![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
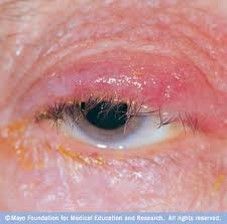
Blepharitis
STAPH species Scrub lid margins daily w/ cotton tipped applicator (baby shampoo) Lid margin massages ABx – lid margins– bacatracin, topical polymixin B, Can use oral Abx if reoccurs - doxycycline - x 6 wks |
|
|
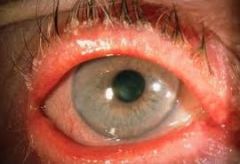
Severe Blepharitis
STAPH species Scrub lid margins daily w/ cotton tipped applicator (baby shampoo) Lid margin massages ABx – lid margins– bacatracin, topical polymixin B, Can use oral Abx if reoccurs - doxycycline - x 6 wks |
|
|
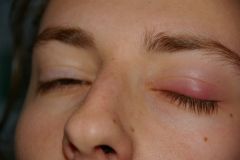
Stye
warm compresses topical ABx drops I&D if abx fails want to prevent cellulitis! |
|
|
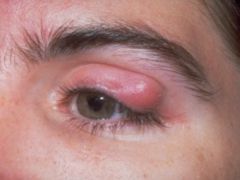
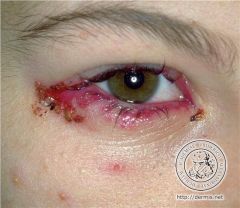
Chalazion
Early tx: warm compresses Intmd tx: injection of triamcinolone (contraindicated) Late tx: surgical |
|
|
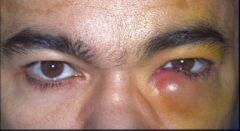
HSV Dermatitis
good hygeine (do not want to spread) mod-severe: topical polysporin Trifluridine drops to prevent herpetic keratitis REFERRAL - to monitor for 2ndary herpetic keratitis |
|
|
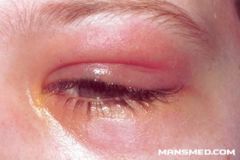
Dacryocystitis
Oral broad spectrum ABX - Augmentin (amoxicillin - clavulanate) I&D if abscess is formed REFERRAL |
|
|
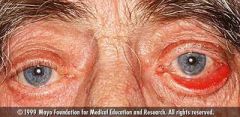
Dacryoadenitis
Idiopathic: oral corticosteroids Inflamm: treat underlying bacterial: broad spectrum - Augmentin REFERRAL |
|
|
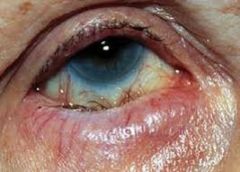
Ectropion
REFERRAL surgical correction |
|
|
Entropion
REFERRAL surgical correction |
|

|
Ptosis
TX of underlying condition congenital: REFERRAL - surgical correction |
|
|
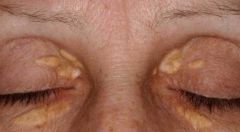
Xanthelasma
REFERRAL - surgical correction for cosmetic purp. only |
|
|
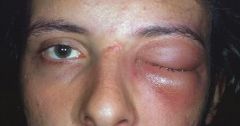
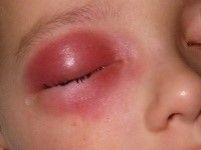
Orbital Cellulitis
IV broad spectrum abx (PCN - or Clindamycin if allerg) surgical drainage if abscess is present sinus drainage if source |
|
|
Pediatric Orbital Cellulitis
IV broad spectrum abx (PCN - or Clindamycin if allerg) surgical drainage if abscess is present sinus drainage if source |
|
|
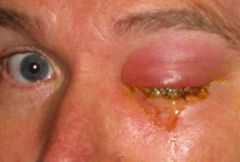
Orbital Cellulitis with discharge
IV broad spectrum abx (PCN - or Clindamycin if allerg) surgical drainage if abscess is present sinus drainage if source |
|
|
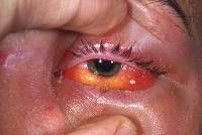
Orbital Cellulitis w/eye open
