul smelling, greasy watery diarrhea, sulfurous belching, flatulance, cramps and bloating. No blood or mucous in the stool and no fever. |
|

|
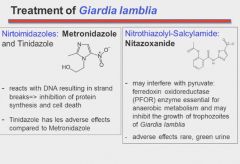
Metronidazole - anaerobes
|
|
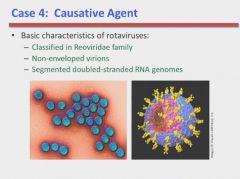
Mostly in children; 2-3 days of fever, diarrhea, vomiting and dehydration that spontaneously resolves. No WBC, RBC, ova or parasites in stool.
Norwalk = adults. |

|
|

Rotavirus pathogenesis
No drugs to treat it; just keep child hydrated. |

|
|
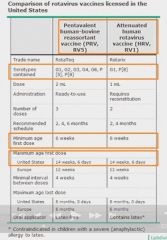
|

ETEC: Traveller's diarrhea
|
|

|

Sometimes a consequence of infection with EHEC.
|
|

|

EHEC epidemiology
|
|

|

|
|
|
Typical presentation is progressively worsening diarrhea and abdominal pain with cramping and multiple watery stools per day.No vomiting, fever or bloody stools. Stool sample negative for blood and positive for leukocytes. Associated with recent antibiotic use.
|
|

|

|
|

Different presentations of C. difficile
|
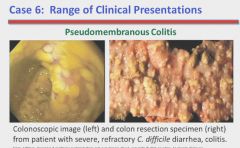
|
|

|

|
|

|

Severity assesed by WBC counts and serum creatinine levels.
|
|
|
Treatment of C. difficile associated diarrhea:
|

|
|
|

|
|
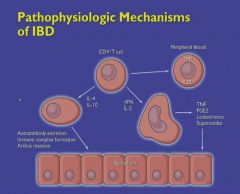
|

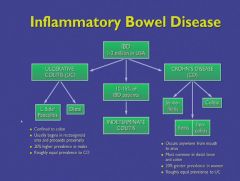
The disease NEVER goes through the mucosa of the colon.
|
|
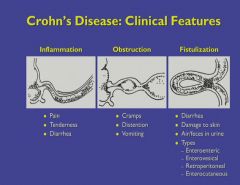
A transmural disease that can form fistulas to the bladder, uterus and other bowel.
Can also form strictures. |
|
|

|
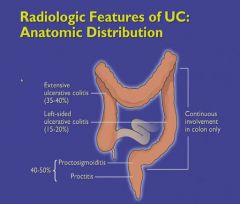
|
|
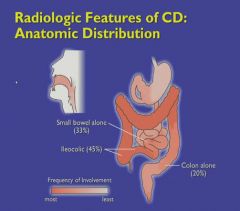
|

|
|
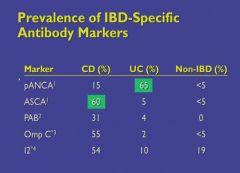
|
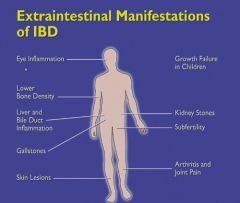
Calcium oxalate stones are the stone of IBD.
|
|
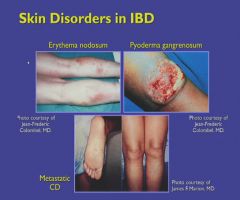
Pyoderma = UC
|
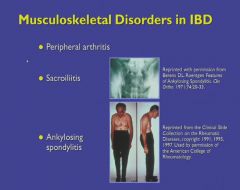
Generally seen in UC.
|
|
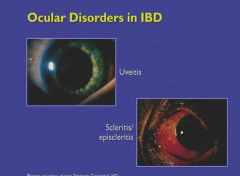
|
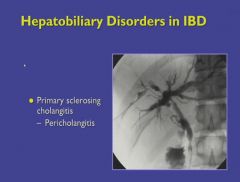
A rising ALP indicates deterioration of the bile ducts.
|
|
|
Oral ulcers in IBD:
|
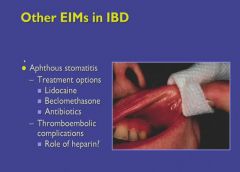
|
|
|
Connection between Ulcerative colitis and cancer risk:
|
1. If just the rectum is involved, there is no greater incidence of cancer.
2. The longer the length of bowel involved, the greater the risk of cancer developing. 3. The more inflammation on a chronic basis, the greater the risk. 4. The longer the duration of disease, the greater the risk (over 8 years; will get colonoscopy at least every 1-2 years. If dysplasia is detected, the colon is removed prophylactically). |
|

|

|
|
|
Affect of IBD on fertility and conception?
|
No significant risks for abortion, congenital abnormalities or stillbirth - unless the woman gets pregnant during a flare.
|
|

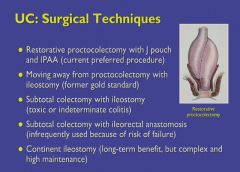
J-pouch is the operation of choice for colon removal; rectal muscles are left in place and sutured to the small bowel. So no colostomy bag is required!
BUT..."pouchitis" is now a problem for these patients, or the false pouch may develop ulcers from Crohn's disease. |
|
|

