![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
176 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
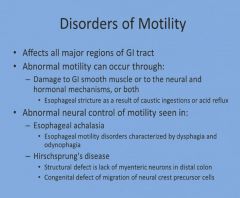
Disorders of Motility in the GI tract:
|
|
|
|
More disorders of motility in the GI tract:
|

|
|
|
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut motility:
|

|
|
|
Disorders of secretion:
|

|
|
|
More disorders of secretion:
|

|
|
|
Disorders of digestion and absorption:
|

|
|
|
GI manifestations of systemic disease:
|

|
|
|
Presentation of acute vs. chronic GI disease:
|

|
|
|
The four most common signs of GI disease:
|

|
|
|
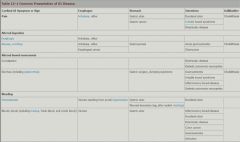
Table of common GI symptoms and diseases:
|
|
|
|
Signs of GI obstruction:
|

|
|
|
Diagnostic tests for upper GI complaints:
|

Manometry: measures internal GI pressure (squeezing ability)
|
|
|
Common complaints/symptoms of lower GI disease:
|

|
|

|

Esophagus
|
|
|
Dysphagia:
|

|
|

(In regards to the previous case)
|
Stricture (from prior acid reflux)
|
|
|
Some other causes of dysphagia:
|

|
|
|
Nausea and Vomiting:
|

|
|
|
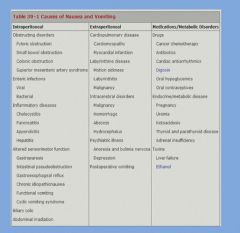
Causes of nausea and vomiting:
|
|
|
|
Indigestion:
|

|
|
|
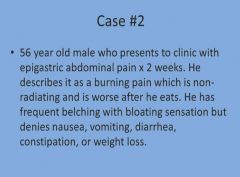
What is eructation?
|
Burping!
|
|
|

Peptic ulcer
Acid reflux Chronic gastritis |
|
|
Diarrhea:
|

|
|
|
Causes of acute diarrhea:
|
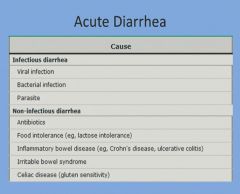
|
|
|
Causes of chronic diarrhea:
|
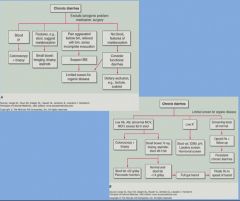
|
|
|
Constipation:
|
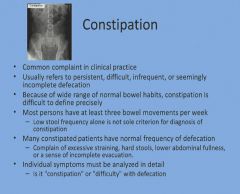
|
|
|
Constipation in the elderly can cause delirium, why?
|
Because not absorbing enough water can cause dehydration leading to delirium...also extreme back up can cause sepsis. AND, malabsorption can cause vitamin deficiencies.
|
|
|
Gastrointestinal bleeding:
|

|
|
|
Levels of lower GI bleeding:
|
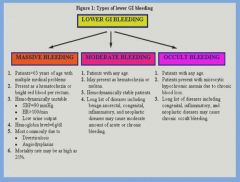
|
|
|
Acute upper GI bleeding:
|
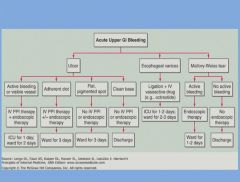
|
|
|
Acute lower GI bleeding:
|
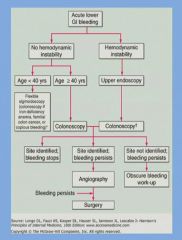
|
|
|
Diseases of the oral cavity:
|

|
|
|
Canker Sores:
|
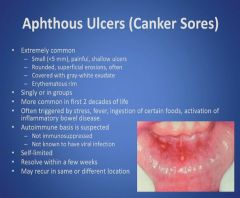
|
|
|
Canker Sore Pearls:
|