IV broad spectrum abx (PCN - or Clindamycin if allerg) surgical drainage if abscess is present sinus drainage if source |
|
|
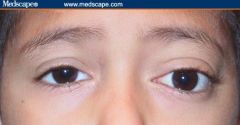
Proptosis (subtle OS)
mild: artificial tears mod to sev: elevate HOB (reduce oc congestion) oral prednisone to reduce edema, congestion severe: orbital radiation (can result in radiation retinopathy) orbital decompression surgery eye muscle surg for entrapment due to compression REFERRAL: eye exam Q3-6mos, VF PRN |
|
|
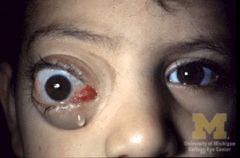
Proptosis (Flagrant)
mild: artificial tears mod to sev: elevate HOB (reduce oc congestion) oral prednisone to reduce edema, congestion severe: orbital radiation (can result in radiation retinopathy) orbital decompression surgery eye muscle surg for entrapment due to compression REFERRAL: eye exam Q3-6mos, VF PRN |
|
|
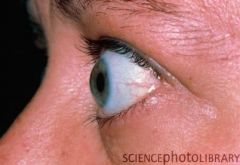
Proptosis (lateral view)
mild: artificial tears mod to sev: elevate HOB (reduce oc congestion) oral prednisone to reduce edema, congestion severe: orbital radiation (can result in radiation retinopathy) orbital decompression surgery eye muscle surg for entrapment due to compression REFERRAL: eye exam Q3-6mos, VF PRN |
|
|
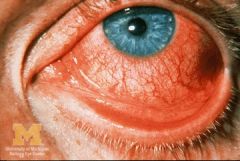
Viral Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
self limiting cold compresses counsel Pt - contagious |
|
|
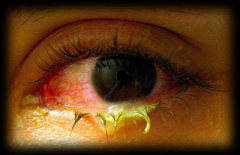
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
any bacteria - staph, haemophilus, strep Broad spectrum ABX - ciloxan (fluoroquinolone) ointment or drops |
|
|
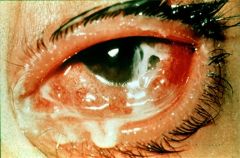
Neisseria Conjunctivitis
may need oral abx - treat underlying issue |
|

|
Allergic Conjunctivitis
systemic antihistamines removal of offending allergen topical vasoconstrictor / antihistamine |
|
|
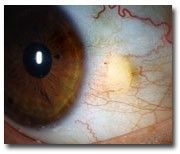
Pinguecula
no treatment necessary |
|
|
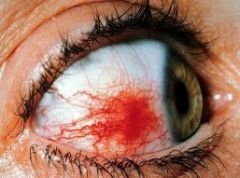
Episcleritis
REFERRAL - but self limiting cold compresses |
|
|
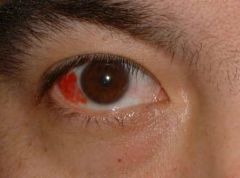
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
no treatment REFERRAL - but self limiting |
|
|
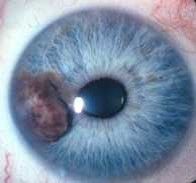
Melanoma
controversial - resection, enucleation, radiation REFERRAL |
|
|
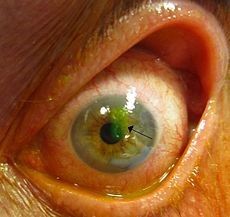
Corneal Abrasion w/fluorescein
topical anesthetic drops (in house) oral analgesics at home abx gtts w/ contact lens patching not used anymore if retained FB - REFERRAL |
