![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The diencephalon is derived from the ___________
|
prosencephalon
|
|
|
The _____________ divides the diencephalon to form the dorsal thalamus (alar &roof plates) and basal plate derived hypothalamus.
|
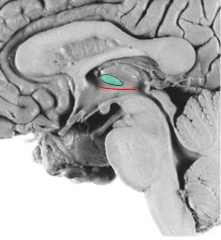
sulcus limitans
(^derivative of hypothalamic sulcus) |
|
|
caudal roof plate of the thalamus develops the
|
epiphysis
|
|
|
epiphysis forms the
|
pineal gland
|
|
|
what makes up the epithamlamus
|
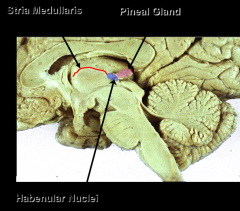
pineal gland
haenular nuclei stria medullaris |
|
|
choroid plexus develops from the _____ along with other specialized ependymal areas, cirnumventricular organs
|
roof plate
|
|
|
subthalamic nucleus and zona incerta develop in the posterior diencephalon and are the ?
|
subthalamus
|
|
|
What else develops from the diencephalon?
|
The neurohypophysis or posterior lobe of the pituitary and the infundibulum
|
|
|
what are the divisions of the adult diencephalon
|
dorsal thalamus (thalamus)
hypothalamus epithalamus subthalamus |
|
|
the 2 lobes of the thalamus are separated by the
|
3rd ventricle
|
|
|
all sensory information which reaches cerebral cortex except_____ will be processed through the thalamus
|
olfaction
|
|
|
the white matter covering the dorsal thalamus
|
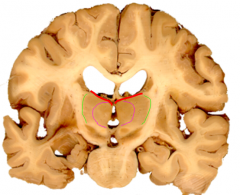
statum zonale (red)
|
|
|
covers the lateral thalamus under the reticular nucleus
|
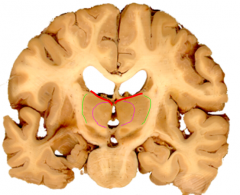
external medullary lamina (green)
|
|
|
The _________________________ divides the thalamus into primary anterior, medial, lateral and intralaminar groups.
|
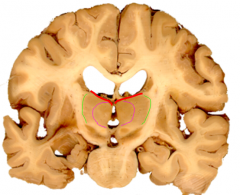
internal medullary lamina (purple)
(These primary groups are further divided into dorsal ventral and posterior areas) |
|
|
anterior nuclear group borders the
|
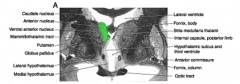
(ant group= green)
lateral ventricle and at the front of the thalamus |
|
|
what is part of the dorsal tier of the lateral groups
|
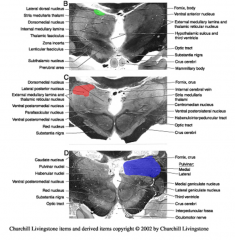
lateral dorsal (green)
lateral posterior (red) pulvinar (purple) |
|
|
what is part of the ventral tier of the lateral groups
|
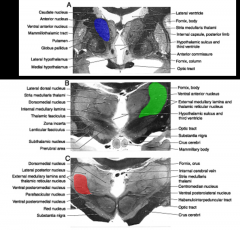
ventral anterior (purple)
ventral lateral (green) ventral posterior (red) |
|
|
what nuclei are part of the medial group
|
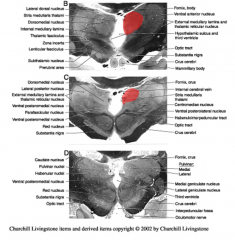
dorsomedial nucleus (upper) and a smaller ventromedial nucleus (lower)
|
|
|
intralaminar nuclei include
|
centromendian (red) and parafascicular (green) nuclei
(surrounded by the internal medullary lamina) |
|
|
metathalamus includes the
|
medial (yellow) and lateral (red) genculate bodies
|
|
|
medial geniculate is part of the ______ system
|
auditory
|
|
|
The __________ is a thin sheet of neurons beyond the external medullary lamina adjacent to the internal capsule.
|
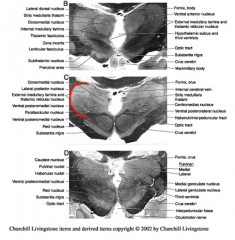
reticular nucleus
|
|
|
lateral geniculate is part of the ______ system
|
visual
|
|
|
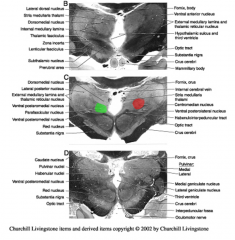
what primary nucleus of the subthalmus is part of basal ganglia connections and involved in large motor movements?
|
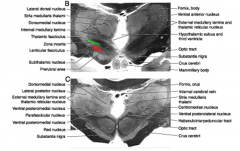
subthalmic nucleus (red)
|
|
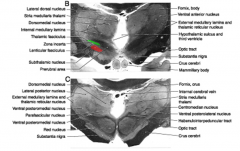
The other primary subthalmic nuclei, the zona incerta (green) is an extension of the
|
reticular formation
|
|
|
subthalamus area contains basal ganglia projections in the
|
prerubral fields of Forel (red)
|
|
|
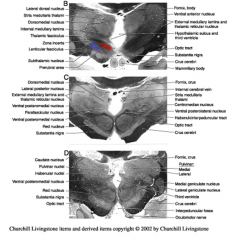
Epithalamus contains the
|
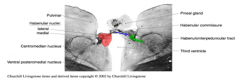
pineal gland, habenular nuclei and the stria medullaris thalami
|
|
|
Pineal Gland is associated with
|
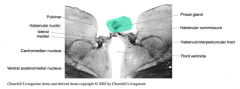
circadian rhythms
*AND recieves indirect light info |
|
|
Pinealocytes synthesize
|
melatonin
(melatonin varies w/ circadian rhythms) |
|
|
habencular nuclei receive basal ganglia information through the
Where do they project to? |
stria medullaris
interpedunclear nucleus of the midbrain |
|
|
What do the habenular nuclei modulate?
|
appear to modulate emotional related facial expressions (mimetic expression) among other possible functions.
|
|
|
what is the arteriole supply to the hypothalamus and subthalamus
|
circle of willis with perforating branches
|
|
|
Most of the thalamus gets its arterole supply from
|
posterior cerebral arteries
|
|
|
Which areas of the thalamus do the thalamoperforating and thalamogeniculate branches of the posterior cerebral arteries supply?
|
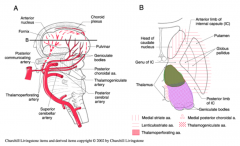
thalamoperforating- supplies the dorsomedial thalamus
thalamogeniculate- supplies the ventrolateral thalamus |