|
|
|
Herpesvirus Infection:
|

|
|
|
Herpes virus infection part 2:
|
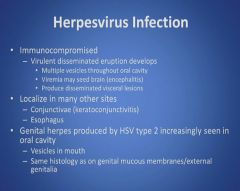
|
|
|
Herpes virus histology:
|
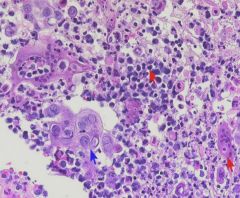
|
|
|
Herpes virus pearls:
|

|
|
|
Oral Candidiasis:
|

|
|
|
Oral Candidiasis part 2:
|
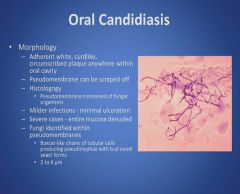
|
|
|
Oral Candidiasis part 3:
|
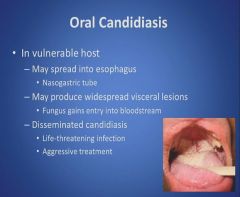
|
|
|
Oral Candidiasis pearls:
|

|
|
|
Hairy leukoplakia and Kaposi's sarcoma:
|
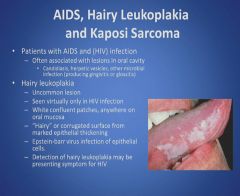
|
|
|
Kaposi sarcoma:
|
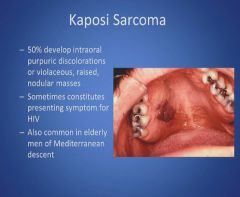
|
|
|
HIV related oral lesion Pearls:
|

|
|
|
Leukoplakia:
|
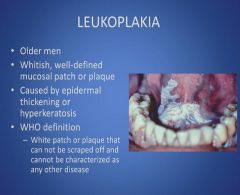
|
|
|
Leukoplakia part 2:
|

|
|
|
Leukoplakia part 3:
|

|
|
|
Leukoplakia part 4:
|

|
|
|
Leukoplakia related lesions:
|
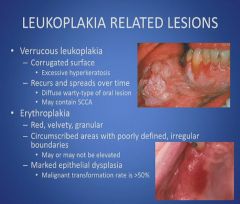
|
|
|
Leukoplakia Pearls:
|

|
|
|
Cancers of the oral cavity and tongue:
|

|
|
|
Cancers of the oral cavity and tongue part 2:
|
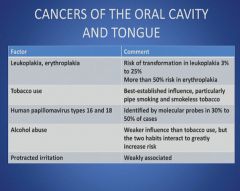
|
|
|
Cancers of the oral cavity and tongue part 3:
|

|
|
|
Cancers of the oral cavity and tongue part 4:
|

|
|
|
Cancers of the oral cavity and tongue part 5:
|
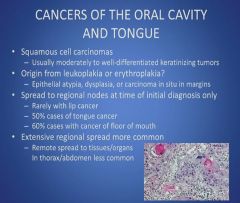
|
|
|
Oral cancer pearls:
|

|
|
|
Inflammation of the salivary glands:
|
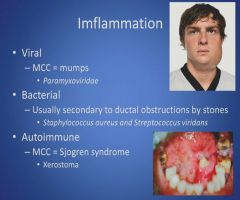
|
|
|
Salivary gland tumors:
|

|
|
|
Salivary gland tumors part 2:
|

|
|
|
Pleomorphic Adenoma:
|

|
|
|
Gross histology of a pleomorphic adenoma:
|
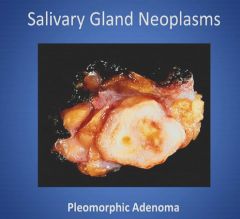
|
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma part 2:
|

|
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma pearls:
|

|
|
|
Histology of a pleomorphic adenoma:
|
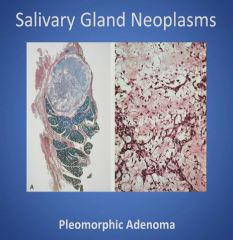
|
|
|
More histology of a pleomorphic adenoma:
|
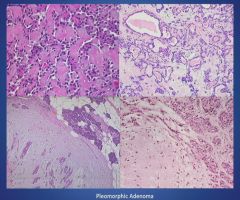
|
|
|
Warthins Tumor:
|

