![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of therapy for each stage of COPD:
|
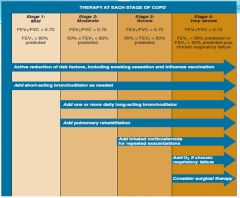
|
|
|
Classes of medication for treatment of COPD:
|

Never give a LABA alone as monotherapy for long term control!
|
|
|
Short acting B2 agonist:
|

|
|
|
Anticholinergic agents:
|

|
|
|
Systemic corticosteroids:
|

|
|
|
Corticosteroids for long term treatment; MOA:
|

|
|
|
Indications for corticosteroid use in long term control:
|

Inhaled corticosteroids do not have the systemic effects that systemic corticosteroids do + they are delivered in a much, much smaller dose.
|
|
|
Benefits of inhaled corticosteroids:
|
- Inhaled Corticosteroids Prevent Death
- THE most effective long term medication for the control of asthma - Useful in every treatment step of persistent asthma - Reduces patient impairment and risk - Preferred long term control medication in adults and in children of all ages |
|
|
Corticosteroid potencies:
|
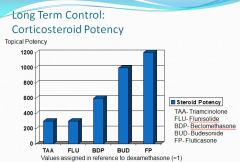
The more potent agents only have to be given one puff once per day.
|
|
|
Adverse effects of corticosteroids:
|

|
|
|
Bioavailability of corticosteroids:
|

Increased bioavailability causes increased systemic absorption. So you want an agent with LOW bioavailability.
|
|
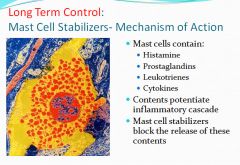
|

|
|
|
Mast cell stabilizer indications:
|

|
|
|
Adverse effects of mast cell stabilizer:
|

|
|
|
Spiriva:
|

|
|
|
Long acting B-agonist MOA:
|

|
|
|
LABA indications;
|

|
|
|
LABA products:
|

|
|
|
LABA/ICS combinations:
|
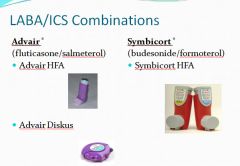
|
|
|
Leukotriene modifiers MOA:
|

|
|
|
Leukotriene modifiers indications:
|

LIs are indicated for long term control and prevention of symptoms in all types of persistent asthma. No evidence that LIs are more effective than inahled steroids. LIs are not superior to LABA/inhaled steroid combinations. LI should be used as add on therapy or in place of steroids or LABA when those drugs are not tolerated.
|
|
|
Adverse effects of leukotriene modifiers:
|

|
|
|
Methylxanthine MOA:
|

|
|
|
Methylxanthine Indications:
|

A systemic drug with systemic side effects with multiple drug interactions. Regular blood testing is required. This is why this is not a preferred drug.
|
|
|
Methylxanthine interactions:
|

|
|
|
Methylxanthine adverse effects:
|

|
|
|
Immunomodulators MOA:
|

|
|
|
Immunomodulator indications:
|
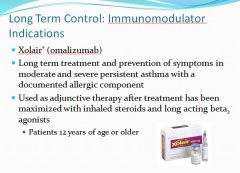
|
|
|
Immunomodulator warning:
|

|
|
|
Immunomodulator Adverse effects:
|

|
|
|
Inhaler Types:
|

|
|
|
Agents used to treat interstitial lung disease:
|

|
|
|
Treatment of ILD with corticosteroids:
|

|
|
|
Corticosteroid adverse effects:
|

|
|

Treatment for insterstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|
|
Immunosupressants for the treatment of interstitial lung disease:
|
- May be used in conjunction with low dose corticosteroids
- These modalities require 8-12 week trial for a fair assessment of benefit - Increased risk for infection - Advise patient and watch carefully for signs of infection - Increased risk for malignancies * Cyclosporine and axathioprine |
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|
|
Monitoring of cyclosporine:
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

Treatment for interstitial lung disease
|

|
|

For treatment of interstitial lung disease
|

|