|
|
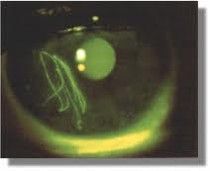
Corneal Abrasion w/fluorescein
topical anesthetic drops (in house) oral analgesics at home abx gtts w/ contact lens patching not used anymore if retained FB - REFERRAL |
|
|
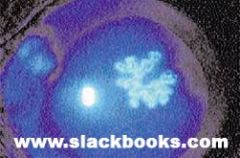
Herpes Simplex Keratitis
U/E REFERRAL!!! topical antiviral meds - acyclovir |
|
|
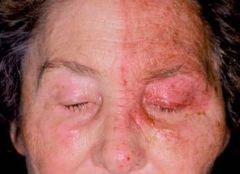
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
U/E REFERRAL!!! Oral acylovir - 7-10 days vaccine |
|
|
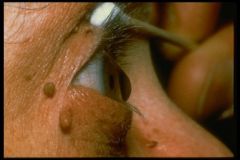
Keratoconus
usually picked up by ophth. exam elearly treatment: gas permeable contacts laser correction (mild cases) keratoplasty to shape cornea later: corneal transplant |
|
|
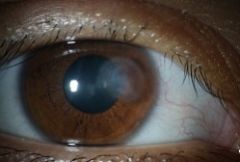
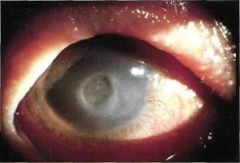
Corneal Ulcer (clouding of cornea)
U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
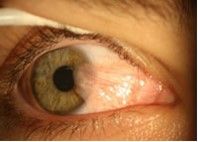
Corneal Ulcer
U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
Pterygium
lubricating gtts, surgical if prob persists (ophth) |
|
|
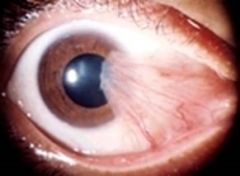
Pterygium (more advanced)
lubricating gtts, surgical if prob persists (ophth) |
|
|
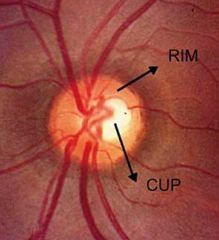
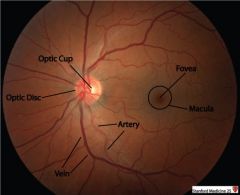
Normal cup to disc ratio
|
|
|
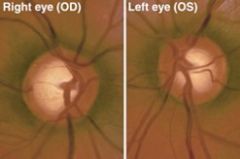
Glaucomatous Cupping
OPEN angle: REFERRAL timoptic gtts (beta blocker) if meds fail - surgery laser or incisional CLOSED angle: U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
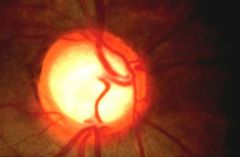
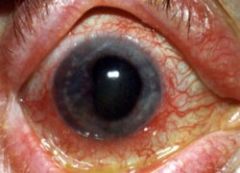
Severe cupping
OPEN angle: REFERRAL timoptic gtts (beta blocker) if meds fail - surgery laser or incisional CLOSED angle: U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
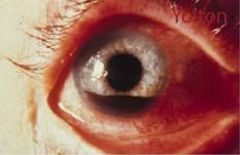
Uveitis (Iritis)
U/E REFERRAL!!! steroid gtts oral steroids mydriatic gtts (helps rest) |
|
|
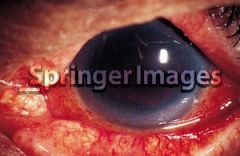
Hyphema
U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
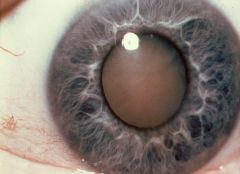
Eight Ball Hyphema
U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
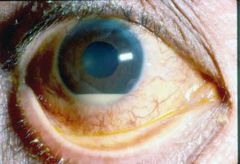
Cataract
REFERRAL wait for maturation - surgical excision w/ repl. of lens |
|
|
Hypopyon
posterior uveitis U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
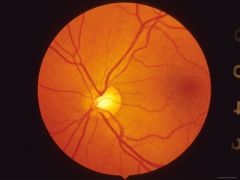
Photo of Normal Retina
|
|
which eye?