|
|
|
Gross picture of a Warthins Tumor:
|
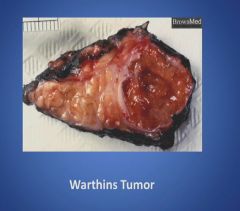
|
|
|
Histology of Warthins Tumor:
|
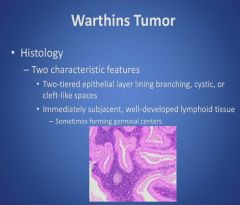
|
|
|
More histology of Warthins Tumor:
|
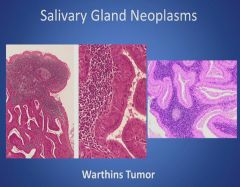
|
|
|
Warthins tumor pearls:
|

|
|
|
Fine needle aspiration:
|

|
|
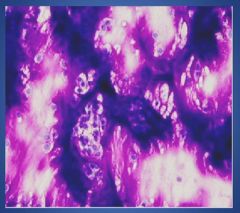
Warthins tumor or Pleomorphic adenoma?
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
Three areas of the esophagus are narrowed:
|
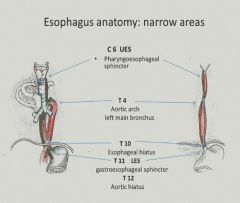
|
|
|
Levels of the esophagus corresponding to vertebral levels:
|
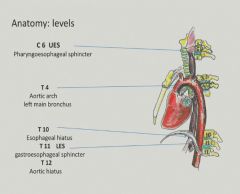
|
|
|
Innervation of the esophagus:
|
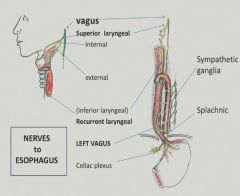
|
|
|
Motility and sphincters of the esophagus:
|

|
|
|
Layers of the esophagus:
|
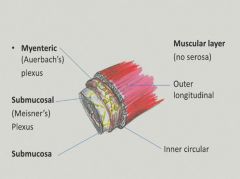
|
|
|
Myenteric plexus:
|
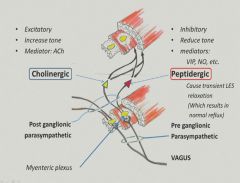
|
|
|
Submucosal plexus:
|
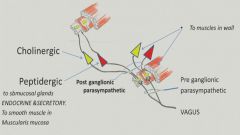
|
|
|
Vocabulary:
|

|
|
|
Diagnostic tests:
|

|
|
|
Esophageal diverticuli:
|

|
|
|
Zenker's diverticulum:
|
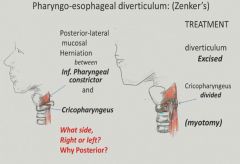
More common on left side b/c esophagus tends to stay leftward. Happens posteriorly because the trachea is blocking the anterior.
|
|
|
Achalasia:
|
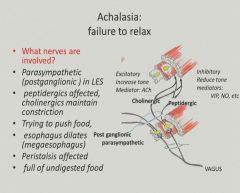
|
|
|
Achalasia part 2:
|

|
|
|
Esophageal rupture:
|
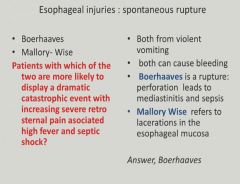
|
|
|
Esophagitis:
|

Relfux is the most common non-infectious cause.
|
|
|
Barrett's Esophagus:
|

|
|
|
Transition from Barrett's to invasive adenocarcinoma:
|
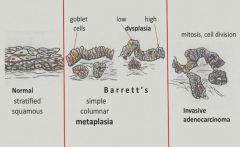
|
|
|
Benign tumors of the esophagus:
|
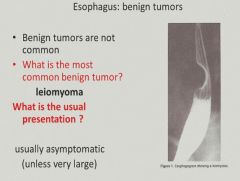
|
|
|
Malignant tumors of the esophagus:
|