|
With multiple resections, the patient can develop short bowel syndrome; you have to have a certain number of cm left to absorb nutrients (100 cm). If you have less than that, you cannot eat anything by mouth anymore because it won't be absorbed.
|
|
|
Liver imaging in order of detail available?
|
1. Ultrasound
2. CT 3. MRI |
|
Used to look at biliary obstruction.
|
Used for liver transplant.
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
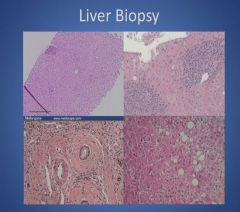
Top left: normal
Top right: WBC infiltrate Bottom left: abnormal bile duct Bottom right: fatty liver |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
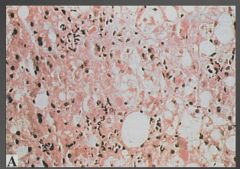
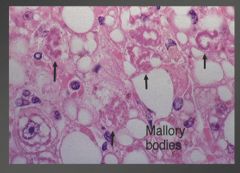
Fatty infiltration and Mallory bodies.
|
|
|

|

|
|
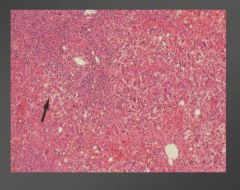
Note infiltrate of plasma cells
|

|
|
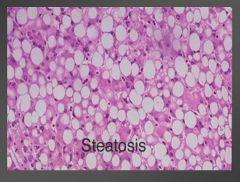
|
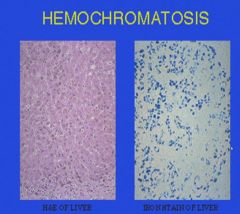
|
|
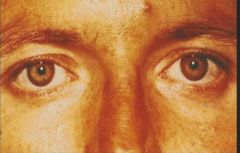
Fleicher rings in Wilson's disease
|

|
|
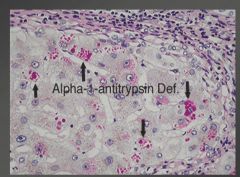
The a-1-antitrypisin made in the liver cannot get out and get to the lungs to scavenge for free radicals
|

|
|

|
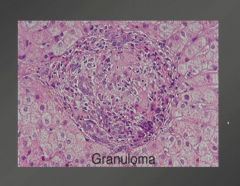
histology of primary biliary cirrhosis.
|
|

|
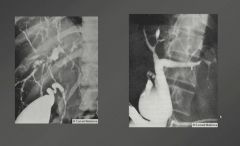
Note areas of stenosis and dilation.
|
|
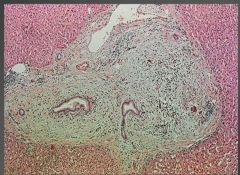
Primary sclerosing cholangitis. Note onion skinning around bile duct.
|

|
|
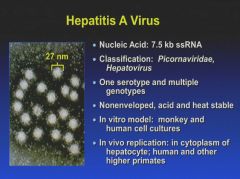
|

|
|
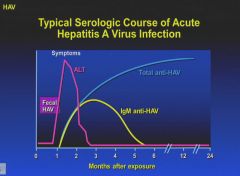
|

Some complications that can arise from HAV infection.
|
|

|
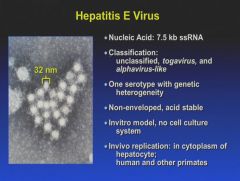
|
|

|

|
|

|
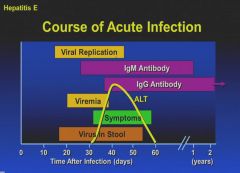
|
|
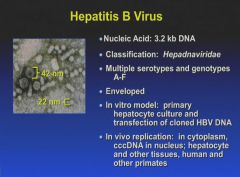
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
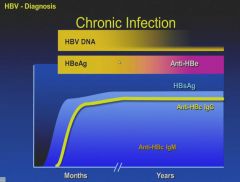
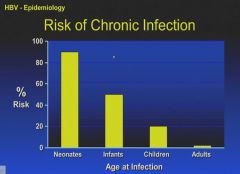
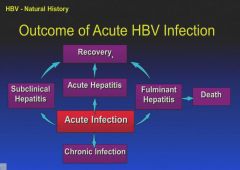
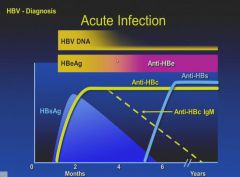
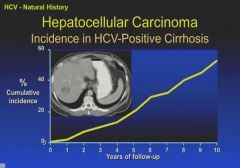
Chronic infection is the presence of the S antigen for more than 6 months.
|
|
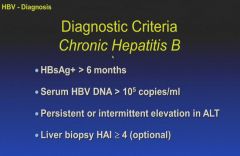
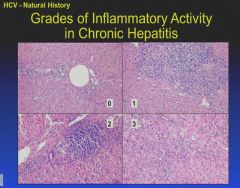
HAI = hepatic activity index; inflammation
|
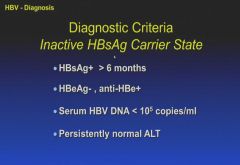
|
|

|

|
|
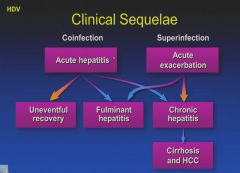
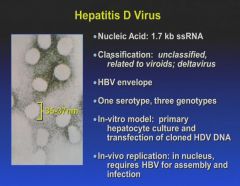
Remember: HepD has to co-infect along with HepB!
|
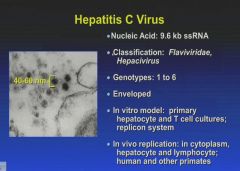
|
|
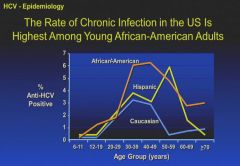
|

|
|
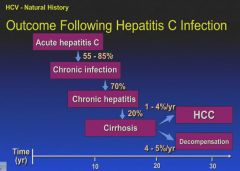
|
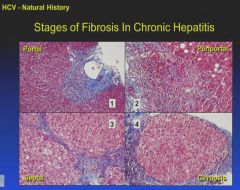
|
|
|
|