|
left eye
|
|
|
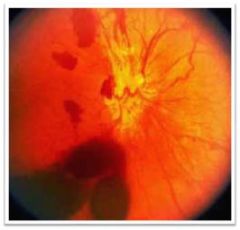
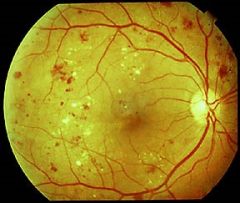
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
tight glyciemic control - decreses progression retinal laser photocoagulation - decreases neovasc. and increases adhesions of retina to choroid REFERRAL |
|
|
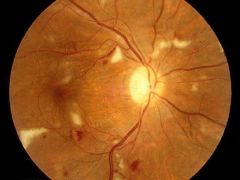
Diabetic Macular Edema
treat underlying REFERRAL |
|
|
Hypertensive Retinopathy
treat underlying cond REFERRAL |
|
|
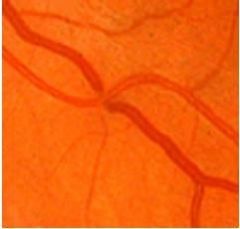
A-V Nicking
Hypertensive Retinopathy treat underlying cond REFERRAL |
|
|
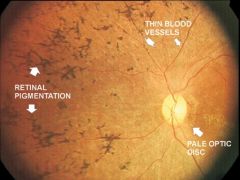
Retinitis Pigmentosa
vitamin A supplements |
|
|
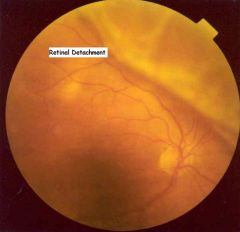
Retinal Detachment
U/E REFERRAL!!! surgical intervention - will result in perm visual loss if not treated |
|
|
Superior rectus
|
pulls eye up
(elevates – IIIrd nerve) |
|
|
Inferior rectus
|
pulls eye down
(depresses – IIIrd nerve) |
|
|
Medial rectus
|
pulls eye inward
(nasally / adduction / medially – IIIrd nerve) |
|
|
Lateral rectus
|
pulls eye outward
(temporally / abduction / laterally – VI th nerve) |
|
|
Superior oblique
|
rotates the eye inward –
intorsion – IV th nerve |
|
|
Inferior oblique
|
rotates the eye outward –
extorsion – IIIrd nerve |
|
|
Levator palpebrae muscle –
|
opens eye
(pulls lid upward) IIIrd |
|
|
Bi-temporal hemianopia
|
Sign of pituitary tumor – vision on outside half of each eye (temporal sides)
|
|
|
Left Homonymous hemianopia
|
Same side (left) half vision
|
|
|
Where is problem of diplopia is pt closes an eye (any eye) and prob goes away
|
Eyes not in tandom
|
|
|
Where is prob if diplopia stays after an eye is closed
|
In that eye
|
|
|
Anisocoria
|
Unequal pupils _ 20% of population
|
|
|
Horner;s syndrome
|
Miosis, ipsilaeral ptosis, anhidrosis
- All on same side |
|
|
Aniscoria increases in bright light ..what caused by?
|
Parasympathetic palsy
|
|
|
Mydriasis
|
Acute pupillary dilation
caused by: Ciliary ganglion dmg Infection Trauma Ischemia |
|
|
Prosopagnosia
|
Difficultly recog faces
|
|
|
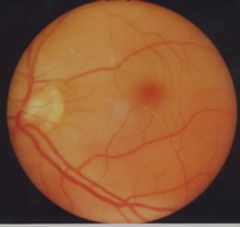
usually from eye infection
blurry or impaired vision in one eye, photophobia, red eye decreased VA, injection |
choroiditis
treat underlying cause (syphilis, TB) steroids - if not infectious REFERRAL |
|
|
retinal artery occlusion
U/E REFERRAL!!! caused by embolus associated with carotid disease may be preceded by amaurosis fugax (mon) impeeding stroke pos pt may only see hand movement or light |
|
|
>60
metamorphosia over several days/longer retinal hemmorrhage seen in macular area |
macular degeneration
U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
associated iwth giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis)
>60 sudden visual loss (monocular) jaw pain, scalp tenderness neck pain, weight loss MG pupil |
ischemic optic neuropathy
U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
MS
women>men colder>wamer 15yrs-45yrs visual loss over several days painful eye movement or periorbital pain (not ocular pain) MG pupil seen on exam |
optic neuritis
REFERRAL REFERRAL to neuro if MS IV steroids |
|
|
fmy Hx
loss of central vision, Drusen on fund exam retinal atrophy or retinal scar in area of macula in late Dz |
atrophic macular degeneration
|
|
|
FB sensation
dry eye, irritation mild redness bilateral excessive mucus punctate staining w/ fluorescein dye idiopathic, elderly younger: contacts, collagen Dz, anticholinergic drugs |
work up - Schirmer test
Tx - artificial tears, restasis (cyclosporine - immunomodulator) |
|
|
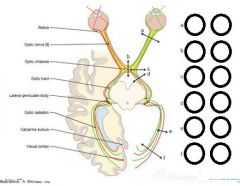
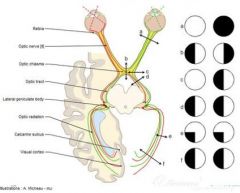
eyelid twitching
caused by irritation or conjunctiva or cornea stress caffeine - stimulants MS - rarely |
Blepharospasm
or benign essential blepharospasm |
|
|
|
|
|
astigmatism
|
irregular shape of cornea
|
|
|
spider webs clouding vision
decreased red reflex, clouding on ophthalmoscopic exam associated: DM, sickle cell anemia |
vitreous hemmorrhage
|
|
|
photopsia, floaters (acute symptoms)