|
|
|
Spread and prognosis of malignant esophageal tumors:
|
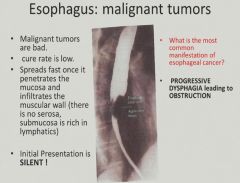
|
|
|
Treatment of esophageal cancer:
|
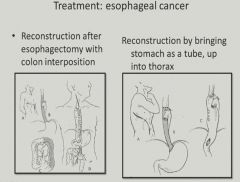
|
|
|
Typical presentation of a hiatal hernia:
|

|
|
|
Things that make GERD symptoms worse:
|

|
|
|
GERD:
|

|
|
|
Symptoms of GERD:
|

|
|
|
Diagnosis of GERD:
|
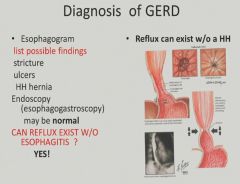
|
|
|
Complications of GERD:
|
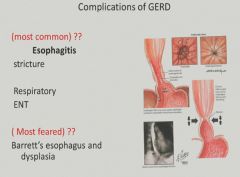
|
|
|
Two types of hiatal hernia:
|
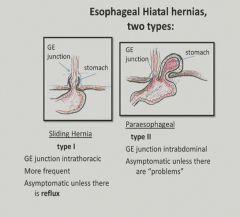
|
|

|
Food stagnation
|
|

|
Dysplastic changes in Barrett's esophagus
|
|

|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|

|
A sliding hiatal hernia with incompetent LES
|
|

|
Dysplastic changes
|
|
|
Congential diaphramatic hernias:
|
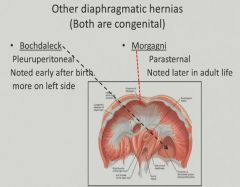
|
|
|
Gatric Anatomy:
|
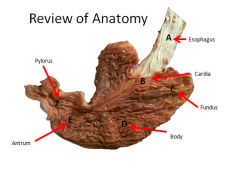
|
|
|
Gastric cell function:
|
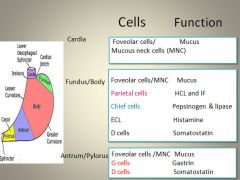
|
|
|
Cell type histology:
|
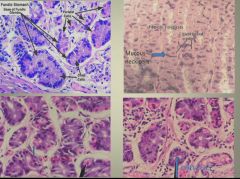
|
|
|
Layers of the stomach:
|
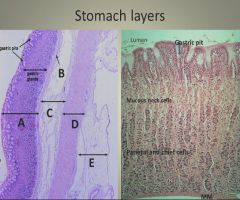
A: Mucosa
B: Muscularis mucosa C: Submucosa D: Muscularis E: Serosa |
|
|
More gastric cell histology:
|
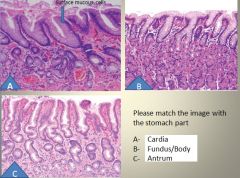
|
|
|
Regulation of acid secretion:
|
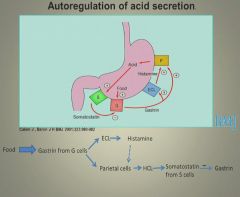
|
|
|
Gastritis:
|

|
|
|
Acute vs. chronic gastritis:
|
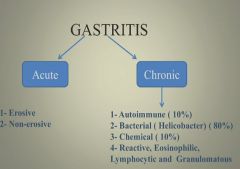
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of gastritis:
|
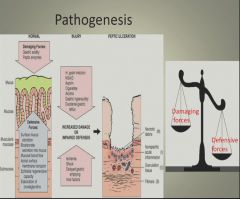
|
|
|
Acute gastritis:
|

|
|
|
More acute gastritis:
|

|
|
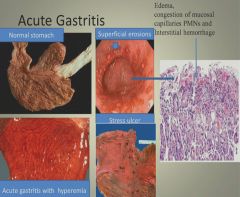
|

|
|
|
Chronic gastritis:
|
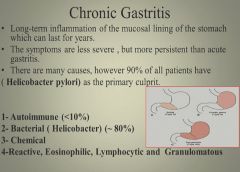
|
|
|
Autoimmune gastritis:
|

|
|
|
Autoimmune gastritis histology:
|
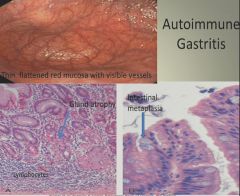
|
|
|
Bacterial Gastritis:
|