curtain covering eye or loss of perip. vision in one eye what pts more likely to have this |
Acute painless
severe myopia, eye surgery, ocular trauma retinal detachment U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
painless
mon ocular vis loss - sudden nearly complete (amaurosis fugax) - hand motion, light motion what is caused by ? |
embolic occlusion - associated with carotid artery or valvular heart disease
Retinal artery occlusion |
|
|
PE: retinal hemorrhages, veins are tortuous and dilated
what associated with? |
acute painless:
retinal vein occlusion HTN and blood abnormalities (dyscrasias) |
|
|
pt has tender temporal artery, MG pupil
no pain in eye sudden visual loss, swelling of optic nerve head |
ischemic optic neuropathy
acute painless vision loss U/E REFERRAL!!! |
|
|
acute painless vision loss
other neuro findings as well |
stroke (cerebral infarction)
|
|
|
normal exam of eye - but sudden painless vision loss
|
functional visual loss
- hx of psychological problems, recent stress psychosomatic or hysterical blindness |
|
|
inflammation/infection of eyeball
post surgery - PAINFUL PE: vision dec, redness, corneal edema, mucopurulent discharge, decrease red reflux (due to vitreous clouding) |
endophthalmitis
|
|
|
visual loss dependent of location involved,
;later stages: AM H/A w N/V PE: pattern of VF loss related to location involved |
brain tumor
|
|
|
Art blood – high pressure = normal venous return is impeded – engourgement of draining veins
Sudden engorgement and redness of eye Bruit in eye Slight proptosis, diplopis, enlarged mscls injected eye Enlarged superior ophthalmic vein in orbits what is? what caused by? tx? |
Carotid cavernous fistulas
U/E REFFERAL!!! Shunts can be eliminated by intravascular embolization causes: Head trauma Surgical Aneurysm (intracavernous) Tissue dsdr Vascular dz Dural fistula |
|
|
Pain
Limited eye mm Proptosis Congestion Imaging – swollen eye muscles with enlarged tendons |
Orbital pseudotumor
note: DDX - grave’s – tendon's spared tx: Diagnosis difficult Trial of systemic steroids with success can confirm dx |
|
|
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
|
Prior surgery or disease of eye
Ex. Nasolacrimal stenosis Blockage of nasolacrimal duct Idiopathic Tumor – rare sign: epiphora If irrigation and probing do not work – surgery |
|
|
Color blindness - test?
|
Ishihara plates
- Detect color vision |
|
|
causes of diplopia (5)
|
Myasthenia gravis
nerve palsies horz gaze (internuclear ophthalmoplegia) vertical gaze (midbrain - parinauds syndrome) nystagmus (jerk, gaze evoked) |
|
|
causes for proptosis (5)
|
graves' ophthalmopathy
orbital pseudotumor orbital cellulitis tumors carotid cavernous fistulas |
|
|
causes for ptosis (5)
|
blepharoptosis
mechanical aponeurotic myogeneic neurogentic |
|
|
chronic visual loss - causes (5)
|
cataract (central)
glaucoma (perip) macular degeneration (central) central serous chorioretinopathy diabetic retinopathy |
|
|
mailes 20-50
leakage of serous fluid from choroid - small localized retinal detachments metamorphopsia, blurred vision seen with fluorescein dye |
central serous chorioretinopathy
|
|
|
transient of sudden vision loss - causes (14)
|
amaurosis fugax
anterior ischemic optic neuropathy posterior ischemic optic neuropathy optic neuritis leber's hereditary optic neuropathy toxic optic neuropathy papilledema optic disc drusen vitrious degeneration retnial detachment migraine TIA stroke functional visual loss |
|
|
leading cause of blindness in US
|
diabetic retinopathy
|
|
|
red or painful eye - causes
|
corneal abrasions
subconj hemorrhage pinguecula blepharitis dacryocystisis conjunctivitis allergic conj.itis keratoconjunj.itis sicca keratitis herpes simplex herpes zoster episcleritis uveitis psoterior uveitis acute angle-closure glaucoma endophthalmitis |
|
|
ruth's spots
visual loss |
endophthalmitis
chron ill, DM, immunosurpressed, IV cath, + blood cultures ruths spots: whit-centered retinal hemorrhages infectious - bac, fun, viral septic emboli - heart valve, dental surgery |