|
|
|
Helicobacter Pylori:
|

|
|
|
H. Pylori mechanism of infection and damage:
|
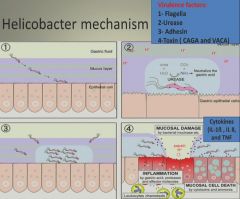
|
|
|
CAGA and VACA strains of H. pylori:
|
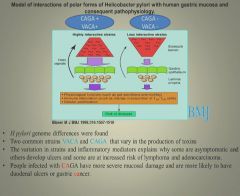
|
|
|
H pylori and acid secretion:
|
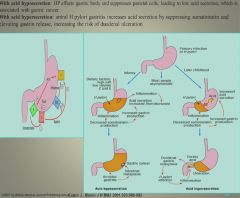
|
|
|
Chronic gastritis histology:
|
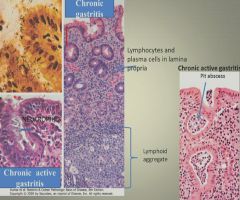
|
|
|
Complications of H pylori infection:
|

|
|
|
Helicobacteri Helimanni:
|

|
|
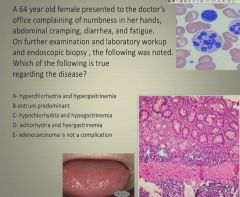
|
D: Achlorhydria and hypergastrinemia
|
|
|
Chemical gastritis:
|

|
|
|
NSAID induced gastritis:
|

|
|
|
Histology of uncommon forms of gastritis:
|
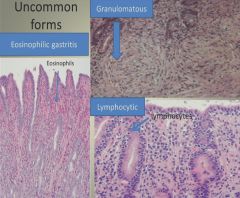
|
|
|
Complications of chronic gastritis:
|

|
|
|
Chronic gastritis pictures:
|
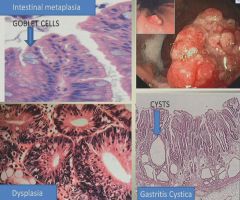
|
|
|
Peptic ulcer:
|

|
|
|
Erosion vs. Ulcer
|

|
|
|
Ulcer histology:
|
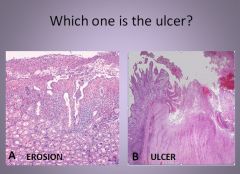
|
|
|
Location of peptic ulcers:
|
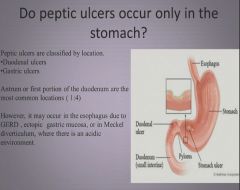
|
|
|
Epidemiology of peptic ulcers:
|

|
|
|
Duodenal vs. Gastric ulcer:
|

|
|

|
First test for H. pylori
|
|

|
First test for H. pylori
|
|
|
Ulcer histology 2:
|
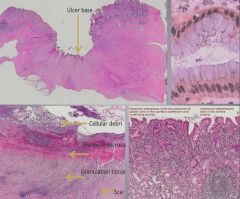
|
|
|
X-ray of perforated ulcer:
|
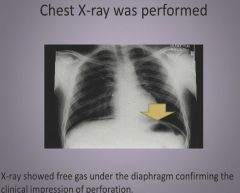
|
|
|
Complications of PUD:
|

|
|
|
Treatment of PUD:
|

|
|

|
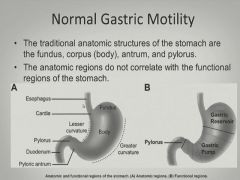
|
|
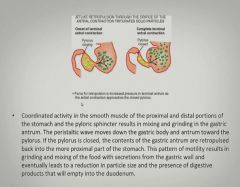
|

|
|
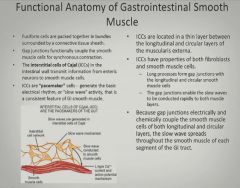
|

|
|
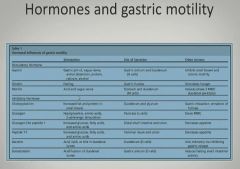
|

|
|

|

|
|
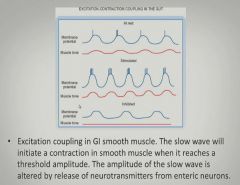
|

|
|

|
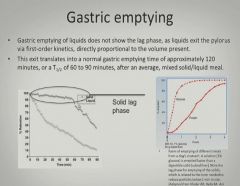
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

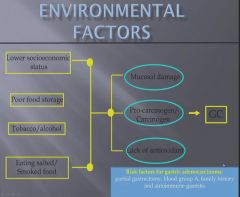
Due to lots of salted fish and smoked food.
|
|

|
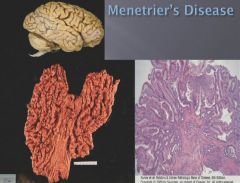
|
|
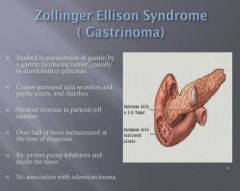
|
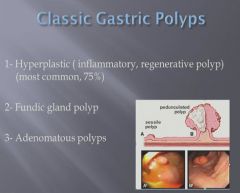
|
|
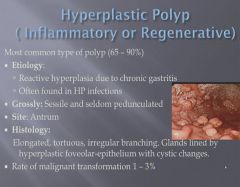
|
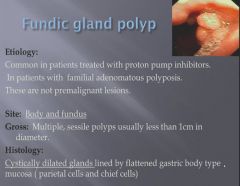
|
|

|
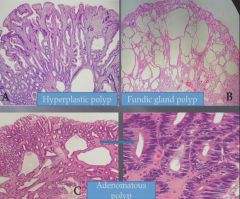
|
|
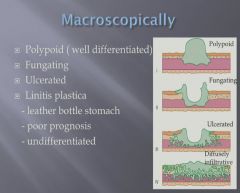
|
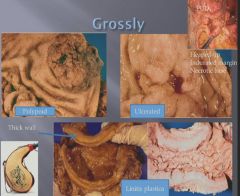
|
|

|

|
|
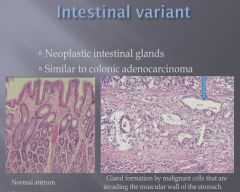
|

|
|
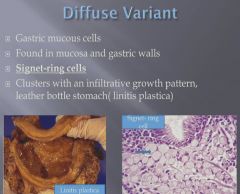
|
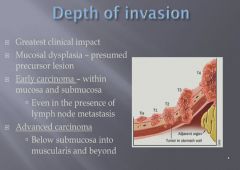
|
|
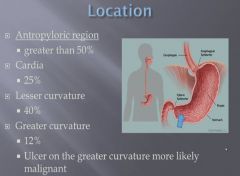
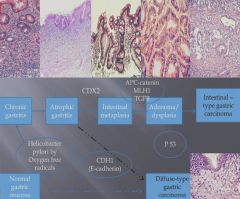
Percentage of carcinomas found in each stomach locations.
|

|
|
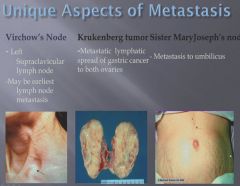
|
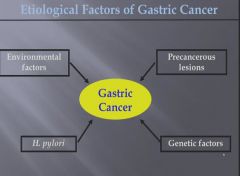
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
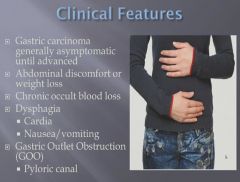
|
|
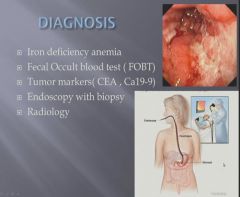
|
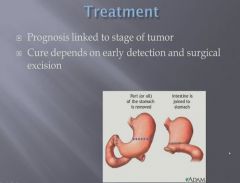
|
|
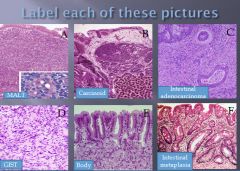
|
|
|
|
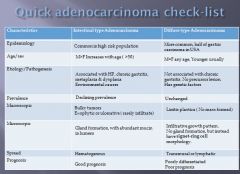
Gastric Carcinoma lecture summary:
|

|

